SaaS vs Self-Hosted Business Models

Most businesses today have a near-zero chance of success without using digital platforms. Businesses use increasingly different technology models to improve their operations and service provision. The SaaS business model and self-hosted solutions are two well-known models.
It’s critical to understand the distinctions between self-hosting and SaaS platforms. This information assists in choosing the best solution based on their unique requirements, considering cost, control, and security.
We will examine the foundations of self-hosted and SaaS business models in this article, along with comparing their prominent characteristics in the financial sector, and recommend the most suitable model for your company.
Key Takeaways
- Self-hosted solutions require a substantial initial investment and ongoing maintenance, while SaaS models offer lower upfront expenses and ongoing maintenance.
- SaaS solutions are perfect for firms with dynamic needs and remote workforces since they offer easy scalability and access.
- Self-hosted solutions are appropriate for companies with particular security and compliance requirements since they offer more control and customisation.
What Is a SaaS Business Model?

A cloud-based software delivery model is called SaaS. Under this system, customers access software applications through the internet, which a SaaS provider hosts. Because the provider manages all parts of the application, including updates and maintenance, the SaaS business model does not need local software installation and management. Dropbox, Salesforce, and Google Workspace are a few well-known SaaS applications.
Let’s take Google Workspace as an example. Instead of installing different word processors, spreadsheets, and email clients on each computer, you can use its services. These programs are available online through this SaaS suite and can be accessed on any device. Google handles data security, upgrades, and software management so customers can concentrate on their jobs without worrying about IT.
SaaS in the Financial Sector
SaaS technologies have completely changed the way financial organisations function. Thanks to Brokerage as a Service (BaaS), a subset of SaaS, financial companies can provide trading services without becoming brokers themselves. Banks and other financial institutions may now provide their clients access to trading platforms, market data, and investment analysis without having to make substantial upfront expenditures in technology, thanks to BaaS, which uses the cloud to deliver a comprehensive suite of brokerage tools and integrations.
Banks can use APIs to seamlessly integrate these products into their current systems and provide a smooth customer experience by leveraging BaaS. Financial institutions may more easily adapt to changes in the market and the needs of their customers thanks to this integration, which enables quick implementation and scaling. BaaS solutions also offer improved security, compliance, and reporting capabilities—all essential in the highly regulated banking sector.
How it Works
SaaS solutions are provided online, enabling clients to access the program without installing it locally using a web browser. This business model usually involves a monthly subscription where customers pay a certain amount to access the service. Typically, the membership covers support, frequent upgrades, and software access.
BaaS uses this concept in the financial industry to give institutions access to full brokerage services via cloud-based platforms. Banks and other financial institutions can easily incorporate APIs into their current systems, allowing for quick adoption without requiring a substantial upfront investment in IT infrastructure. This configuration is very beneficial in the highly regulated financial sector, where BaaS solutions provide improved security, compliance, and reporting features that are essential for upholding regulatory standards.
Key Features of SaaS
Let’s now break down the characteristics of SaaS solutions:
- Without requiring any manual involvement, SaaS providers handle all upgrades and maintenance, guaranteeing that users always have access to the newest features and security patches.
- SaaS solution is easily scalable to handle more significant usage levels or more users. This adaptability helps companies modify their software usage according to their requirements.
- SaaS platform allows users to operate from different devices and locations without being restricted to a specific physical infrastructure. They can be accessed from any location with an internet connection.
- BaaS platforms offer straightforward API connections with current banking systems in the financial sector. Because of this, financial institutions can easily add brokerage services without making major adjustments to their existing IT setup.
- Because BaaS solutions are so scalable, financial institutions may swiftly develop their services to meet the increasing demand. This flexibility guarantees banks to effectively serve their customers’ requirements.
- BaaS systems provide a full brokerage infrastructure, comprising trading terminals, analytical platforms, and real-time monitoring tools. These characteristics enable financial institutions to provide their clients with extensive brokerage services.
- BaaS systems come with cutting-edge protections for security and compliance tools that are necessary for the strictly regulated banking industry. By doing this, industry standards for data management and transactions are met.
The Concept of Self-Hosted
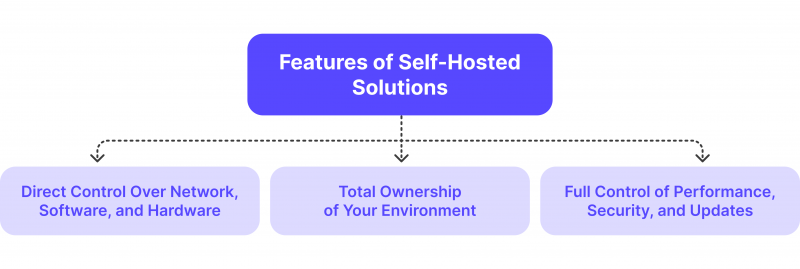
Using your servers or infrastructure to run software programs or services instead of depending on outside vendors is known as a self-hosted solution. This method gives you direct control over the network, software, and hardware. You have total ownership and control over your environment when you self-host. Web servers such as Apache or Nginx, and content management systems such as WordPress are typical instances of self-hosted apps.
You want to build a website and create it from scratch rather than have someone else maintain it.
You will require a web server to host your website’s files. Nginx and Apache are well-liked choices for this. These software packages can be installed on your PC or server. After it’s installed, you have total control over how the server runs. You are in charge of performance, security, and updates.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Self-Hosted Solutions in Fintech
Financial institutions can control their infrastructure and software directly using self-hosted solutions. Banks, brokerages, and investment businesses can tailor their systems to specific operational requirements by hosting software on their servers. This strategy allows the integration of proprietary technologies, guaranteeing that every system complies with the organisation’s particular needs.
Self-hosting is frequently used in the financial industry due to its improved security and compliance features. Organisations can put in place customised security measures and guarantee that all data processing complies with legal requirements. This is especially crucial in a sector of the economy where data security is vital.
Also, self-hosted solutions allow you to change the software and hardware components. Financial institutions have complete control over the operating environment, can optimise performance, and can upgrade systems as needed. Because of this, self-hosting is a desirable choice for businesses that need a lot of customisation and control over their IT setup.
How Self-Hosting Works
Software must be installed on local servers or private cloud environments to self-host. You execute the software on your servers or specialised hardware, not the infrastructure of a cloud computing service. This frequently involves paying a one-time license fee for the program. The company oversees and maintains the infrastructure, which includes backups, security, and upgrades. Configuring the environment to match particular needs, installing software, and configuring servers are all common steps in migrating to a self-hosted solution.
Key Features of Self-Hosting
Below, we discuss the main features of the self-hosted solution:
- When you self-host, you have complete control over the software environment—from configuration to security settings. You control who has access to the data, where it is kept, and how it is handled.
- Both the hardware and the software can be altered to meet particular needs. This includes interacting with other systems and setting software features.
- When you self-host, you are in charge of updating, maintaining, and guaranteeing data security. This involves managing security protocols to prevent data breaches and preserve compliance with data protection laws.
Salesforce introduced its CRM platform in 1999, making it the first SaaS vendor created from the ground up to experience rapid growth.
The Comparison of Business Models
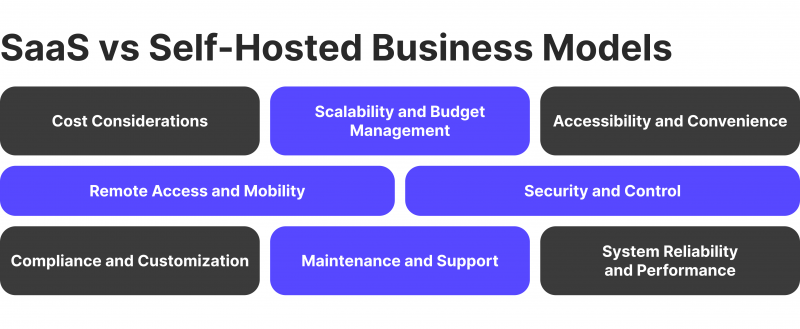
After understanding the concepts behind both business models, it’s time to compare them to simplify decision-making even further.
Cost Considerations
The advantages of the SaaS business model include reduced initial expenses because you do not need to purchase any licenses. The software and upkeep are covered by the membership price you pay.
When implementing a self-hosted solution, more money upfront on specialised software and hardware licensing is necessary. In addition, maintenance, IT support, and infrastructure upkeep are ongoing expenses.
Scalability and Budget Management
SaaS apps have adaptable pricing structures that change according to your needs. This model makes budget management easier because providers handle the infrastructure scalability and cost scale with usage.
To scale, a self-hosted software must invest significantly more in hardware and IT resources. Depending on the capabilities of the infrastructure and the necessary improvements, the costs associated with scaling can be unpredictable.
Accessibility and Convenience
SaaS apps don’t need to be installed locally; therefore, they can be quickly deployed. The setup process is simple and requires user access and integration with current systems.
Setting up a self-hosted solution requires extensive time and specialised IT knowledge. It involves installing software on private clouds or local servers and ensuring the system is secure and set up correctly.
Remote Access and Mobility
SaaS solutions can be accessed anywhere with an internet connection. This allows users to access software applications from different devices, making them perfect for remote work.
To access a self-hosted application remotely, setting up secure remote access solutions may be necessary, which can be a complex process. These systems are usually restricted to local networks unless they have extra equipment for remote communication.
Security and Control
The service provider is in charge of overseeing data security in SaaS systems. Although SaaS providers use robust security protocols, the data is kept off-site, which raises the possibility of vulnerabilities relating to internet-based access.
Self-hosted programs provide you with total control over the security of your data. It is kept on local servers or private clouds, which lowers the possibility of unauthorised access and allows for customised security measures to satisfy specific organisational and legal requirements.
Compliance and Customisation
The provider’s configurations and security guidelines frequently restrict customisation in SaaS models. The provider manages compliance with data protection regulations, which might not perfectly match all unique organisational requirements.
On premise solutions can be extensively customised to match business requirements and regulatory restrictions. Enterprises have complete authority over security procedures and can customise solutions to comply with data security laws.
Maintenance and Support
SaaS providers maintain and upgrade their software, keeping it up-to-date and functional. Usually, the business’s committed staff offers support and quickly resolves problems.
Updates and maintenance for an on premise solution is handled internally or using external IT services. This calls for specialised staff to maintain system dependability, handle technical problems, and carry out routine updates.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
System Reliability and Performance
SaaS providers usually employ managed infrastructure and disaster recovery solutions to guarantee excellent system performance and stability. They also manage speed optimisations and system uptime as part of their service.
The quality of internal resources and infrastructure determines the dependability and performance of self-hosted systems. Companies are responsible for managing their uptime and disaster recovery, which can differ depending on how the system is built and maintained.
How to Make a Decision?

First, evaluate your company’s technical capabilities and resources. Assess the importance of customisation and control to your operations. Consider security and compliance standards unique to your industry, such as handling sensitive data and adhering to data protection laws.
Compare the one-time and recurring expenses of self-hosted vs. SaaS options. Analyse the predictability and financial flexibility that each solution provides. Predictable subscription rates and lower upfront costs are standard features of SaaS, whereas self-hosted solutions require a more significant initial outlay and continuous infrastructure upkeep.
Find out how each model handles the firm’s expansion and scalability. SaaS solutions typically provide alternatives for flexible scaling, but self-hosted systems could require significant initial investment and result in irregular costs.
Speak with peers in the sector and IT specialists to determine which model best meets your objectives. Consider implementing pilot projects or trials to determine whether self-hosted or SaaS solutions are a good fit for your company.
Final Thoughts
It’s essential to compare several aspects before making a decision. SaaS models are ideal for companies with limited IT capabilities since they typically have cheaper upfront costs, flexible pricing, and easy setup when offered by a third-party provider. On the other hand, self-hosted alternatives provide greater customisation and control but come with a hefty infrastructure cost and continuing maintenance requirements.
Examine each model’s benefits and drawbacks, consider your demands for flexibility and future expansion, and select the one that best satisfies your strategic goals.