AI Agent – An Emerging Trend in Crypto Explained

Artificial intelligence has taken the world by storm, and what’s better than combining it with disruptive blockchain technology? This mixture is expected to be the hottest topic in 2025, with AI agents rising in popularity and more cash poured into development efforts.
Unlike regular chatbots, artificially intelligent agents can perform much more complex tasks, from responding to messages to making investment decisions and finding the best way to grow a business.
Companies are experimenting with AI and Bitcoin, capitalising on the striking BTC prices and wide adoption rates. Today, you can find multiple crypto projects built entirely around AI, which we will discuss in this comprehensive guide.
Key Takeaways
- AI agents are automated models powered by artificial intelligence that process large amounts of data, perform complex tasks, and make decisions.
- AI models are often compared to chatbots. However, they perform more tasks than responding to text prompts. They make fact-based decisions and analyse large volumes of data.
- The rise of AI coins and bot-based cryptocurrencies came with the rising practices of artificial intelligence models.
- Automated models can be used in different sectors other than blockchain, including trading, financial services, healthcare, self-driving vehicles, and more.
What is an AI Agent?
AI agents are artificial intelligence software powered to make decisions to achieve certain goals. They can respond to messages similar to chatbots, streamline team operations, track performances, analyse data, act as virtual assistants, and provide advisory.
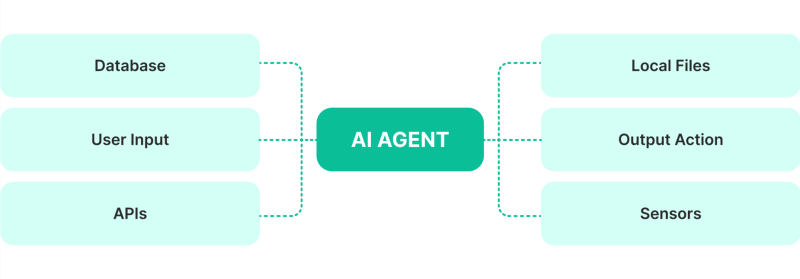
They can independently make decisions, such as spending, attracting investors, controlling a company’s financials, engaging in sales activities, and performing other tasks that require advanced skills and experience.
AI-based systems can perform these duties with little to no human intervention, and they are designed to learn, adapt and improve over time to optimise their accuracy and cope with market developments.
In the crypto world, many autonomous agents operate as decentralised ecosystems, creating coins, offering investment opportunities, managing tokenomics, and optimising token supply.
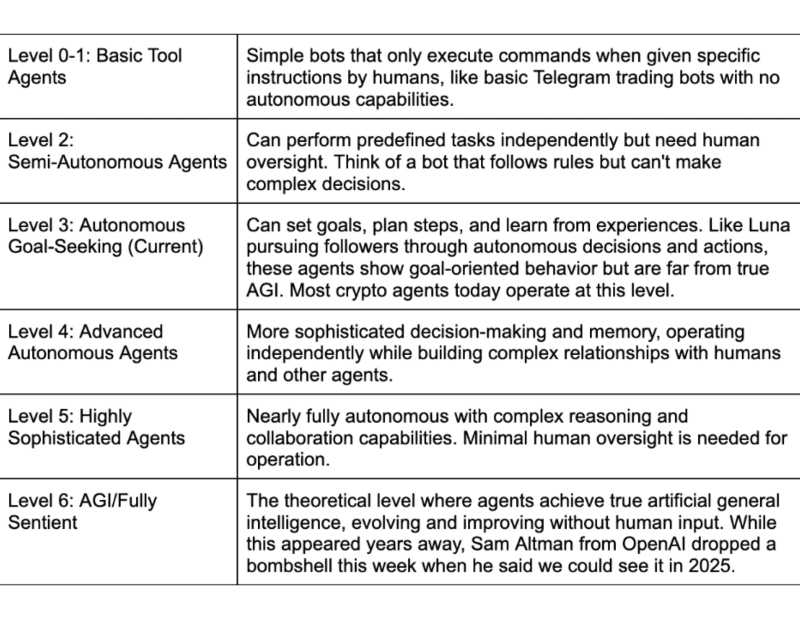
Nevertheless, AI agents range from simple reflex agents to fully sentient artificial general intelligence capable of independent decision-making and other agents serving various purposes in different industries.
Industry Overview
When did it all start? And why now?
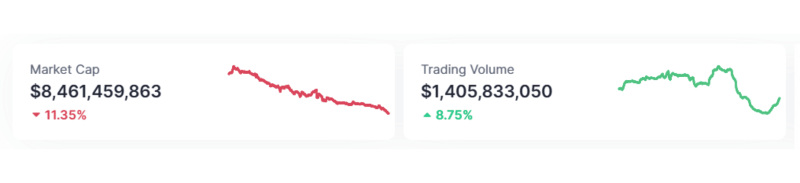
Artificial intelligence itself is not necessarily new, and many companies have been developing such systems for years. However, the market size for crypto AI agents peaked in January 2025 at $15 billion before retracting down to over $8 billion.
In 2024, an AI developer, Andy Ayrey, created “Infinite Backrooms”, an experimental project controlled entirely by artificial intelligence using two instances of a large language model.
Later, the same creator developed “Terminal of Truths”, a new AI model powered by extensive internet subcultures, academic research, and, most importantly, an account on the X platform.
The AI agent on Twitter started posting and interacting with people on its own for several months. However, things peaked when it convinced ai16z founder Marc Andreessen to donate $50,000 for its research fund and started promoting its own memecoin, $GOAT.
As a result, the Goatseus Maximus ($GOAT) coin exploded, reaching $1.3 billion in market capitalisation in November, compared to less than $300 million the previous month. Its price also almost tripled in the span of two weeks.
These two events are believed to have been the foundation for many DeFi companies that created independent crypto projects, tokens, and complete ecosystems using artificial intelligence.
AI Agent vs Chatbot
Chatbots have been in use for years as customer service, receiving and analysing customer queries and responding to them faster than human agents.
Some of these systems use keywords to redirect users to desired products or services, while others collect basic client information before a real customer service operator takes over.
An artificial intelligence agent does this and more, similar to virtual assistants. It takes actions based on market input, research, business performance, advanced analytics, and other complex tasks.
Capabilities
AI Agents: Advanced decision-making, task execution, and predictive analytics.
Chatbots: Primarily focused on providing responses to user input or pre-defined tasks.
Learning Mechanism
AI Agents: Utilises machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) to learn and improve performance over time.
Chatbots: Basic chatbots rely on static rule sets, while advanced versions use limited ML and NLP.
Functionality
AI Agents: Can perform multi-step processes autonomously, make decisions, and adapt to complex scenarios.
Chatbots: Offers straightforward Q&A or performs simple actions based on input.
Applications
AI Agents: Used in crypto trading, supply chain management, personal assistants, and customer support with automation.
Chatbots: Mostly used in customer service, FAQs, and basic information retrieval.
Interactivity
AI Agents: Capable of contextual understanding and handling dynamic interactions across various tasks.
Chatbots: Restricted to linear or predefined conversational flows, often lacking deep context.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Scalability
AI Agents: Easily scales to handle extensive workloads and integrates within larger systems or workflows.
Chatbots: Limited scalability due to static programming or predefined responses.
Personalisation
AI Agents: Highly personalised, adapting to user behaviours and preferences over time.
Chatbots: Basic personalisation with scripted responses, often lacking deeper customisation.
Autonomy
AI Agents: Operates independently with minimal human intervention, making real-time decisions.
Chatbots: Requires user interaction to proceed and cannot function autonomously.
The first chatbot, ELIZA, was created by MIT professor Joseph Weizenbaum between 1964 and 1966. It simulated conversations between a patient and therapist using simple pattern matching and template-based responses.
Crypto Agent Top Benefits
Launching a crypto business or DeFi project requires close monitoring of the fast-paced crypto market, blockchain technology development, innovative decentralised applications, and more. This is where an automated agent comes in handy. It streamlines and optimises your operations more effortlessly and, in some cases, more effectively.
Task Automation
AI agents excel at automating advanced and repetitive processes, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and improving businesses.
By reducing manual effort, companies can focus on strategic objectives, increase productivity, and minimise errors. For example, in crypto trading, AI agents can execute trades, monitor market trends automatically, and manage portfolios to ensure optimal outcomes.
Personalised Service
AI agents leverage advanced data analytics and observe user interactions to deliver highly customised experiences tailored to individual needs.
From personalised marketing strategies to adaptive learning systems, these capabilities ensure clients receive content, services, and recommendations aligned with their preferences and behaviours, improving customer engagement, satisfaction and retention.
24/7 Availability
Unlike human workers, fully automated agents function continuously without fatigue. This round-the-clock operation ensures uninterrupted support, whether in customer service, system monitoring, or executing financial transactions, especially when serving customers in diverse time zones.
This approach enables businesses to maintain consistent service quality across different markets, enhancing customer trust and loyalty.
Scalability
Artificially intelligent agents are designed to handle increasing workloads with minimal additional resources or investment.
They can scale effortlessly, managing more data, users, or transactions without compromising performance. This adaptability is particularly valuable for startups or fluctuating demands in dynamic crypto markets.
Autonomy
These automated systems can operate independently to fulfil complex tasks with minimal human interference. They can analyse data, make decisions, and adapt to dynamic conditions in real time.
This autonomy enhances efficiency, reduces reliance on manual input, and ensures seamless execution of processes across industries, from crypto trading to supply chain management. This not only saves time and resources but also allows organisations to scale their operations effectively without the constant need for oversight.
Where are AI Agents Used?
While AI agent development is still in its infancy and mostly concentrated in the blockchain space, many industries can benefit from reliable data processing, automated task delivery and fact-based decision-making.
Financial Services
AI capabilities are revolutionary in trading, asset management, and fraud detection systems. In crypto investments, they can execute automated trading strategies, monitor trends, manage orders, and provide real-time analytics using live market updates and newsfeeds.
For traditional banking, they can provide advisory and budgeting services to improve credit scoring, loan approvals, and customer service.
Healthcare Systems
These systems efficiently support diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient management, especially in highly demanding areas or when resources are limited.
They analyse patient data to detect diseases early, recommend personalised treatments, and streamline administrative tasks, such as scheduling and billing.
AI agents can also help research and store data on new diseases or outbreaks, providing first-hand data and best practices.
Customer Service
AI agents provide 24/7 support, handling queries, resolving issues, and managing requests similarly to chatbots. However, their ability to personalise interactions enables companies to provide customised solutions that resonate with each customer much faster, enhancing user satisfaction and reducing operational costs.
Supply Chain Management
These systems help optimise inventory, route planning, and demand forecasting, especially during peak seasons or delivery challenges. They improve efficiency and reduce costs by predicting potential bottlenecks and adapting to real-time changes.
Autonomous Systems
In robotics and Internet-of-things (IoT), AI plays a pivotal role in enabling seamless automation across various sectors. In manufacturing, they optimise production lines, track equipment performance, monitor the warehouse, and predict maintenance needs to minimise downtime.
In transportation, automated agents power autonomous vehicles by processing real-time data for navigation, safety, and traffic management.
For home automation, these agents integrate with IoT devices to create intelligent ecosystems, automating lighting, climate control, and security systems. This transformative capability reduces manual intervention while boosting accuracy, efficiency, and productivity across the board.
How Crypto and AI Work Together?
AI thrives in the context of cryptocurrencies, such as in market analysis, pattern recognition, and automated decision-making. It enables faster and more accurate trading strategies.
Blockchain technology provides a decentralised, secure, and transparent framework for AI data management and model sharing, providing an ideal environment to interact with other DeFi projects and ecosystems.
This ensures data integrity and eliminates reliance on centralised entities while improving smart contract execution, fraud detection, and scalability solutions. Together, crypto and AI empower decentralised marketplaces, enabling the creation and monetisation of AI models in a trustless, global environment.
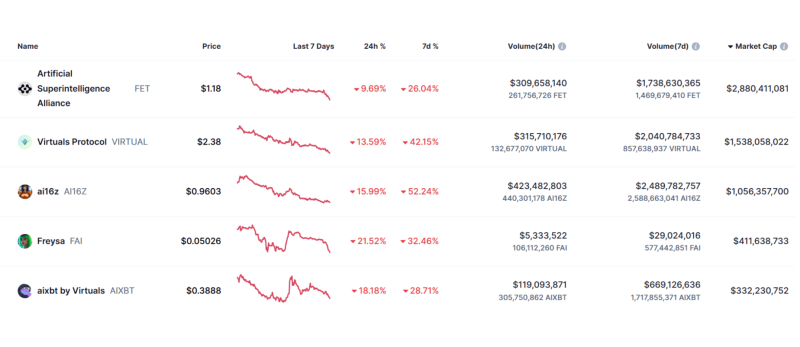
Top AI Agent Projects
Despite being in its preliminary stages, many crypto projects exist on the premise of full automation, nurturing autonomous growth, user interaction and decision-making without human intervention. Here are the top 3 AI crypto agents that offer unique use cases.
Virtuals Protocol
Virtuals Protocol is a decentralised platform minted on BASE, a layer-2 network built on the Ethereum blockchain. It is designed to simplify the creation, deployment, and monetisation of AI agents.
It enables users to develop virtual agents that can autonomously execute tasks across various applications with little technical expertise or skills. Virtuals Protocols has multiple notable products in its ecosystem:
Luna: an AI-powered virtual idol and lead vocalist of an AI girl band boasting over 500,000 followers on TikTok. Luna by Virtuals has its own token with a market cap nearing $50 million, demonstrating its capability to connect AI agents and users across multiple platforms.
VaderAI: a decentralised investment manager that trades AI-agent coins on behalf of its user. It uses advanced machine learning algorithms to analyse market trends, execute trades, and optimise investment strategies without human input.
AI16Z
ai16z was launched in October 2024 as a decentralised AI-powered trading platform operating within the Solana ecosystem. It utilises sophisticated AI systems to analyse market trends, evaluate community sentiment, and execute trades autonomously, both on-chain and off-chain.
A key component of its ecosystem is the Eliza Framework, which integrates seamlessly with platforms like Discord and Twitter to facilitate the creation of agents for various digital functions, such as moderating discussions and participating in online social games.
By combining AI-driven trading strategies with decentralised governance through an AI Investment DAO, ai16z offers investors efficient, data-driven trading opportunities with enhanced transparency, positioning itself as a leader in AI-powered decentralised trading.
BitTensor
A decentralised platform that integrates blockchain technology with machine learning, facilitating the development of AI agents for more users within its ecosystem.
The TAO token is central to the BitTensor ecosystem and is used as an incentive for contributions and to facilitate transactions. The platform enables the creation of specialised AI agents tailored for diverse applications, including language processing, image generation, and predictive analytics.
Each system operates autonomously, allowing for focused development and deployment of AI models. BitTensor’s approach ensures that crypto AI development is open and accessible, reducing reliance on centralised entities and promoting a collaborative environment.
How to Create an AI Agent?
Developing an AI agent involves several structured steps to ensure it functions effectively within its intended environment. It requires advanced programming and technical skills, as well as using the following AI agent builder guide.
1. Define Your Purpose and Scope
Clearly determine the specific tasks and objectives you expect from the AI agent. This step is crucial because each functionality requires a different skillset, integration points and connectivity.
Whether you are creating an autonomous crypto trading model, gamification token, an entire decentralised ecosystem, or a mere memecoin, knowing your needs helps assess the project’s success.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
2. Data Collection and Preparation
Data collection is critical to building an AI agent, as the model learns patterns and behaviours from the data it processes, such as texts, images, and numbers.
First, identify relevant data sources, such as public datasets, APIs, or web scraping, and ensure the data aligns with the agent’s intended tasks. Next, clean the data by removing errors, duplicates, or irrelevant information, and standardise formats for consistency.
This collected data is then split into data training, validation to fine-tune parameters, and testing to evaluate performances in real-world settings.
3. Select the Appropriate Algorithms and Tools
Choose suitable machine learning algorithms and frameworks based on your agent’s requirements. For instance, if you are developing a language-based agent, consider using large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4.
As such, tools like LangChain can facilitate the development process by providing pre-built components for AI agents.
4. Develop Architecture
Design the internal model of the rational agents, including reasoning engine, memory management, and interaction protocols. This architecture should enable the agent to process inputs, make decisions, and execute actions autonomously.
5. Train the AI Agent
Train the agent using your prepared data. This involves feeding it into the chosen algorithms and adjusting parameters to optimise performance. Techniques like reinforcement learning can be employed to enhance decision-making capabilities.
6. Testing and Deployment
Assess the performance through rigorous testing to evaluate its ability to handle various scenarios, decision-making accuracy, and model responsiveness. Identify and address any shortcomings or biases before launching it.
Once tested, deploy generative AI agents into a full operational environment. Continuously monitor its performance to ensure it functions as intended and make necessary adjustments based on real-world interactions.
Advantages and Disadvantages
While AI crypto agents are highly useful and revolutionary, they are still in their early stages. Therefore, their usage presents multiple challenges and limitations. However, during this short lifespan, they offer multiple benefits and advantages that we can highlight.
Pros
- Automation: AI agents handle complex and repetitive tasks efficiently, freeing up human resources and reducing costs.
- 24/7 Availability: AI agents operate continuously without downtime, ensuring round-the-clock service and support.
- Personalisation: They tailor relevant responses using individual user data and preferences, improving customer satisfaction.
- Scalability: AI models handle increasing workloads with ease, making them ideal for growing businesses or fluctuating demands.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI agents analyse large volumes of data to provide actionable insights, improving decision accuracy and speed.
Cons
- High Costs: Designing, developing, and deploying AI agents involve significant financial investments and technical expertise.
- Data Dependency: AI systems require large, high-quality datasets to function effectively, and any errors can lead to flawed outcomes.
- Lack of Context: AI often struggles with tasks requiring human-like intuition or understanding of emotional situations.
- Ethical Issues: AI agents may unintentionally create biases during data training, raising concerns about fairness and accountability.
- Security Risks: As digital entities, AI agents are prone to hacking, breaches, or misuse, potentially endangering data privacy.
Conclusion
AI agents are taking over the crypto world, with multiple DeFi tokens, memecoins and decentralised ecosystems built with innovative autonomous systems.
These capabilities exceed the mere command execution that chatbots perform, fulfilling more complicated tasks using data feeds, market research, and business intelligence to make decisions, manage trading orders, improve organisational resources and more.
Artificial intelligence agents work similarly to virtual assistants, interacting with users and observing patterns to make data-driven decisions and provide personalised services.
Many blockchain projects are built around AI-powered models for different purposes, including cryptocurrency trading services, AI pop culture, optimising tokenomics and more.
FAQ
Is ChatGPT an AI agent?
ChatGPT is not a true AI agent but rather a large language model designed to assist with tasks and engage in conversations. It lacks autonomy and the ability to independently take actions or pursue goals.
How do AI agents work?
They work by processing inputs, analysing data, and executing predefined or adaptive actions using algorithms like machine learning and natural language processing to make decisions.
What are the types of AI agents?
Simple model-based reflex agents, model-based agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, and learning agents are five categories that vary in complexity, from basic reactive systems to advanced goal-seeking models with learning capabilities.
Why do you need AI agents?
Artificial intelligence systems automate complex tasks, provide 24/7 service, and deliver personalised experiences. They help improve efficiency, reduce human workload, and enable better decision-making through real-time data analysis.







