Model Portfolio in Investment: What It Is and What Are the Advantages?

Wouldn’t it be great if you had a professionally designed investment strategy that required minimal effort yet delivered solid returns? That’s exactly what model portfolios offer, and they’re quickly becoming a game-changer in the investing world.
As of late 2024, assets in custom model portfolios surpassed $125 billion, marking a 50% surge in just over a year. This growth reflects a major shift in how investors—both beginners and seasoned pros—approach wealth management.
In this article, we’ll break down how model portfolios work, why they’re growing in popularity, and whether they might be the right fit for your investment journey.
Key Takeaways
- A model portfolio is a pre-designed collection of assets managed under a specific investment strategy.
- These portfolios streamline decision-making for investors, saving time and reducing complexity.
- Model portfolio providers can tailor solutions based on risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizons.
What Is a Model Portfolio?
A model portfolio is a pre-constructed selection of investments that adhere to a particular strategy. It outlines how much of the portfolio should be in equities, bonds, or alternative assets and may specify which vehicles (like ETFs or mutual funds) best represent each segment.
Typically, professional investment managers, financial advisors, or dedicated model portfolio providers design these portfolios. They account for factors like market conditions, desired rate of return, and risk tolerance, aiming to deliver consistent, predictable outcomes over the long run.
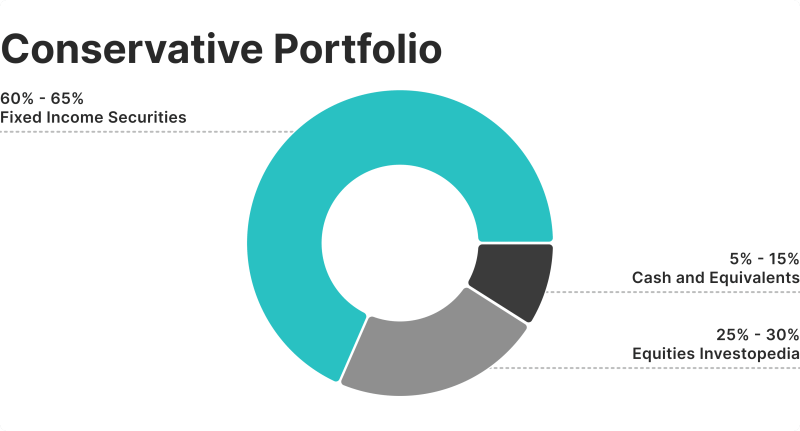
Unlike simply picking random stocks or bonds, a model investment portfolio sets clear proportions for various types of investments—sometimes referred to as the asset allocation mix.
For instance, a moderate-risk portfolio might specify 50% stocks, 40% bonds, and 10% real estate. This ratio becomes a blueprint that can be duplicated or adjusted based on the investor’s unique circumstances.
Why Model Portfolios Are Gaining Popularity?
- Rather than juggling 20 different funds or stocks, you refer to a concise framework that outlines where your capital should go.
- Model portfolios offer a baseline that can be replicated across multiple client accounts, especially in advisory firms.
- Routine tasks like rebalancing and performance tracking become more straightforward once the portfolio strategy is set.
- By adhering to a pre-established ratio of asset classes, you mitigate emotional decisions that could derail your investment goals.
How Do Model Portfolios Work?
To understand how to make a model portfolio effectively, let’s see how these portfolios operate in practice:
- Strategic Allocation: First, the portfolio architect determines the ratio of asset classes—stocks, bonds, cash, real estate, etc. The anticipated risk profile and the investment horizon influence this allocation.
- Security Selection: Next, the portfolio is populated with specific securities designed to fulfil each allocation segment. This step might involve thoroughly analysing market trends, historical data, and forward-looking research.
- Implementation: Once the model is set, users replicate this blueprint in real-world accounts. Whether you’re an individual investor or an advisory firm serving hundreds of clients, the same guidelines apply across portfolios.
- Monitoring and Rebalancing: Over time, markets fluctuate, leading to deviations from the original allocation. Model portfolio guidelines often specify how and when to rebalance—returning the portfolio to its target percentages.
- Ongoing Adjustments: If the manager sees a need to tweak the portfolio strategy due to economic shifts or changes in the risk landscape, they issue adjustments that automatically propagate across all accounts following the model.
For instance, an advisor might rely on a major asset manager’s portfolio as the baseline. From there, the advisor can customise fund choices, add or remove certain sectors, and tweak the allocation mix as necessary.
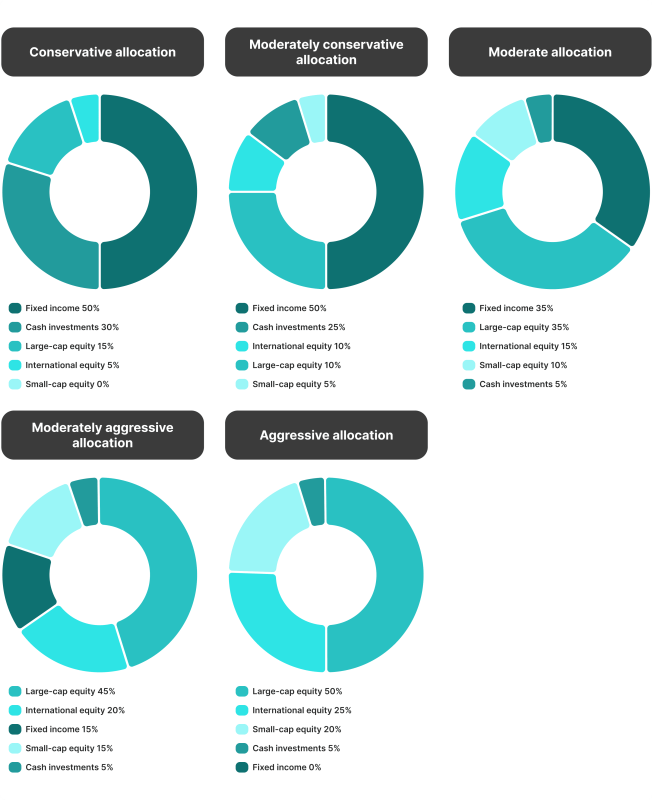
Model Portfolio Example
Let’s illustrate a simple portfolio example suitable for a moderately aggressive investor aiming for balanced growth over a 10-year horizon.
Equities (60%)
- 40% in Large-Cap Stocks (e.g., a diversified S&P 500 ETF)
- 10% in Mid-Cap Stocks
- 10% in International Stocks
Bonds (30%)
- 20% in Government Bonds
- 10% in Investment-Grade Corporate Bonds
Alternative Assets (10%)
- 5% in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
- 5% in Commodities (e.g., a broad-based commodity ETF)
Why This Mix?
60% in Equities delivers higher growth potential, acknowledging that the investor is comfortable taking on some volatility.
30% in Bonds provides a level of stability, aiming to dampen equity market swings.
10% in Alternatives diversifies the portfolio further, potentially offering returns that do not correlate directly with the stock or bond markets.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Of course, this is just an example. A retiree might select a more conservative mix—say 40% stocks and 60% bonds—while an aggressive investor with a very long time horizon might go with 80% or even 90% in equities.
According to Vanguard, over 90% of a portfolio’s long-term return variance can be attributed to asset allocation, highlighting the importance of choosing the right mix of assets.
Where Model Portfolio Providers Fit In
A model portfolio provider is typically an investment firm, advisory service, or platform that creates and maintains various portfolio models designed for specific investment goals or risk profiles. These providers conduct rigorous research and performance analysis to build portfolios that cater to a range of investor needs.
Why Consider a Model Portfolio Provider?
- Expertise: Providers often have teams of analysts who are dedicated to researching market opportunities.
- Scalability: Large providers can handle multiple types of model portfolios—ranging from conservative income-focused approaches to more aggressive growth models—ensuring there is something for nearly everyone.
- Automation: Many providers automate rebalancing and reporting, so you don’t have to manually adjust your portfolio every quarter.
- Cost Efficiency: Depending on the platform, fees might be lower than hiring a personal financial advisor. However, it’s essential to compare the provider’s management fees and additional expenses to ensure you’re not overpaying.
Some of the biggest names in the industry are heavily invested in model portfolio technology, constantly refining their offerings to meet the growing demand for both standard and custom solutions.
Advantages of Leveraging Model Portfolios
If you’re investing with a plan, a model portfolio can be a powerful tool for achieving your financial goals. Here are the main benefits of using a one as your strategy:
Saves Time and Effort
Rather than researching thousands of potential investments, a model portfolio narrows down your selection. This is a huge benefit for beginners who may not have the time or expertise to conduct extensive due diligence on each investment option.
Maintains Discipline
Emotional investing—buying when you feel excited, selling when you feel anxious—is a common pitfall. By following a model portfolio template, you commit to a systematic approach that reduces the impact of market emotions.
Provides Access to Expertise
If a model portfolio provider or financial advisor designed the portfolio, you effectively tap into their market insights, research capabilities, and professional experience without paying for a fully customised plan.
Facilitates Easier Rebalancing
Portfolios should be rebalanced periodically to ensure the asset mix remains aligned with your goals. With a model portfolio, this rebalancing is simpler and more transparent, as you just follow the predetermined guidelines.
Transparency and Clarity
You know the proportion of stocks to bonds, the types of funds you hold, and the strategy driving the portfolio. This transparency helps investors of all levels understand what they own and why they own it.
Potential Drawbacks of Model Portfolios
Despite their clear advantages, it’s important to note some of the possible downsides associated with model portfolios:
One-Size-Fits-Most Approach
Even a well-researched model investment portfolio cannot perfectly cater to each investor’s unique tax situation, personal preferences, or short-term liquidity needs. You might need to adjust the base model to suit your individual circumstances.
Limited Customisation
Some model portfolios come with predetermined allocation bands and securities, restricting your ability to fine-tune specific aspects of your investments.
Market Fluctuations
Though predefined portfolios provide structure, they cannot fully protect you from market volatility. An abrupt economic downturn can still result in substantial losses.
Overdependence on Provider
If you rely on a model portfolio provider, there’s a possibility that a change in their strategy, or a transition of key analysts, could impact the consistency you rely on.
Potential Fees
Some model portfolio providers charge for rebalancing or for access to premium investment models. Over time, these fees can erode overall returns.
Why Some Advisors Forego Model Portfolios
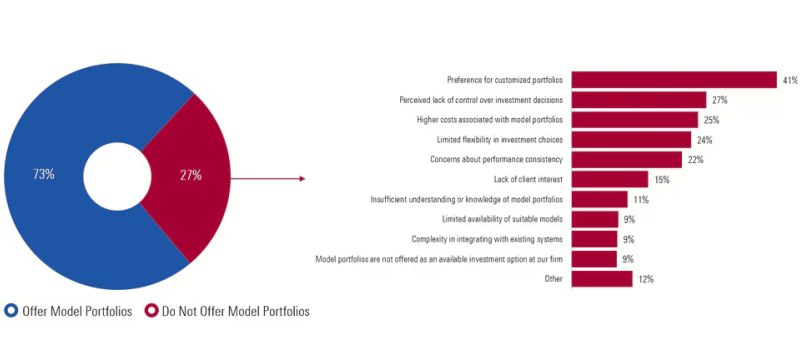
Recent data by Morningstar shows that while model portfolios remain popular in the advisory world, around 27% of advisors still opt not to incorporate them into their practice.
The biggest reason, mentioned by 41% of those providers, is that they prefer building custom solutions for each client’s unique goals. Another common issue, cited by 27%, is the feeling that relying on a pre-built model takes away their control over investment decisions.
Meanwhile, some providers point to higher overall costs and say existing predefined portfolios aren’t flexible enough to adjust to changing markets. Others worry about maintaining consistent performance and see little interest from their clients.
Some even mention a variety of other reasons—such as regulatory constraints or personal philosophies—showing that, despite the clear benefits, factors like customisation, control, and cost are still major barriers to integrating such portfolios in practice.
Robo-advisors, which automate portfolio construction and rebalancing, are a type of model portfolio provider. They use algorithms to allocate assets according to an investor’s risk profile and time horizon.
Growing Trend: Custom Model Portfolios
Despite their established benefits, model portfolios have sometimes been dismissed by those who favour a highly personalised approach. In response, custom model portfolios are becoming an important middle ground, merging standardised investment frameworks with room for strategic adjustments.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
A significant concern among advisors and investors alike is retaining enough discretion to address unique risk tolerances, tax considerations, or personal preferences. Custom model portfolios achieve this by letting advisors swap funds, tweak allocations, and introduce new asset classes.
- Personalisation: Advisors can inject a personal touch—whether it’s adding a socially responsible ETF or introducing an alternative investment that matches an investor’s philosophy.
- Flexibility: Substituting one fund for another within an established model may slightly alter the risk profile, but it also ensures the portfolio remains relevant to the client’s goals.
- Balance of Control: These custom models preserve the efficiency and research integrity of the core strategy while giving advisors the freedom to pivot as needed.
If the base model invests 40% in large-cap stocks, an advisor might replace one actively managed fund with a low-cost index ETF for cost reduction. Or, if a client’s primary goal is income, the advisor could substitute a portion of the equity allocation with dividend-focused funds or bond ETFs.
Model Portfolio vs. Traditional Investing
A modelling portfolio approach (i.e., using a model designed by professionals) often contrasts with do-it-yourself (DIY) investing. Here are some distinctions:
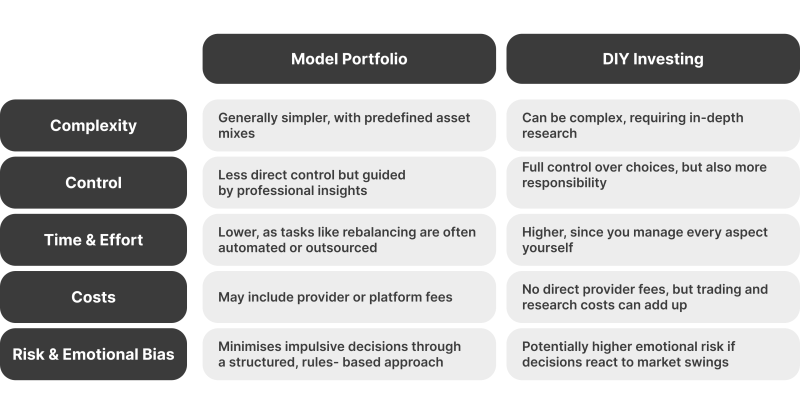
If you’re new to investing and want guidance while still maintaining control over your money, a modelling portfolio can become an educational stepping stone. Conversely, if you relish the research process or have specialised knowledge in certain market segments, DIY investing could be more appealing.
Bottom Line
Model portfolios are practical, ready-to-use frameworks that simplify the complex world of investing. By following clear guidelines on asset allocation and risk management, you can reduce guesswork and stress in your investing.
A model portfolio is not a magic bullet that guarantees profit or eliminates risk altogether. Rather, it’s a structured guide—a blueprint that still needs thoughtful monitoring, periodic rebalancing, and occasional tailoring to suit personal circumstances.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. It is not finance advice and should not be relied upon for investment decisions. Always do your own research and consult a financial advisor before investing.
FAQ
How to build a model investment portfolio?
Start by defining your investment goals and time horizon. Assess your risk tolerance, then choose a suitable mix of stocks, bonds, and any alternative assets. Lastly, establish a rebalancing plan—either time-based or triggered by allocation drift.
What is the 5% portfolio rule?
This guideline says you shouldn’t let any single asset (like a single stock or a high-risk fund) exceed 5% of your overall portfolio. This way, you reduce the chance that a single bad investment can cause big losses.
Are model portfolios suitable for beginners?
It depends on your situation. Standard model portfolios are easier to set up and follow, but might not perfectly suit all your needs. Custom model portfolios offer more flexibility. However, creating and managing a custom portfolio can be more time-consuming and expensive.
What if the market changes drastically?
Model portfolios are generally built to handle market ups and downs through strategies like regular rebalancing. If the market shifts a lot, you may need to update your portfolio based on any preset rules or personal comfort with risk.