What is The International Fisher Effect?

When you trade in the financial market, you will come across different terminologies and theories that originated tens of years ago and are still used today by economists and experts.
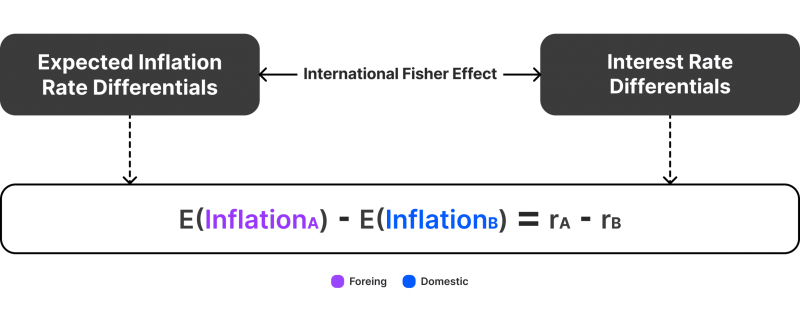
The international Fisher (IFE) effect is one of the most practical and popular theories that explain the relationship between interest rates, currency exchange rates and inflation between different countries. Understanding this relation helps predict currency performance and impact economic announcements.
Key Takeaways
- The international Fisher effect theory interlinks the nominal interest rates and exchange rates between different countries.
- The IFE can be used to predict currency rate changes based on spot and future nominal interest rate changes.
- Fisher’s theory can be used for market predictions, risk analysis, decision-making, and the introduction of financial policies.
Understanding The International Fisher Effect
The theory states that the difference in the nominal interest rate between two countries is directly related to the disparity in their currency exchange rates. The international Fisher effect takes into account the distinction between nominal and real interest when it comes to inflation.
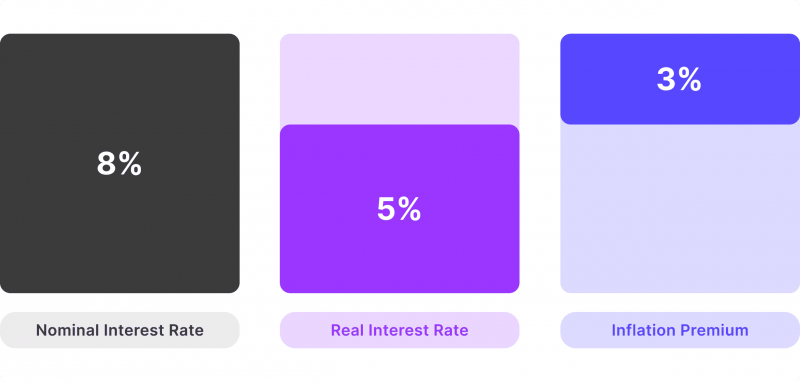
The real interest rate is the percentage the central bank charges for loans and other financial instruments based on economic conditions. However, the nominal interest rate considers the (expected) inflation rate, which affects the actual value of money.
Therefore:
Nominal Interest Rate = Real Interest Rate + Inflation Rate
This paradigm predicts current and potential currency exchange rate changes by studying the current and potential nominal interest rates, taking inflation into consideration.
Why is The IFE Important?
The international Fisher theory is important because it helps Forex traders predict potential exchange rate changes based on the performance and difference in nominal interest rates between two economies.
It assists in analysing current economic conditions, possible currency risks, investment decisions and hedging strategies in global markets.
Explore Deeper Industry Insights
Learn from experts shaping the future of financial services — get the latest strategies and trends.
However, it is vital to differentiate between the IFE and Fisher effect.
- Fisher’s effect studies expected inflation and nominal interest rates in the same economy.
- The international Fisher effect studies the inflation/interest rate dynamics in two different countries.
Theory Background and Process
This exchange rate model was developed by the economist Irving Fisher in the 1930s, designed to measure and predict potential cross-currency rate changes based on nominal interest rate changes. Unlike other economic models, the international Fisher effect (IFE) focuses on risk-free investments like treasury bonds for forecasting purposes.
The International Fisher effect theory considers the real interest rate to be unaffected by inflation because it is already part of the nominal rate. As such, economies with low interest rates would have low inflation figures, leading to currency appreciation. On the other hand, countries with higher nominal interest rates will have higher inflation and currency depreciation.
The Fisher equation suggests that capital moves freely between countries, which allows for parity in real interest rates across countries when adjusting for proportional exchange rate movements. However, the argument stands that predicting future exchange rates is almost impossible because future interests cannot be predicted accurately.
In the 1970s, the theory gained traction as more economies opened to free-float markets, giving the chance to test these principles in more instances. Many investors and economists today consider the IFE in risk assessment and currency analysis for international trade agreements.
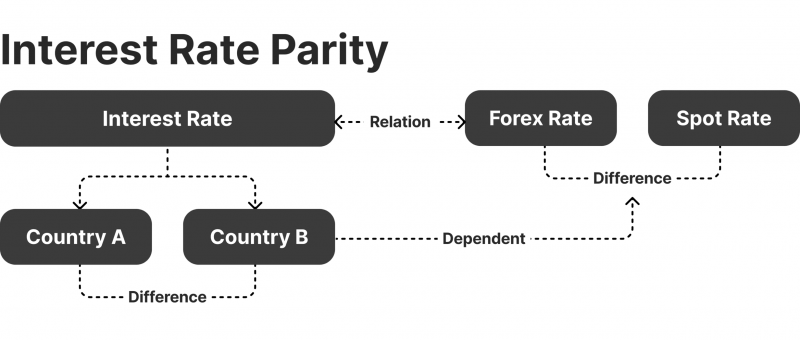
International Fisher Effect and Interest Rate Parity
Fisher assumes that in a well-ordered economy, exchange rates adjust due to changes in countries’ nominal interest rates. As such, the free-market forces could equalise these rates and allow currencies to reach parity with each other.
Therefore, the interest rate parity minimises market manipulation using arbitrate opportunities.
Explaining The International Fisher Effect Formula
To start with, the Fisher effect formula is as follows;
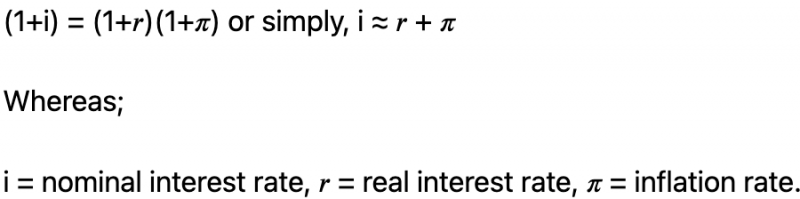
Conversely, the international Fisher effect equation is as follows;
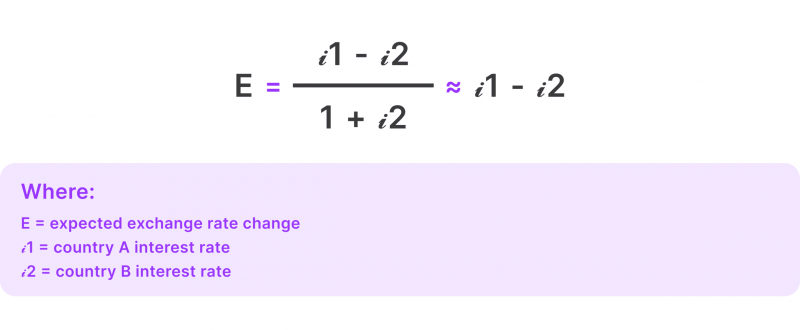
Advantages and Disadvantages
Fisher’s theory is a solid approach to predicting macroeconomics and analysing trading indicators while trading in financial markets. However, there are some challenges that make it debatable. Let’s review the advantages and disadvantages of international Fisher effect.
Pros
- Reliance on the well-known Fisher effect that has proven credibility in analysing economic factors like interest and exchange rates.
- Solid tool to hedge trading positions and optimise the risk factor when predicting currency changes.
- Assisting in future currency exchange rate forecasting, which helps investors and policymakers make fact-based decisions.
- Its simplicity stems from focusing on nominal interest rates rather than other complex economic variables.
Cons
- Markets are not perfectly efficient, and capital does not always move freely between economies.
- The equation focuses on long-term dynamics and does not explain short-term movements, such as speculations and swan events.
- Fisher’s equation ignores some crucial factors like government spending, trade balance and political risks.
Practical Applications
This theoretical approach has multiple practical applications in real life. Economists and market members rely on it for various reasons. Let’s review some of these usages.
For governments
Central banks use the theory to understand how interest rate changes would affect the local currency’s value on the global stage. This aids decision-making in trade agreements, foreign investments and inflation.
Policymakers use this concept to analyse and influence capital outflows and inflows, which drive investments and the domestic economy.
For institutions
Financial companies and commercial banks use this theory to drive investment decisions, foreign direct investment and other activities. Currency and interest rate predictions can be helpful for risk assessment and hedging strategies to avoid excessive losses.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
At the same time, these predictions drive various institutional investment decisions in foreign currencies.
For investors
Forex traders use the IFE as part of their fundamental analysis to predict possible changes in currencies and banks’ interest rates. Understanding and predicting interest rate differential and potential trends in different countries drives real estate investments, FDI, and the Forex market.
Arbitragers may use the theory to take advantage of minor market imperfections and execute significant market positions before corrections happen.
Conclusion
The international Fisher effect is an economic theory that analyses the nominal interest rate between two countries to predict possible currency exchange rate movements between them. These estimations rely on excluding inflation in the real rate of interest and considering capital-free flow between economies to drive decisions.
However, many argue that market imperfections and economic complexity render this theory ineffective in predicting future trends.