The Role of KYC/KYB Technologies in FinTech and Finance Industries
Articles

The popularisation of cryptocurrency technologies has led to a massive paradigm shift in the financial paradigm, which has become a catalyst for developing a new way of interaction between businesses and their customers within the concept that combines financial solutions and technologies, better known as Fintech.
The high level of popularity of Fintech solutions, as well as cryptocurrency technologies, became the reason for increased attention to the issue of security and safety of assets of clients of different types of business, which allowed the evolvement and adoption of KYC (Know Your Customer) and KYB (Know Your Business) verification technologies in the process of interaction between individuals and legal entities of the financial industry.
This article will help to understand what KYC/KYB technologies are, their differences, and their prospects for development within the framework of financial sector regulation.
Key Takeaways
- KYC and KYB procedures are innovative tools providing a full range of verification measures aimed at identifying users in the financial niche.
- KYC and KYB technologies form a group of solutions that are part of the AML system aimed at combating money laundering.
- In the future, both types of identity verification procedures will have additional functionality to assess the identity of individuals or the legitimacy of legal entities, thanks to AI and machine learning technologies.
What is KYC Technology and How Does It Work?
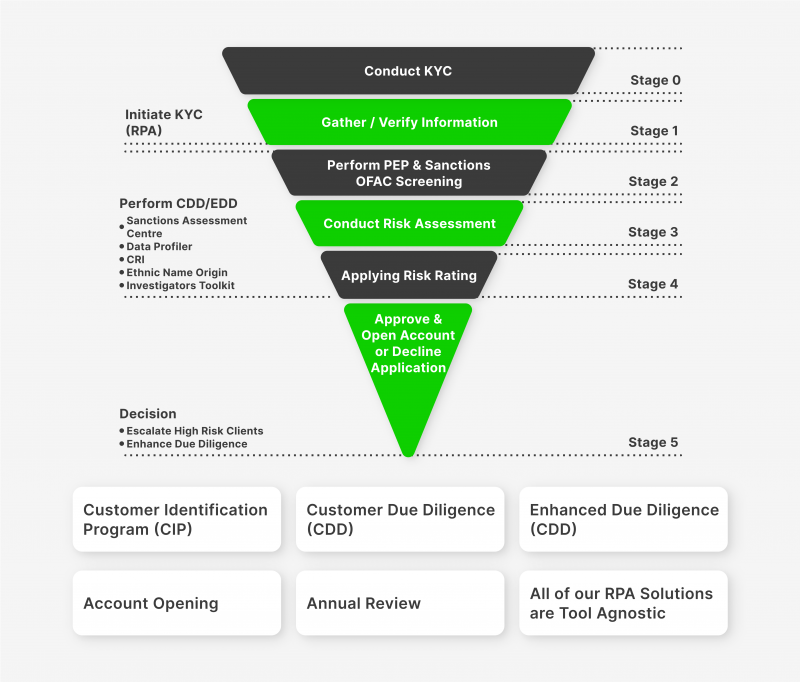
Today, KYC technology is a universal set of methods for identifying the identity of users within the framework of their interaction (cooperation) with the fintech companies and other entities of the financial world. Being one of the fundamental elements of the security system based on the principles of the Customer Due Diligence model, EDD and its more extended version, Enhanced Due Diligence, KYC procedure provides access to a wide range of advanced professional tools aimed at creating a secure environment for interaction between businesses and their customers.
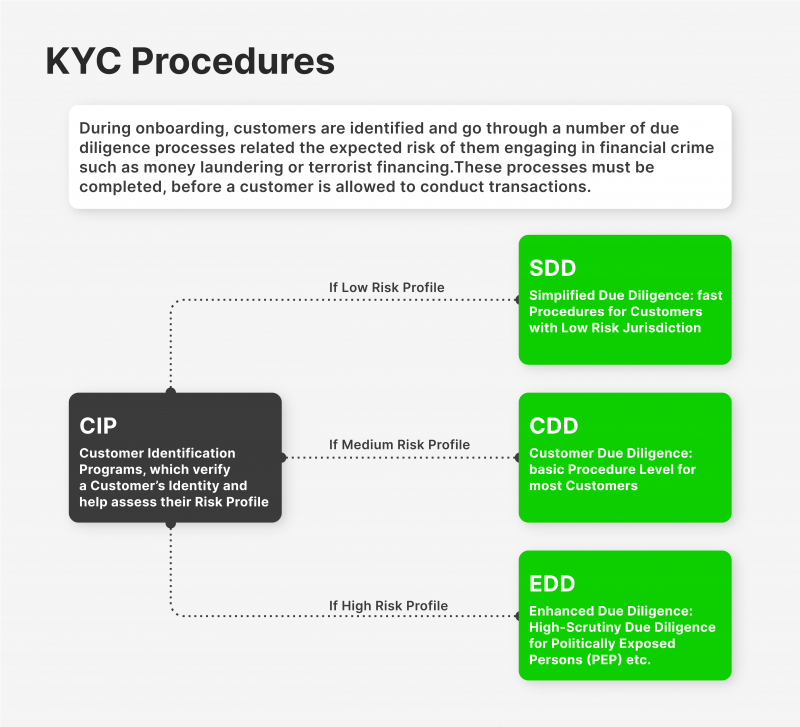
The protocols of any KYC solutions are written using a variety of programming languages and take into account many aspects of security standards describing the user verification process that is an integral part of registering new accounts in cooperation with most entities in the financial world. Using models embedded in top-level financial security protocols, in particular, personal data encryption used in all areas related to finance, KYC technology is the only tool of its kind that performs a full range of necessary measures aimed at comprehensive customer identity verification and analysis of each user’s identity, which helps to achieve a high level of trust and reliability when working with investment and other similar types of products.
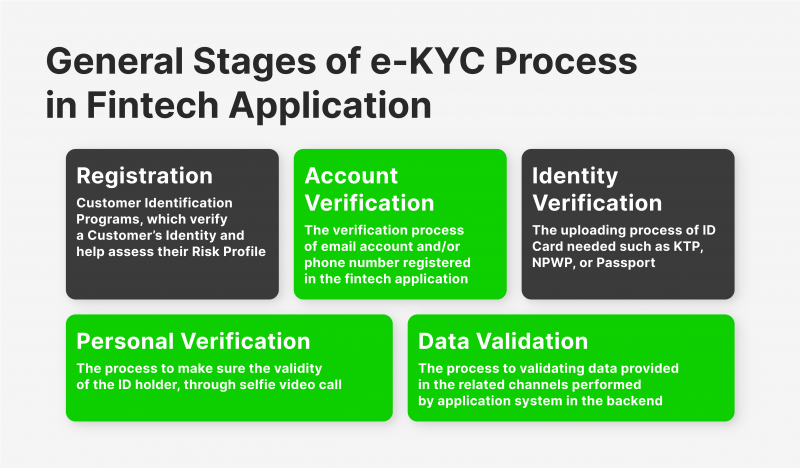
Thanks to the rapid development of new generation technologies, in particular, solutions based on artificial intelligence and blockchain, the KYC process has gained a new stage in the world of systems and tools designed to provide a comprehensive process of identification of the identity of users interacting with any type of entities in the world of finance, especially with financial institutions that give access to trading on the capital markets, whether Forex, cryptocurrencies or complex derivatives. Thanks to AI, it has become possible to use intelligent systems in KYC onboarding to recognise suspicious activity, signs of financial crime, money laundering, terrorist financing, fraudulent activity and other activities contrary to legal norms as part of verifying users’ identity.
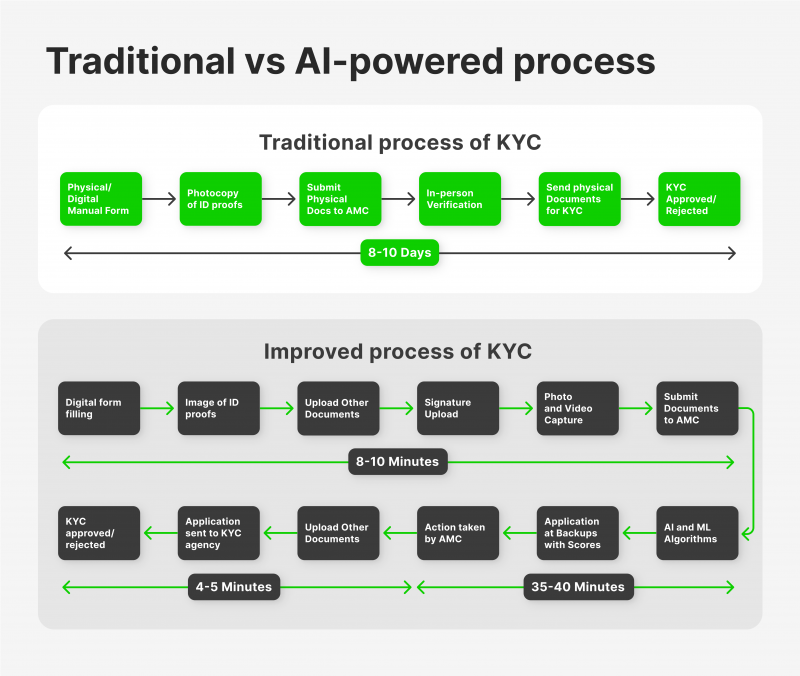
According to a report by Market Quadrants, as of 2022, many KYC solution vendors are emphasising the adoption of AI and machine learning-based technologies.
What is KYB Technology and How Does It Work?
Unlike when a business interacts with an individual, KYB is a verification procedure utilised when one business interacts with another. It helps establish and verify the identity of business customers in a manner akin to that of KYC. The degree of risk associated with initiating a business partnership with the organisation in issue can also be precisely evaluated by it. With the use of KYB, companies can ascertain if an entity is a legitimate corporation or if its owners have created a shell company — a business that serves as a front for some sort of illegal activity.
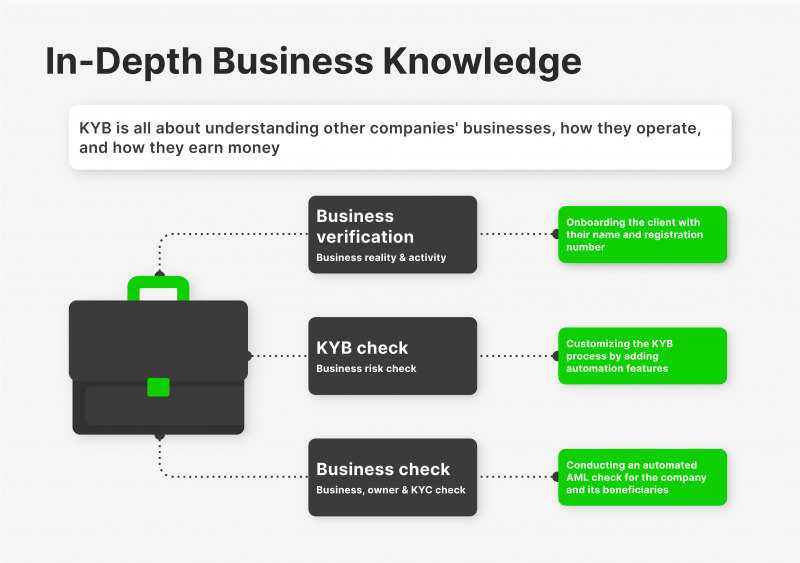
Following the verification of a business’s legitimacy, the ownership structure of the enterprise, comprising the directors and ultimate beneficial owner (UBO), is determined. Finding out who these people are can assist in revealing information about the legitimacy of the company, any connections to criminal activity, and the involvement of anonymous parties. In addition, the KYB process may assist companies in evaluating risk by revealing if the organisation or individuals under investigation have ever faced penalties, been found guilty of a crime, or been the subject of unfavourable press due to past actions.
As in the case of KYC technology, it is expected that KYB solutions will also receive a new round of development due to the introduction of their functionality of tools based on AI and machine learning technologies, the symbiosis of which will help to create a reliable ecosystem of know your business requirements that includes all aspects of the process of ensuring the security of business relationships, taking into account the individual characteristics of the activities of each of them, including recording and automatic processing of all financial operations, monitoring and analysis of channels of interaction between the two companies based on statistical data and models of the historical picture of activity for a prompt response and elimination of any signs of fraudulent activity in all forms of its manifestation.
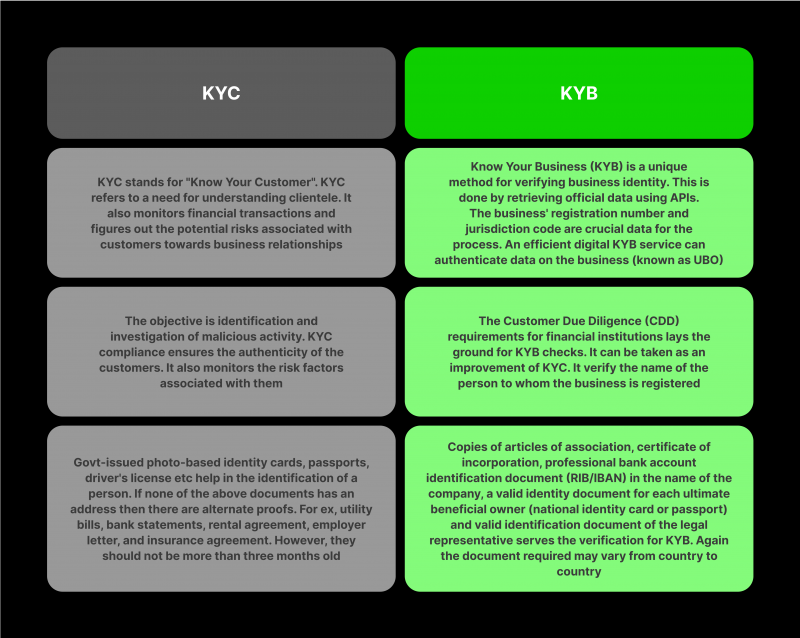
KYC/KYB Comparison: Main Differences and Peculiarities of Application in the Financial Sphere
As mentioned above, KYC and KYB technologies are integral elements of the system of ensuring a full range of measures aimed at obtaining comprehensive information about the identity of an individual interacting with a financial institution in the first case, and business units interacting with another business unit within a certain type of activity. Both types of procedures pursue the same goal — to reduce or completely eliminate the probability of adverse consequences associated with any type of illegal activity. At the same time, they have a number of significant differences and peculiarities of application, which are presented below.
Processes and Procedures
KYC procedures are applied in almost all financial structures, as well as in the work of such financial institutions as Forex brokerage houses and cryptocurrency exchanges, as well as financial institutions engaged in providing various services related to trading in foreign exchange, stock and other types of capital markets. The KYC process includes a customer identity verification process, comprehensive AML monitoring, which helps identify signs of money laundering, and a multi-level risk assessment system, allowing one to conclude whether it is worthwhile to cooperate with a particular client.
In turn, the KYB procedure implies using a set of measures to verify the legal entity (business) for its legality, including analysing its licenses and special permits to operate. Moreover, KYB provides for the assessment of shareholder structure and UBO (Ultimate Beneficial Owner), evaluation of business risks that may arise in the process of cooperation, as well as continuous monitoring of business processes of the organisation, helping to understand the degree of change in the level of risk that determines the level of safety of conducting business.
Applications and Purposes
The KYC process involves a comprehensive and thorough verification of the identity of customers intending to use the services or products of financial service providers and other financial institutions by scrutinising their identity documents, biometrics, as well as addresses, contact numbers, etc. KYC checks also include assessing the potential criminal risk of each customer, continuously monitoring for suspicious activity and archiving all personal, financial and other types of documents.
In turn, the KYB procedure includes several operations related to the verification of the legal status and ownership of the company, its registration data, and all related documents confirming its financial solvency and viability, as well as legality. The KYB procedure also includes some operations related to verifying the legal status and ownership of the company, its registration data and all related documents confirming its financial credibility and legality.
Solutions and Challenges
Today, the use of KYC technology is complicated by the widespread problem of identity theft, which leads to the illegal use of another person’s identity to commit fraud or other criminal activities related to financial crime. Digital identity verification solves this problem. On the other hand, there is the problem of using forged or distorted identity documents, which today is solved by biometric authentication systems.
The use of KYB solutions is hampered by the lack of standardisation of verification processes, as there is no clear or universal way to conduct KYB verification or measure its effectiveness. This problem is solved by using KYB services with a template evaluation model. On the other hand, this procedure has a complex work structure as it often requires multiple sources and valuation tools such as commercial or public registers, AML and KYC checks to get a complete picture of the business.
Technological Enchantments and Innovations
Today, both KYC and KYB systems keep pace with progress and use advanced solutions based on artificial intelligence, machine learning and blockchain technologies to extend the functionality of analysing any type of data for authenticity and validity.
For example, AI automates processes such as anti-money laundering screening and determining the risk level of a person or entity, while OCR systems help extract data and match live selfies with users’ identity documents. In turn, blockchain makes transaction records more secure and easy to retrieve and read. This builds trust and privacy and simplifies the verification process.
Regulatory and Legal Frameworks
KYC requirements have been around for a while and have, therefore, been honed over time, making them more straightforward. Many nations have legislation regarding KYC that outlines both acceptable and prohibited procedures, including the software that must be utilised during the process. The ID check business is highly developed, and established guidelines specify how the procedure should be performed.
Conversely, there is a great deal of uncertainty around KYB rules, which leads to significant variations in the procedures that companies and KYB providers adhere to. The process of creating a standard is still in progress. The basic procedures and directions, such as figuring out who the real owners are, looking up sanctions, making sure to use at least two trustworthy data sources, and evaluating the risk according to one’s risk appetite, are hazily outlined in the legislation.
Future of KYC & KYB in Financial Regulatory Frameworks
The process of digitalisation is making its mark in all spheres of human activity, and in particular, it concerns the financial sphere as one of the fundamental ones in the structure of any country’s economy. The improvement of various technologies, including blockchain, has become a fertile ground for the development of various financial organisations offering an incredibly large number of different solutions and systems in one way or another related to money transactions, including trading on capital markets.
Existing security methods based on the use of KYC and KYB systems find practical application in many areas of the financial sector, from banking organisations to various financial institutions, where they have gained particular popularity due to their functionality. At the same time, the current KYC and KYB tools, while providing a satisfactory level of security and supporting the necessary check protocols to detect fraudulent activity, still have certain shortcomings associated with various aspects of the behaviour of criminals who gain access to users’ personal data using ingenious schemes.
With an unprecedented abundance of new technological breakthroughs now available in the public domain, it is expected that in the future, identity and business legitimacy verification tools such as KYC and KYB will undergo significant changes in terms of their functionality and operating principles. One of the most significant changes is expected to be the full automation of the manual processes of KYC and KYB procedures. Artificial intelligence and machine learning will keep gaining ground on tedious, repetitive, manual KYC activities that would otherwise require significant time and effort. Fintechs, banks, cryptocurrency exchanges, and IT security service providers are already implementing AI-based KYC solutions for Customer Due Diligence (CDD).
In addition, Real-time risk profiling using AI and IoT is expected to be introduced into KYC and KYB procedures. The IoT market is still in its early stages, with a 25% CAGR. Including machine learning and artificial intelligence will raise the bar for digital KYC and KYB solutions. By creating digital client personas and tracking financial behaviour in real time, banks, fintech, and other businesses will be able to reduce costs further and save time by utilising IoT. In order to reduce fraudulent activity, it will also benefit businesses that profile their customers’ risk.
Another innovation in the world of KYC and KYB solutions will be a dramatic change in the framework of company owner disclosure. With its final revisions, the U.S. Corporate Transparency Act of 2021 has made it plain that beneficial owners of businesses incorporated in the United States can no longer stay anonymous. Due to impending legal changes, identity and ownership data verification with all relevant registration documents will now be necessary. Nevertheless, a significant portion of the KYC issue is still unidentified business owners or UBOs. Business owners’ information is frequently incomplete, making implementing an efficient KYC procedure difficult.
Certain nations, like Luxembourg, the British Virgin Islands, and Panama, are referred to as tax havens, and it could take them some time to abide by legislative reforms. Governments will soon exchange information on beneficial ownership to bolster and adhere to KYC protocols.
Conclusion
The fintech industry is evolving rapidly, and with it, technologies designed to ensure the interaction of different financial entities with each other and with their customers are improving in parallel. Modern KYC/KYB solutions play a significant role in maintaining a high level of security for financial organisations, helping to preclude financial crimes of any kind.














