What is Crypto Exchange Liquidity, And Where Can You Source It?
Articles


The global cryptocurrency market is valued at $1.99 trillion, reflecting a 0.5% decline in the past day. The total crypto market volume has also dropped by 6.72%, amounting to $63.45 billion. Of this, 4.95%—or $3.14 billion—is traded in the DeFi sector over the past 24 hours.
These figures highlight the rapid fluctuations in market capitalisation and trade volume within a single day. We present these numbers to emphasise liquidity’s critical role, enabling efficient trading and ensuring swift transactions at stable prices.
This article will explain the importance and necessity of liquidity for crypto exchanges and present several sources of finding it.
Key Takeaways
- How quickly assets may be purchased or sold without impacting their price is known as crypto exchange liquidity.
- Asset liquidity is unique to individual cryptocurrencies, whereas market liquidity is the general ease of trading on a platform. Liquidity on centralised exchanges is typically higher than on decentralised ones.
- Cryptocurrency exchanges use market makers, arbitrage traders, liquidity aggregators, and internal liquidity to maintain high liquidity levels and lower price volatility.
What is Crypto Exchange Liquidity?
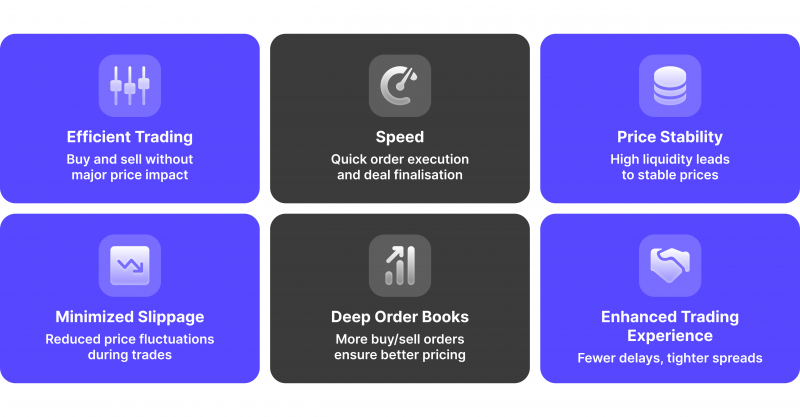
The ease and effectiveness of digital assets being purchased or sold without substantially affecting their price is known as liquidity in crypto exchanges. In other words, it concerns the speed at which an exchange can connect buyers and sellers and finalise deals.
There are more active market participants when there is high liquidity, which leads to more stable prices and fewer instances of slippage—the price fluctuates between when an order is made and when it is executed.
Liquidity is a key component of a cryptocurrency exchange that influences the trading experience. Trades can be completed swiftly and at prices near market value when there are many buy and sell orders or deep order books.
On the other hand, exchanges with insufficient liquidity could experience increased slippage, larger discrepancies between buy and sell prices, and delays in order execution.
Factors Influencing Liquidity
To further understand the concept, let’s break down what affects liquidity. It can be influenced by several factors, such as:
Trading Volume
Due to increased buyer and seller activity in the market, higher trading volumes typically translate into better liquidity.
Depth of Order Book
Improved liquidity results from deep order books with many buy and sell orders at different price points.
Transaction Charges
Exchanges that reduce transaction fees can potentially draw in more traders, raising trading volume and liquidity.
Market Maker Participation
Because they consistently place buy and sell orders, market makers are essential to the supply of liquidity because they guarantee that there is always a counterparty for transactions.
Quantity of Exchange Pairs
More traders are drawn to exchanges with a large selection of trading pairs, which can improve liquidity.
Crypto Liquidity Providers
These organisations or businesses provide sizable asset pools to exchanges to provide liquidity. They facilitate the maintenance of high liquidity levels, enabling traders to execute sizable orders with little fluctuations in price.
Types of Liquidity in Crypto Markets

Everyone interested should have a thorough understanding of the various forms of liquidity. Every kind contributes differently to how the market functions, impacting everything from price stability to trade efficiency. Let’s break them down.
Market Liquidity vs. Asset Liquidity
Market liquidity is the general ease with which assets can be purchased or sold in a particular market without significantly changing their price. This includes everything related to trading, such as the number of deals, the number of users, and the effectiveness of order matching on a platform.
Many buyers and sellers actively participate, which results in narrower spreads between ask and bid prices, which indicates high market liquidity. Low liquidity markets, on the other hand, are characterised by larger spreads and more challenges in placing transactions without affecting prices.
In contrast, asset liquidity is unique to individual crypto assets. It measures how quickly and simply a specific cryptocurrency may be exchanged without depressing the price on the market. An asset’s trading volume, the number of orders in the order book, and its popularity among exchanges all affect how liquid it is.
It is possible to trade quickly and with little price slippage with highly liquid assets like Ethereum and Bitcoin. Still, less popular tokens may have low liquidity, making acquiring or selling at desired rates more challenging.
Centralised vs. Decentralised Liquidity
Centralised exchanges (CEXs), where the exchange serves as the middleman by maintaining the order book and retaining customer cash, are the usual places to find centralised liquidity.
These platforms typically offer superior liquidity because of their substantial user bases, wide selection of trading pairs, and well-established market presence.
CEXs frequently use market-making techniques and sophisticated algorithms to preserve liquidity and guarantee quick trade execution.
Decentralised liquidity, on the other hand, functions on decentralised exchanges (DEXs), where users transact directly using smart contracts. Because these platforms don’t need a central authority to oversee trades, user-contributed liquidity pools serve as the source of liquidity.
Automated market makers, or AMMs, are a common source of liquidity maintenance and trading support for DEXs. Although decentralised liquidity gives consumers more control and transparency, it can also be more volatile and fragmented.
Internal vs. External Liquidity
The term “internal liquidity” describes the liquidity a cryptocurrency exchange manages with its assets, like liquidity pools and internal order books. Exchanges frequently use their own algorithms and market-making techniques to ensure enough liquidity is available for trading. Exchanges can improve trading conditions, such as tighter spreads and less price slippage, by keeping sufficient internal liquidity.
Obtaining liquidity from sources outside the exchange, such as partnerships with external liquidity providers or market integration, is known as external liquidity. By using this strategy, exchanges can access a larger pool of liquidity, improving the stability and depth of the market.
External liquidity becomes even more critical when excessive market volatility or internal liquidity cannot meet trade needs. Exchanges can provide users with a more reliable and effective trading platform by merging internal and external liquidity sources.
Why High Liquidity is Important for Crypto Traders
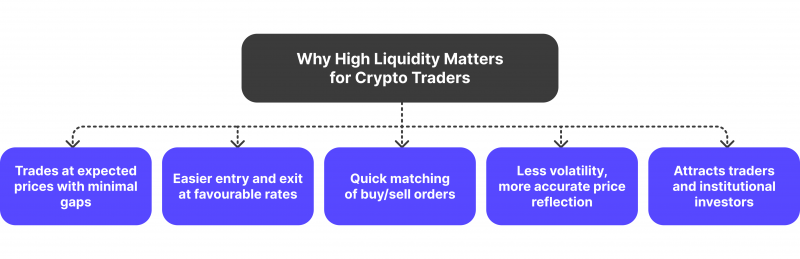
In crypto markets, slippage is the gap between the predicted and actual prices at which a trade is executed. Minimising this difference requires high liquidity. Many buy and sell orders ensure that trades can be performed at or near the expected market price in a highly liquid market, reducing price slippage.
In addition, tighter spreads—the difference between the ask and bid prices—resulting from increased liquidity make it simpler for traders to enter and exit positions at advantageous rates. This immediately affects the profitability of traders; thus, it’s especially critical for those busy and working with small margins.
Faster Trade Execution
The speed at which trades are executed is also significantly influenced by liquidity. Because many orders are available at different price points in liquid markets, trades are matched and executed swiftly. This is vital in unstable cryptocurrency markets where price swings can happen quickly. Trades that are executed promptly enable individuals to profit from market opportunities and save possible losses. To maintain effective trading operations, high liquidity guarantees that traders may execute big orders without suffering from appreciable delays or changes in the market price.
Stability of the Market
High liquidity plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall stability of markets. Large buy or sell orders are less likely to result in abrupt price fluctuations in a highly liquid market since there is enough market depth to accommodate these transactions. Stopping excessive volatility and price manipulation contributes to the preservation of market stability.
Institutional investors and active traders seek out environments where market prices accurately reflect supply and demand dynamics, and they are more likely to participate in a stable market.
High liquidity also boosts investor confidence, which promotes a stable and healthy environment for trading where sentiment in the market is less vulnerable to abrupt changes.
A liquidity ratio compares a company’s liquid assets to its current liabilities in order to determine how well-positioned it is to satisfy its short-term obligations. The quick ratio (Current Assets minus Inventory / Current Liabilities) or the current ratio (Current Assets / Current Liabilities) are two formulas used to calculate it.
Sources of Crypto Exchange Liquidity

Anyone trading cryptocurrency needs to be aware of the sources of liquidity. Here, we’ll explore the key contributors to liquidity on crypto exchanges and how they impact the trading environment.
Depth of Order Book
To keep cryptocurrency exchanges liquid, a deep order book is essential. It shows how many buy and sell orders are available at different price points. Large orders can be processed in exchange for a deep order book without having a noticeable effect on prices.
This is so that the volume may be absorbed without significantly changing the market price because there are enough orders at various price points. Order book depth is crucial for traders looking for adequate trading conditions because it is a significant indicator of an exchange’s capacity to manage large trading volumes.
Market Makers
Market makers are essential to maintaining constant liquidity. They accomplish this by simultaneously putting buy and sell orders at various price points, establishing a market for traders. Traders or businesses who profit from the difference between the ask and bid prices are market makers.
Their existence on an exchange facilitates traders’ ability to execute orders promptly and at expected prices by lowering price volatility and maintaining narrow spreads. Although market makers are crucial for supplying liquidity, they could charge for their services, and for exchanges to keep them on board, they might have certain volume requirements.
For example, the crypto exchange wants to ensure a deep and liquid market for one of the coins. To achieve this, they partner with a market maker firm. Let’s see how this firm operates:
They put buy and sell orders at different prices while closely monitoring the market. They modify their quotes in response to market price changes to keep the spread constant. They may, for instance, put up a bid order to purchase the coin for $29,990 and an ask order to sell it for $30,010.
The firm’s algorithm automatically matches an order placed within this spread and executes the trade, profiting $20 for each coin. By using hedging strategies, they diversify their trading across several markets, control risk, and restrict exposure to inevitable price fluctuations.
Arbitrage Opportunities
Arbitrage traders increase market liquidity by exploiting price disparities between cryptocurrency exchanges. To level the playing field for prices across platforms, they purchase assets at a lower price on one exchange and sell them at a higher price on another.
This action guarantees that liquidity is dispersed more equally throughout exchanges and assists in preserving market efficiency. Arbitrage traders contribute to market stabilisation by profiting from these price differences and lessening the possibility of substantial price differences across various trading platforms. Their activities are essential to preserving an enduring and well-balanced market.
Assume that Exchange A experiences a sudden increase in demand for coin X, pushing its price to a brief peak of $30,000. Due to decreased demand, the price on Exchange B stays at $29,500.
An arbitrage investor may profit from this discrepancy in pricing by:
- Purchasing X on Exchange B: They pay $29,500, which is a reduced price.
- Selling X on Exchange A: They sell their newly acquired X immediately, charging $30,000.
- Making Money off of the Difference: $500 is gained by the arbitrage trader for each X ($30,000 – $29,500).
The arbitrage trader contributes to the equalisation of prices between the two exchanges and ensures a more efficient market by taking advantage of this price differential.
Liquidity Aggregators
Liquidity aggregators significantly improve cryptocurrency exchange liquidity by connecting to a vast network of outside providers. By aggregating liquidity from various sources, such as market makers, OTC desks, and other exchanges, these platforms enable exchanges to provide broader order books.
Liquidity aggregators assist in guaranteeing competitive prices and lessen market impact by effectively directing trade orders to the best available sources. Their capacity to distribute liquidity across several sources and mitigate risk renders them a crucial constituent for exchanges striving to furnish an enhanced trading encounter through more precise spreads and profound market depth.
Let’s say an exchange wishes to increase ETH liquidity. They collaborate with Liquidity Aggregator, which offers links to some other liquidity providers, such as OTC Desk, market maker A, and market maker B.
Aggregator gathers order book information and real-time price quotes from many liquidity sources. For example, market maker A may offer to purchase ETH for $1,990 and sell it for $2,000, whereas market maker B may quote $1,985 and $1,995. The aggregator finds the best available prices and overall liquidity at each price level by combining various quotes into a comprehensive picture of the ETH market.
The aggregator evaluates an order placed by a trader to buy or sell Ethereum and sends it to the best liquidity provider based on volume, pricing, and other considerations. For instance, if the trader wishes to purchase Ethereum for $1,995, the order may be routed to market maker B by the aggregator since they have the best pricing.
The aggregator employs risk management techniques, including limiting order sizes, hedging market risk, and monitoring counterparty risk to protect the exchange and liquidity providers.
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, the concept of liquidity is essential to efficient operations. Maintaining a stable trading environment requires an exchange to accommodate orders without massive price swings, which is ensured by sourcing liquidity from numerous providers.
Good exchanges offer traders a more appealing platform and lower the risk of slippage and volatility. Adopting a resilient liquidity solution builds user trust and improves trading experience.
FAQ
What is liquidity in a crypto exchange?
It refers to how simple it is to buy or sell assets without having an impact on the price. Reduced price disparities, quicker transactions, and less market volatility are all allowed by high liquidity.
How to increase crypto liquidity?
As more people purchase, sell, and trade, the liquidity increases.
Where do I check liquidity?
The trading volume on exchanges, which you can see on websites like CoinMarketCap or CoinGecko, can be used to determine it. More volume typically translates into more liquidity.
Seeking answers or advice?
Share your queries in the form for personalized assistance