What Does Derivatives Stand for, and How Does it Work?

The global financial market is filled with numerous opportunities both individuals and organizations can leverage as far as they possess the right skill set. Derivatives trading is one such opportunity that has existed for a long time. It has, however, expanded its tentacles to cryptocurrency trading.
Assets classified as derivatives are derived from an underlying asset upon which their price/value is dependent. These assets include stocks, bonds, currency, oil, and cryptocurrency. They can be traded over the counter (OTC) or through an exchange.
Derivatives trading is different from conventional spot trading as it is usually associated with using leverages. And as such, traders can control a large position in a derivative contract with a relatively small amount of capital.
Understanding What Derivatives Trading Means
Derivative trading is a form of speculative, high-risk investment that allows individuals to trade a particular asset at a future price without necessarily owning that asset. One interesting thing is that users can trade any asset class, provided a derivative market exists for them.
Before trading a derivative market, users must consider the underlying asset, its expiration date, and their position (long or short).
The underlying asset — can include cryptocurrencies, stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, interest rates, and other derivatives. However, the fluctuation or inconsistency in the price of these underlying assets determines the value of their derivatives.
Moreover, the underlying asset price can be affected by several factors, including supply and demand, economic conditions, and government policies. Therefore, you should keep track of such factors as a derivatives trader since they will also influence your trade.
The expiration date/time — is when the derivative contract expires and the differences are settled. It may also be referred to as the last day a derivative contract remains valid.
At expiration, the buyer and the seller of the derivative contract are obliged to settle the difference in the contract’s value or enter into a new contract.
A trader’s position — is the stance a counterparty takes during the bet on the future price of an underlying asset. It can either be a long or short position.
In a long position, a trader profits if the price goes above his entry point at the time of settlement. For a short position, the trader only profits if the underlying asset’s price goes below his entry point. Since it’s between two parties, they can’t take a long or short position at the same time; they must have different views concerning the asset’s future price.
What Types of Derivatives Trading Exist?

The four major types of derivatives are Forward, Futures, Swap, and Option. As a financial investor/trader, futures and options trading are the types of derivatives that you’ll most likely get accustomed to.
Forward
A Forward derivative is a financial contract that involves both counterparties agreeing on an asset’s specified (set) price while the trade occurs in the future. This means the underlying asset’s price is locked before the trade occurs.
The primary purpose of a forward derivative is to hedge or balance risks due to the market’s high volatility.
Let’s take an example of a maize farmer and a cereal manufacturer. Assuming the farmer senses there’ll be a decrease in the price of maize in the next three years and the manufacturer feels differently that the price of maize might increase. They can both agree on a forward derivative contract that allows them to set the price of maize now and will enable the trade to occur later, i.e., three years later.
Although the forward derivative is usually risky since it takes place over the counter (OTC) and is not fully regulated, it’s easily customized and can yield even more significant profit. The settlement can also be physical or cash, depending on the underlying asset, and it’s usually remitted after the contract expires.
Swaps
Swap derivatives are financial contracts that allow two parties to exchange cash flows in the future. The most common swap derivatives are interest rate and currency swaps.
Interest rate swaps allow two parties to exchange a fixed interest rate for a floating one and vice versa. This can be useful for a company that has borrowed at a fixed rate but expects interest rates to rise. In that case, they can swap their fixed rate for a floating rate to mitigate their risk.
On the other hand, currency swaps involve the exchange of cash flows in one currency for cash flows in another. It can be used to hedge against currency risk or obtain financing in a foreign currency.
Swap derivatives can also be customized to meet the parties’ specific needs. For example, an inflation swap allows two parties to exchange a fixed rate for an inflation-linked rate, which can be useful to hedge against inflation risk.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
They are used by various market participants, including corporations, governments, and financial institutions. However, investing in swap derivatives can be complex and risky and is typically used by sophisticated investors with a high-risk tolerance.
Futures
Both futures and forward derivatives are quite similar since the price of the underlying asset is agreed upon before trading it in the future. Unlike the forward derivative, the futures market is traded on regulated exchanges including Chicago Mercantile Exchange, and New York Mercantile Exchange. However, crypto traders can use exchanges like Binance, Bybit, OKEx, etc., to execute such trades.
Although the futures market permits traders to hedge their position, the liquidity on exchanges makes speculating for profits more attractive. In futures, investors can either go long (buy) or short (sell); it all depends on their view of the market.
With leverage, investors/traders can borrow more than their initial capital to increase their profit margin. Leverage ranges from “1x to 100x,” depending on the traded derivative assets. However, it’s important to note that the higher the leverage, the higher the risk of getting liquidated. As a result, the settlement comes in as the price goes up or comes down.
Options
Options derivatives are financial contracts that allow a trader to buy or sell an underlying asset at a stipulated price and date. But it’s worth noting that whenever a buy or sell order is made, the counterparty must respond immediately.
Options can either be a call or a put option. The most common type of options is the call option. It allows the buyer to purchase an asset at a specified price called the strike price. On the other hand, a put option allows the buyer to sell an asset at the strike price.
When an investor/trader takes a “long” position in a call option, they essentially bet that the underlying asset’s price will go above the strike price. If the price should go lower, then the option becomes worthless, and the investor loses his money.
On the other hand, if an investor takes a “short” position in a call option, they are betting that the underlying asset’s price will not go above the strike price. If the price does not increase, the option will expire worthless, and the investor will keep the premium paid by the buyer of the option.
When an investor takes a “long” position in a put option, they are betting that the underlying asset’s price will go below the strike price. If the price does not drop, the option will become worthless, and the investor will lose the premium paid for the option.
On the other hand, if an investor takes a “short” position in a put option, they are betting that the underlying asset’s price will not go below the strike price. If the price does not decrease, the option will expire, and the investor will keep the premium paid by the buyer of the option.
Options derivatives are settled in cash. The buyer of the option pays the seller a premium, and the seller keeps the premium regardless of whether the option is exercised or expires.
These types are further classified into two parts: the commitment class and the contingent class.
The commitment class requires both parties to oblige to the derivative contract successfully. There’s no room to walk away. Examples of this are Forward, Futures, and Swap.
In the Contingent class, one of the counterparties can decide not to execute a buy or sell anymore. However, once a buy or sell order is made, it must be executed by the other party. An example of this is Option.
What are the Pros and Cons of Trading Derivatives?

Pros
Derivatives trading entails that two counterparties invest in underlying assets without actually owning those assets. Investing in derivatives is usually for two primary purposes; hedging and Speculating. However, there are other uses, like leveraging through margin trading or arbitrage.
Hedging
Derivatives can be used to manage risk by balancing the potential loss from an underlying asset. For example, a trader may use a derivative to lock in the price of an asset, protecting against a decrease in market price.
Speculating
Traders/investors can also use derivatives to speculate on the price movement of an underlying asset. They will try to gamble on how the underlying asset price will move. This is a higher-risk strategy but can also lead to higher profits.
Leveraging
Derivatives also utilize the use of leverage through margin trading. Traders/investors can borrow money to increase position size. However, leveraging can amplify potential gains, but it can also increase the risk of loss.
Arbitrage
Derivatives can be used to take advantage of price fluctuation between different markets/exchanges. For example, a trader may buy a derivative on one exchange and sell it on another, profiting from the price difference.
Cons
Complexity
Derivatives are complex financial instruments and may be difficult for some investors/traders to understand. This can lead to misunderstandings and mistakes and result in significant losses.
Risk
Since the price of derivatives relies on that of the underlying asset, it can pose a big risk to traders as the price of that asset can fluctuate massively. The fluctuation in price of the underlying asset can be due to various factors including government policies, news, etc. Obviously, this can lead to significant losses if the price moves against the position taken by an investor.
Counterparty Risk
Since derivatives are often traded between two parties, counterparty risks may exist. This is because one party may default on the contract which can lead to losses for the other party. However, such risks can be minimized if the trade takes place on a regulated exchange.
Lack of Regulation
In some jurisdictions, derivatives trading may not be as heavily regulated as other forms of trading, which can create additional risks for investors. However, this is only for over-the-counter (OTC) derivative trades. Derivative exchanges are fully regulated and can avert additional risk for investors.
Lack of Transparency
Derivatives markets are often opaque, meaning it can be challenging to determine the true value of a contract or the level of risk involved. This can make it difficult to accurately price a derivative, leading to market inefficiencies and increased risk.
Spot vs. Derivatives Trading
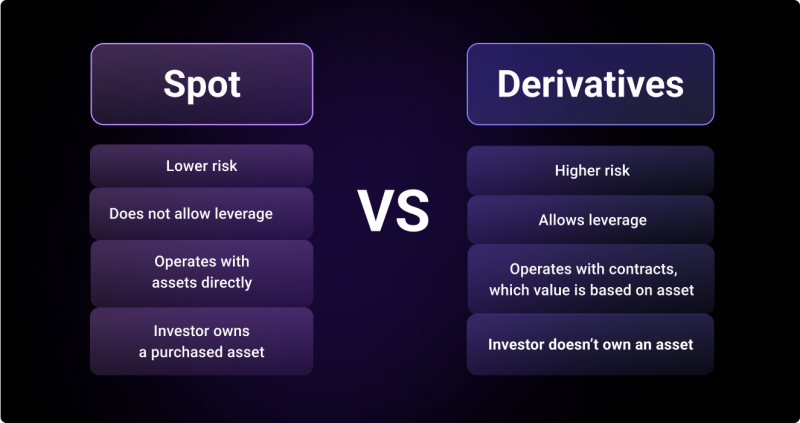
Spot and derivative trading are financial instruments used to buy and sell different assets. Although they almost serve the same purpose, there are still a few differences between them.
While spot trading involves buying and selling an asset to be delivered immediately, derivative trading refers to buying and selling contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset, and it’s settled in the future.
Regarding ownership, the spot market gives the investor ownership of whatever asset is bought. While for a derivative market, a contract with the same value as the underlying asset is owned.
In terms of risk and return, spot trading is less risky than derivative trading. Although their prices can be affected by external factors, including government policies and various fundamentals, traders are usually exposed to more risks in derivatives trading. Since derivatives trading allows the use of leverage, it also increases a trader’s potential returns.
Who Can Trade Crypto Derivatives?
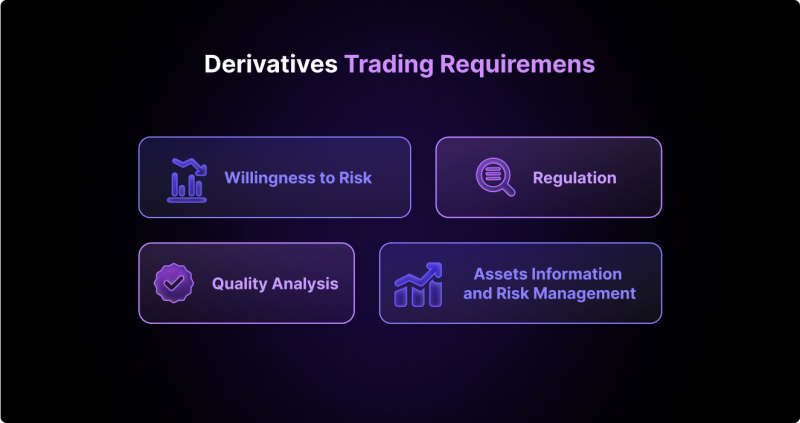
The risks that come with trading derivative is quite alarming, especially now that investors or traders can access liquidity and leverage easily on those assets. Certain prerequisites or necessities are needed from those willing to trade crypto derivatives.
Regulation
In some countries, trading crypto derivatives is restricted to accredited investors only. However, in some other countries, it is available for retail investors to trade crypto derivatives. Potential traders need to check the regulations in their country before trading crypto derivatives.
Quality Analysis
It is generally recommended that only experienced and well-informed investors should trade crypto derivatives. They must be able to make qualitative decisions by doing specific fundamental and technical market analyses.
This is because crypto derivatives can be highly volatile and risky, and the market is still relatively new and less mature than traditional markets.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Assets Information and Risk Management
Before trading crypto derivatives, individuals should understand the underlying assets and risks. They should also be familiar with the terms and mechanics of the specific derivatives they are considering trading. It is also essential to have a well-defined risk management strategy in place.
Willingness to Risk
In general, crypto derivatives trading is unsuitable for individuals unwilling to risk losing their investment. Traders need to understand that the crypto market is highly volatile, and there is a potential for significant losses. Therefore, investing only what you can afford to lose is very important.
How to Trade Crypto Derivatives
Trading crypto derivatives (Futures or Options) is more complex than trading the cryptocurrencies themselves, but it promises higher returns. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to trade crypto derivatives:
Understand the Market
Study the market trends, historical charts, and price movement of assets to be traded, and stay updated with events that could affect the market.
Choose an Exchange platform
Several exchange platforms are available for trading crypto derivatives, such as BitMEX, Kucoin Futures, and Binance Futures. Each platform has fees, trading limits, and a user interface, so choosing one that suits your needs is quite important.
Fund Your Account
After creating an exchange platform, you must fund the account with the cryptocurrency you wish to trade with. Using credit cards or bank transfers, you can deposit fiat currencies to buy these cryptos.
Choose Your Trade
Crypto derivatives can take many forms, such as futures, options, and swaps. Each type of derivative has unique characteristics, so choosing the one that best suits your trading strategy is essential.
Place Your Trade
Once you have chosen your trade, you will need to place an order. Most platforms offer a variety of order types, such as limit, market, and stop orders. Understanding how each type of order works is important before placing any trades
Monitor Your Position
This is done by watching the market to ensure it is moving in the expected direction. This includes keeping an eye on the underlying asset’s price and any relevant news or events that could affect the market.
Have a Risk Management Strategy
Crypto derivatives are highly speculative and volatile, and it’s crucial to have a risk management strategy in place before placing a trade. This involves setting stop-losses and having other plans to manage your position if it moves against you.
Conclusion
While spot trading involves lesser risk, crypto derivatives allow investors to speculate on the future price of an underlying asset. Using leverage to trade, as in the derivatives market, increases traders’ potential returns while exposing them to a more considerable risk.
However, to make the most of derivative trading, especially if you want to avert trading risk, you must have a trading strategy and risk management.