What is Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT), and How to Invest

Successful investors benefit greatly from portfolio diversification. Despite the generous return in classic financial instruments and the high volatility of cryptocurrencies, for example, properties offer a unique proposition for traders, like long-term profitability and value appreciation.
Many financial institutions and multi-asset corporations invest in real estate to improve portfolio diversification and longevity.
Traders are split between two types: stock market and real estate investors. However, REITs provide the best of the world, offering equities in property-holding firms. This keeps stock traders in their realm and exposes the unique advantages of property investment.
So, what is a real estate investment trust and shall you invest in these markets? Let’s explain.
Key Takeaways
- REITs are holding companies that own properties in different sectors, such as residential, commercial, healthcare, retail, etc.
- REIT investments allow individuals to earn from real estate opportunities by owning shares in real estate trusts.
- REITs offer a more affordable way to invest in properties that do not require significant capital investment.
What Is a Real Estate Investment Trust?
REIT – a combination of companies that own or finance income-producing real estate, offering lucrative returns to REITs and their shareholders.
REITs earn from property managing or flipping properties, including buying and selling or renting apartments, lands, social houses or commercial spaces. REITs are traded on the stock market, making it possible for individual or institutional investors to own shares in the estate market.
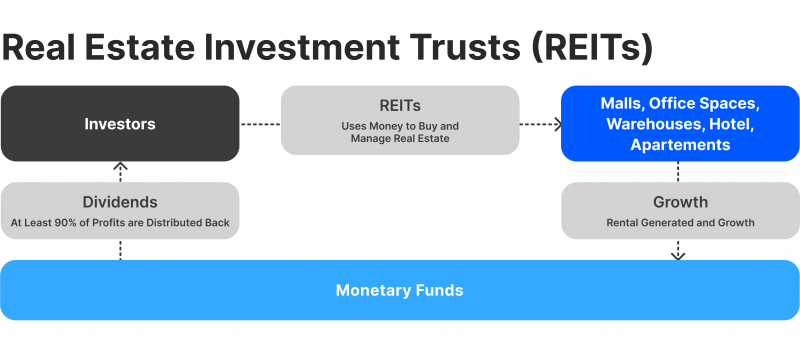
This approach makes it possible for traders to invest in properties without having the significant capital that most real estate investments require. Instead, traders can buy and sell shares in REITs, whose profitability originates from the property market dynamics.
Should You Invest in REITs or Stocks?
After understanding the real estate investment trust definition, discuss if they are worth investing in compared to other instruments.
At a glance, stocks offer higher annual returns than REITs. The S&P 500 yielded 24% returns in 2023, with ongoing estimated returns of 18% in 2024. On the other hand, REITs provide a moderate return of 4-8% annually.
However, investing in stocks has more risks than REITs. Equities are more volatile, and their prices are prone to speculations, which can take prices up and down very dramatically.
Real estate offers a more stable source of income, consisting of monthly rental payments that last for many years. REITs offer shareholders long-term gains, including dividends from property revenue.
Overviewing REIT Growth and Trends
REIT is a highly booming industry, which is expected to grow at a 2.87% CAGR between 2024 and 2028, or $350 billion. In 2024 alone, the market grew by 2.68% on a YoY comparison.
Most of these trends are driven by rising commercial and industrial needs in North America. However, the global rising trends are attributed to the increasing demand for personal household spaces, especially in Asia.

The first REIT was created in 1960 and consisted of mortgage companies that offered a more facilitated way to invest in this booming industry. Small investment firms and traders used REITs to own shares in skyscrapers, shopping malls and business centres in the US.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Several laws were introduced, like the Tax Reform Act of 1976 and of 1986, to regulate the work of business trusts and prevent taxpayers from using partnerships to hide their revenues from other sources.
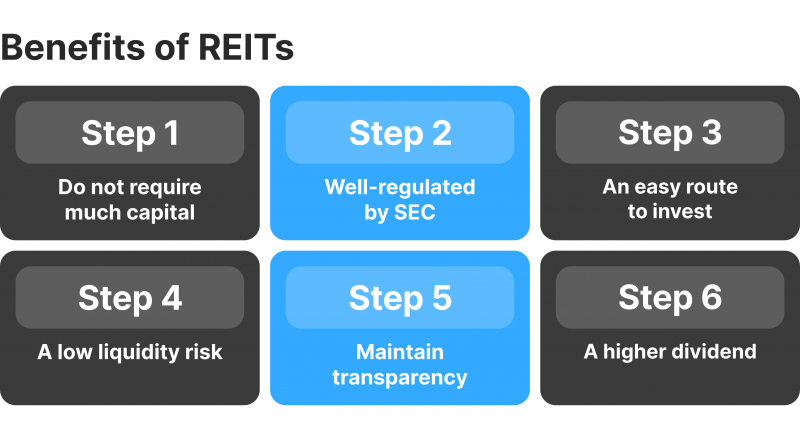
Today, the SEC oversees the REIT market, and for companies to become legitimate property trusts, they must meet the following requirements:
- Register at the SEC as a taxable corporation.
- Formulate a board of directors or trustees managing the company.
- Invest a minimum of 75% of total assets in property.
- Receive a minimum of 75% of gross profit from rental properties, mortgage interests financing properties or the estate sales.
- Pay at least 90% of gross income as dividends to shareholders.
- Have 100 shareholders at least.
- Not having five individuals or less holding more than 50% shares.
Types of REITs
After being founded initially for the mortgage market, public and private REITs now actively offer investments for the following asset classes.
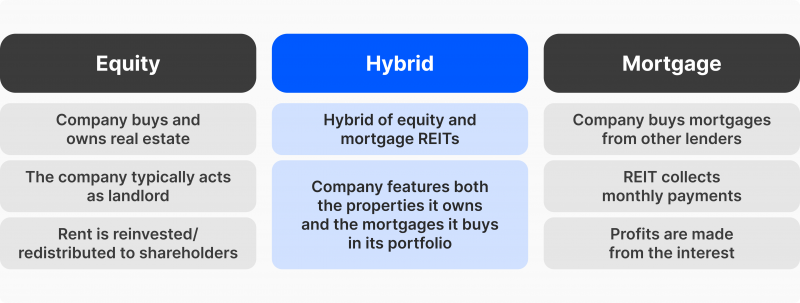
Equity
Equity REITs are the most common type of REIT. They earn money from buy-to-let strategies, which involve buying properties, leasing them and collecting rental returns.
This approach makes up almost 95% of the real estate investment market because it is the most regulated and affordable to customers.
Mortgage
Mortgage REITs (mREITs) issue mortgages or co-financing property development and purchase. mREITs generate income from collecting loan payments or mortgage-backed securities.
This type is more sensitive to interest rates because they earn returns from mortgage-financed instruments, which affect the profitability of property assets and the net asset value.
Hybrid
Hybrid REITs combine equities and mortgage payments. However, this type is gradually disappearing, and the US regulations require property trusts to be more specialised.
Which REIT is The Most Profitable?
REIT companies offer investment opportunities in residential and commercial estate. Moreover, commercial REIT opportunities expand to business offices, healthcare, production plants, and retail spaces.
Each of these types has distinct benefits and challenges based on local economic conditions and demands. Let’s review the top REIT investment property assets.
Residential REIT
Housing REITs include corporations that own and operate multi-family housing units, residential complexes, and duplex apartments. Earning equities from these opportunities comes from rental income.
Therefore, investing in residential REITs requires understanding the market condition of the owned properties, including locations and prices. For example, owning an estate in tourist areas or high-rent-prices like New York or London can generate more profits because residents rely on rent rather than full ownership.
Retail REIT
Retail REITs consist of commercial spaces offered to stores, showrooms or warehouses. These tenants rent properties for many years and engage in fixed rental contracts that offer stable payments.
Retail REITs offer lucrative returns during economic growth when businesses expand their operations and investments, generate more income and pay high lease rates.
However, the only concern in this type is if the tenant runs out of business due to low performance, rendering them unable to pay the rent.
Healthcare REIT
Healthcare REIT companies invest and offer property to hospitals, clinics, care homes and other nursing facilities. This sector benefits highly from the striking healthcare costs in the US.
Investing in this segment must be done through experienced and large corporations because wealthy healthcare businesses require highly advanced facilities and high-tech buildings, which only some REITs can afford.
Office REIT
Investing in office buildings can be highly lucrative, especially if the real estate is located in highly demanded areas, like city centres and business areas. Business office REITs can offer striking returns combined with long-term cash flow.
However, their profitability depends highly on the tenant’s profitability and national economic metrics like inflation and unemployment rates.
How to Invest in a REIT?
REIT is no longer a niche market. Today, you can find many such trusts on NASDAQ, such as Wheeler Real Estate Investment Trust. Here’s how you can start.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Find a REIT company
Publicly traded REITs offer better conditions, including low investment requirements, while private REIT companies are only available for selected individuals and have higher investment requirements. Then, inspect the REIT company’s reputation, service fees and portfolios.
Start Small, Grow Gradually
As a beginner, choose a portfolio that offers low exposure with limited returns. This approach provides a moderate 2-3% yearly return but will mitigate your market risks. You can gradually increase your investments.
Ensure Portfolio Diversification
Investing in REIT companies in various sectors (healthcare, retail, and residential) is the best way to capitalise on the growing property trends. While the market is less responsive to speculations, changing regulations and demands impact the profitability of REIT sectors.
Review Corporation Tax Implications
REITs are subject to different tax laws, which must be calculated to accurately estimate your returns. It is worth noting that REITs are legally required to pay 90% of their taxable income as dividends.
Stay Ahead of Market Updates
Unlike stocks, currencies and commodities, real estate is less volatile and rental prices are less affected by short-term speculations and news.
However, macroeconomics can highly affect REIT returns or property prices. Therefore, keep up with economic news to adjust your portfolio and minimise any potential losses.
Conclusion
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) are corporations that own and operate properties in different markets and industries. Investors can buy shares in REITs and grow their portfolios as rental prices or mortgage rates increase.
This approach offers easy entry into the estate business without having to pay significant amounts to own a property or a commercial space and rent it out. Instead, REITs finance and manage these properties while shareholders reap returns and dividends.








