What is Embedded Finance, and How Does it Shape the Modern Financial Industry?

For some, financial tools and routines are a burden and a complicated process. That’s why multiple organisations are trying to simplify it. The transition from traditional financial services to solutions incorporated straight into nonfinancial platforms is symbolised by embedded finance.
Integrating these services into the platforms and procedures users are already familiar with streamlines their delivery and helps them understand everything better.
Clients may quickly obtain financial products and services through their usual apps and platforms instead of dealing with various financial organisations.
Key Takeaways
- Embedded finance simplifies access to multiple industries by integrating financial services into nonfinancial platforms.
- To integrate financial services into digital platforms and enable smooth transactions without requiring users to leave the original website, APIs are crucial.
- Innovations in technology, such as real-time data processing and cloud computing, drive embedded finance solutions’ expansion and effectiveness.
Embedded Finance Definition

Embedded finance represents directly integrating financial services into nonfinancial platforms, including lending, payments, insurance, and banking.
With the help of this idea, consumers can obtain financial services without dealing with traditional financial institutions directly. Instead, to give customers a smooth experience, financial services are integrated into the platform of a nonfinancial organisation.
The concept of integrating financial services is not wholly new in history. Retailers’ store-branded credit cards are among the earliest financial services supplied directly via a retail platform.
These early integrations set the foundation for today’s advanced embedded financial systems, which smoothly integrate services like digital wallets, embedded payments, and embedded lending into web and mobile applications.
There is a strong synergy of embedded finance in fintech. It presents many opportunities in various domains by fusing embedded financial services into non-financial platforms. Cryptocurrency exchanges, for instance, can offer insurance products, margin trading, and embedded payment channels.
Brokerage platforms can access wealth management services, research, and advanced trading tools. Data analytics and embedded risk management solutions are advantageous for liquidity providers.
Fintech companies can provide integrated payment, insurance, and banking services. Customer experience benefits from these linkages by having a more convenient and smooth experience, which promotes industry growth and innovation.
The Mechanics of Embedded Finance

APIs serve as a way of bridging financial institution with nonfinancial platforms, which allows embedded finance. Without starting from scratch, nonfinancial organisations can integrate financial service providers like lending, insurance, and payments into their current digital platforms thanks to APIs.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
For example, an API might use an e-commerce platform to incorporate a digital wallet, allowing users to make payments within the platform. Likewise, an API can connect a Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) service, enabling users to divide their payment amount into instalments at purchase.
Thanks to these API interfaces, customers can more easily access and use financial services without ever leaving the site they are on, which expedites financial transactions.
Or, let’s say, a trading platform that aims to provide its customers with the option to transfer money directly from their bank accounts onto the site without ever leaving it. The trading platform can use APIs offered by banks or payment processors to do this.
An API from a bank or payment gateway can be integrated into the trading platform. A user chooses the preferred bank or payment method to deposit money. The money is safely transferred to the user’s trading account by the platform submitting a request to the bank’s API.
Similarly, the platform can start a withdrawal through its API. The user chooses the payment method or bank account from which they wish to receive the money. To authorise the transfer, the platform requests the bank’s API.
Technological Advances Driving Embedded Finance
The development of the embedded finance industry depends on several technological advancements. The smooth integration of nonfinancial platforms with financial services has been largely made possible by fintech advancements and cloud computing.
Specifically, cloud computing enables flexible and scalable infrastructure that can handle the large number of data processing and transactions needed for embed financial services.
Real-time data linkages and digital onboarding have improved the consumer experience even more. Users can use digital onboarding to open accounts, apply for loans, or access financial products directly within a nonfinancial platform without going to a traditional bank.
Real-time data links make Instantaneous verification and processing possible, saving clients time and effort when obtaining financial services. This smooth connection gives users a more effective and fulfilling experience, increasing customer loyalty and spreading embedded finance usage.
Embedded Finance Examples and Use Cases
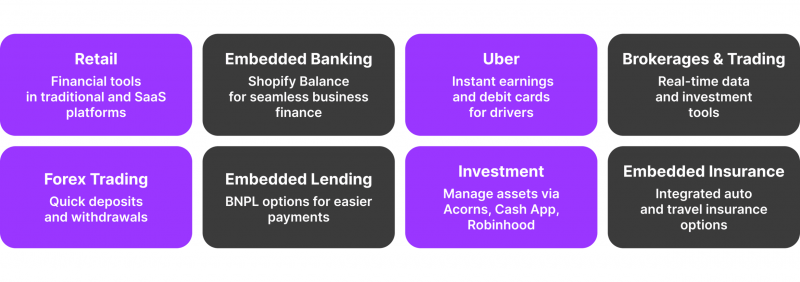
In several industries, embedded finance is being used, including traditional retail, on-demand services, and e-commerce. Traditional retail and SaaS enterprises integrate financial tools and services into their software and payment systems. Let’s clarify the use cases a little more.
Embedded Banking
Embedded banking allows financial services to be directly integrated into non-financial platforms. For example, Shopify Balance enables companies to handle their financial activities directly within the Shopify platform, including banking and spending monitoring.
Similarly, Uber gives its drivers instant profits and debit cards so they can access their money faster and handle their money better. These integrations offer a smooth and cohesive experience, which improves financial management and increases client engagement.
Embedded Finance in Brokerages and Trading
In trading platforms and brokerages, embedded finance is becoming increasingly important. These days, many trading platforms include integrated financial services, like automatic investment advice and real-time trading information.
Specific brokerage platforms, for example, incorporate financial analytics tools into the trading interface to give consumers access to current market data and investing methods. The trading experience is improved by this integration, which provides quick access to vital financial data and resources.
Brokers are integrating financial services into Forex trading to enhance customer relations and expedite processes. Some Forex platforms, for instance, provide payment options that facilitate speedy deposits and withdrawals straight from the trading account.
The smooth merging of financial services enables brokers to manage transactions efficiently and offers traders a unified and enhanced trading encounter.
Embedded Lending and Investing
Integrating financial services into digital platforms, embedded lending, and investing gives consumers quick access to credit and investment options. E-commerce platforms incorporate BNPL options, such as those provided by Klarna and Afterpay, enabling customers to divide their payments into instalments at checkout.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Users may purchase and manage assets from their smartphones thanks to integrated investment services offered by investing platforms like Acorns, Cash App, and Robinhood. These technologies give business models access to new revenue streams and increase their financial capacities.
Embedded Insurance
Embedded insurance offers ease and expanded coverage possibilities by integrating insurance products into digital transactions and platforms. The insurance program streamlines the process for Tesla owners by providing direct access to auto insurance options via its app.
Booking platforms can incorporate travel insurance, enabling customers to buy coverage when booking. These integrated insurance options increase accessibility to financial products and enhance customer comfort.
Buy Now, Pay Later services emerged as the first application of embedded finance. E-commerce platforms started integrating BNPL solutions, including Klarna and Afterpay, which let clients make purchases and advance payments over time.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Embedded Finance
After understanding the concept, market size and trends in embedded finance, let’s discuss its benefits and drawbacks.
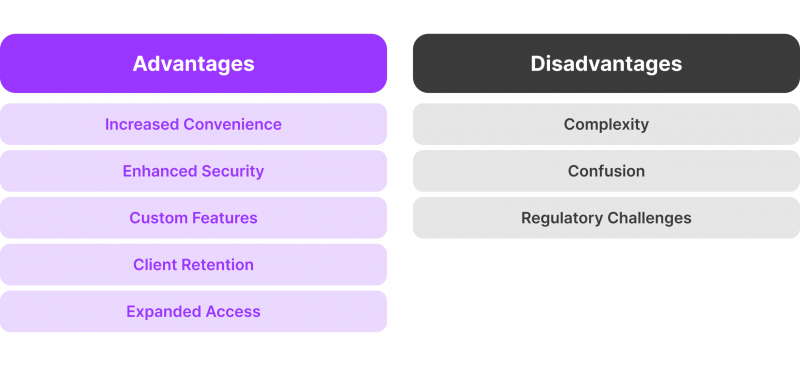
Advantages
- Because financial services are directly integrated into digital platforms, embedded finance increases convenience. This smooth process improves security and makes customised financial features that meet specific demands possible.
- Businesses that integrate financial services can increase client retention. Smooth financial transactions on well-known platforms strengthen the bond between customers and the brand.
- Financial services are provided through non-financial channels through embedded finance solutions that assist in reaching neglected populations. This strategy facilitates the involvement of underprivileged populations and increases access to financial goods.
Disadvantages
- Complexity arises when financial services are integrated into non-financial applications. Users and businesses are at danger from technological problems and possible data breaches.
- Users may become overwhelmed by the sheer number of financial possibilities integrated into one platform. Confusion and decision fatigue can result from having too many options.
- Embedded finance suppliers have to manage through complex regulatory frameworks. Protecting consumer data and complying with financial regulations are essential issues that must be handled carefully.
Final Thoughts
It’s necessary to keep up with developments in embedded finance. The financial services industry is evolving tremendously, with new technologies and applications constantly changing how things are done. Professionals can understand better and predict changes in market demands and technical improvements by staying up to date with these changes.








