Will a US Stagflation Hit Again? What Does The Economy Look Like

The US economy is at a crucial crossroads. President Trump’s arrival, combined with extraordinary policies, has created fears of stagflation.
Despite improving job market indicators, rising consumer prices, tariff trade wars, and Federal Reserve policies cast uncertainty over economic stability.
The restrictive trade policies and aggressive monetary orders create pressure on businesses and consumers, causing many corporations to reshuffle their financial cards and bear the tariff-heavy costs. Will we witness a new US stagflation? Or is it a temporary surge before thriving?
What is Stagflation – Historical Overview
While inflation and stagnation are commonly encountered terms, let’s explain what stagflation is. It is a rare economic phenomenon marked by consistently high inflation and slow economic growth.
While inflation happens as prices and the economy grow uncontrollably, stagflation is characterised by soaring consumer prices and sluggish demand.
It last occurred in the US during the 1970s, when inflation skyrocketed to over 13% while GDP growth declined. The oil crisis, excessive monetary expansion, and geopolitical instability caused the crisis, which took years to recover from.
While the shadow of US stagflation resurfaced over the last few years without actually happening, today’s economy faces these fears again.
The shifts in labour supply, strict trade policies, rising production costs, and large financial overseas spending put the national economy at a complex challenge.
Explore Deeper Industry Insights
Learn from experts shaping the future of financial services — get the latest strategies and trends.
Some economists argue that the current situation is temporary, while others cannot undermine the huge impact of Trump’s tariffs and the signs coming from the bond and stock markets.
Key Reasons Behind a Possible Stagflation
Higher inflation rates and stagnating growth are the key indicators of this economic phenomenon. However, it is more challenging to find the real reason behind these happenings. Let’s review the mixture of events happening in the US economy.
Trump’s Tariff Policies
Donald Trump implemented significant tariffs as part of his plan to boost the US economy. These changes include a 25% tariff on imports from Mexico and Canada, 10% on Canadian energy sources, and 10% on Chinese imports.
While some of these policies were postponed for a month at the beginning of February, they will eventually arrive and lead to higher production costs as American producers bear the added taxes, causing the consumer price to rise and creating inflationary pressures.
Global businesses operating in the US rely heavily on supplies from foreign and developing countries, and increasing the import costs will scatter their financial plans and investments.
Fed Reserve Rates & Meetings
In the 2nd half of 2024, the Federal Reserve conducted several interest rate cuts, taking the funding rate from as high as 5.5% to 4.5%, recently introduced in December 2024.
These policies aimed to tame soaring inflation to a target score of 2%. However, Trump’s policies changed this strategy, as the Fed decided not to initiate further cuts in its recent meeting in January 2025.
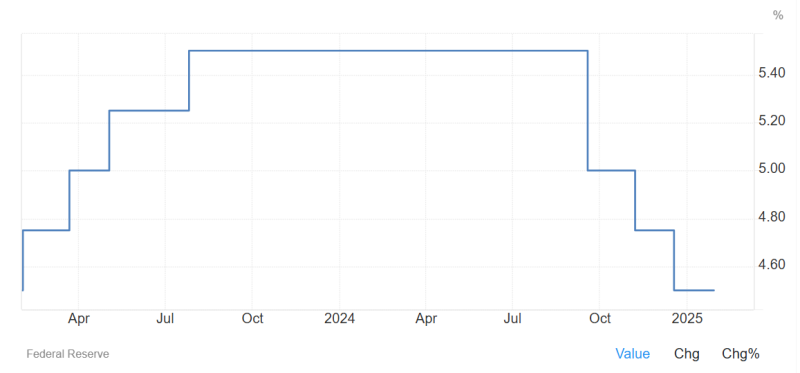
The Federal Open Market Committee emphasised the need for more substantial progress toward the inflation target before considering further rate adjustments. This cautious stance reflects the dilemma: easing monetary policy too quickly could exacerbate inflation while tightening might hinder economic growth.
Local Market Conditions
Rising production costs and shifts in the labour market are significant challenges for US businesses. In addition to the increasing import taxes from Canada, Mexico, and China, the aggressive immigration policy is another hardship for local companies.
The deportation of immigrants and workers without visas can cause a lack of workforce, increasing hiring expenses and productivity in some sectors, like construction, agriculture, groceries, healthcare, and more.
Elevated production costs and a diminished workforce contribute to economic stagnation, which Mark Zandi, chief economist at Moody’s Analytics, describes as “a recipe for inflation and hurt growth.”
Rising Consumer Prices
Inflationary pressures have intensified, with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) rising by 0.5% in January 2025, bringing the annual inflation rate to 3.0%.
Essential commodities, such as food items, have seen significant price hikes. For example, the US egg prices surged by 15.2% in January alone, partially caused by the bird flu outbreak.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
These increases are attributed to higher production costs from Trump’s tariffs, supply chain challenges, and labour shortages. While wages have seen some growth, they have not kept pace with inflation, leading to a reduction in real income for consumers.
Conclusion
The US economy faces mounting stagflation risks due to inflationary pressures, trade policies, Federal Reserve actions, and declining growth.
Whether these factors lead to full-blown US stagflation depends on how policymakers respond. Balancing economic growth and inflation control will be critical in the coming months as businesses and consumers brace for potential turbulence.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. It is not finance advice and should not be relied upon for investment decisions. Always do your own research and consult a financial advisor before investing.