US Inflation Rate is on The Rise Again – Why is That?

The inflation and interest rates in the United States have been pivotal discussion points this year. Major changes and shifts have happened in the economy, which is facing presidential elections, geopolitical instability, changing consumer prices, and other challenges taking local markets up and down.
After successfully driving the inflation rate to record-low numbers, the prices are picking up again, and US policymakers who planned to reach a target rate by the end of this year might have to wait until the next year.
Why are consumer prices up again? What factors could have affected this increase? Let’s find out.
US Inflation Rates in 2024
The Federal Reserve was determined to stimulate the economy through multiple reforms that could spur local demand and boost borrowing. Interest rates have never been that high since 2000, while the inflation, despite post-COVID improvements, is still far from being ideal.
Consumer prices peaked this year at 3.5%; that’s when the Fed introduced a plan to decrease this rate to a target level of 2%. The borrowing rate cut promises and close monitoring of labour markets, spending, and treasury holdings helped lower inflation month by month.
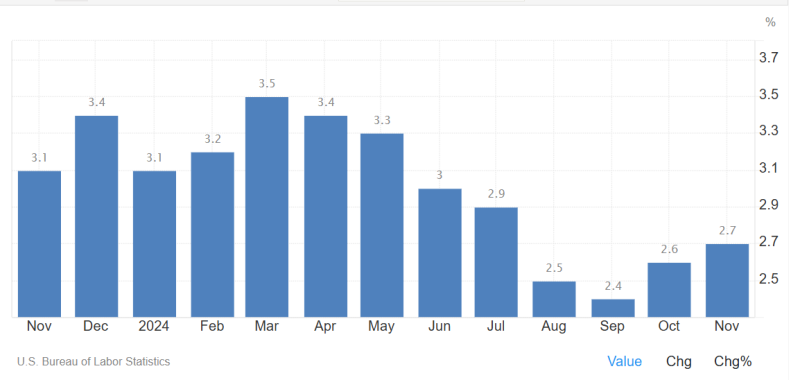
By September 2024, the inflation rate reached its lowest level since 2021, at 2.4%. However, the number quickly bounced back, recording 2.6% and 2.7% in October and November, respectively.
How Does it Affect The Economy?
The US regulators face the challenge of balancing inflation and interest rates. If the borrowing costs are significantly low, consumers will take credits and spend more, leading to higher inflation. However, higher interests may curb prices but deter business growth.
Explore Deeper Industry Insights
Learn from experts shaping the future of financial services — get the latest strategies and trends.
Corporations, economists and multinational companies plan their local and foreign investments based on these numbers. Higher inflation rates lead to pricing challenges, increasing costs and market volatility.
Experts argue that the 2% aim encouraged many businesses and money holders to put their cash on the side until the inflation drops to this level. In addition, the uncertainty surrounding the new president’s arrival at the White House creates speculation.
Why is US Inflation High?
When it comes to US consumer prices, many socioeconomic, political, and international disputes, currency performance, and other factors affect the local market.
Many attribute the uptick to the rising prices in some key sectors:
- Grocery Prices: The cost of groceries rose by 0.5% over the month, with significant increases in meats, poultry, fish, and eggs. Beef prices increased by 3.1%, and egg prices surged by 8.2%.
- Utility Gas Service: Prices for utility gas services increased by 1% in November compared to October, contributing to higher household expenses.
- Used Vehicles: The prices of used cars and trucks rose by 2% between October and November, reversing a previous downward trend and impacting overall inflation.
Other factors leading to this increase could be the pre-election investments and the demand for fiscal spending, which affects inflation rates. The geopolitical tension in the Middle East also influences oil, gas, and food production and prices, adding inflationary pressures.
Can Fed Interest Rate Cuts Help?
Many argue that the interest cuts the Federal Reserve introduced in the previous month have affected prices and spending. As the Fed rate decreases, individual and institutional consumers can take low-cost loans and increase expenditure on non-essential goods and services.
This surge in spending triggers higher prices, especially if the production does not grow at the same level, creating demand and supply gaps.
The Federal Reserve is expected to cut interest rates by 25 basis points at the upcoming December 17-18 meeting, bringing the federal funds rate to a range of 4.25%-4.50%. However, a more cautious approach could maintain prices more effectively.
Future Outlook
Many believe 2025 will be bullish for stocks, cryptocurrencies, and other financial markets. Much of these predictions are driven by the recovering US economy and the arrival of Trump the office, who is known for his pro-corporate approach as a successful businessman.
Analysts debate that no more interest rates are needed the next year, and it is time to stabilise and observe the outcomes of the current policies.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
The argument is that there is an abundance of money on the side waiting to be invested, even without another Federal cut, because the latter would lead to higher inflation and increased production costs.
Conclusion
The US inflation rate is climbing again amidst interest rate cuts and geopolitical changes. However, if we take a closer look at the rising prices in the US, the rising automobile, energy, and housing costs are the main drivers for this growth.
With the Federal meeting expected to lower the borrowing rate even further in December, will another cut exacerbate or curb the growth?
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. It is not finance advice and should not be relied upon for investment decisions. Always do your own research and consult a financial advisor before investing.