Best Futures Trading Strategies for Beginners and Professionals

One of the most versatile tools in a trader’s arsenal is futures trading, which enables them to leverage market movements and hedge against risks. In futures trading, a contract is made to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price at a specific time in the future.
It is an attractive market due to the high liquidity and availability of diverse assets, from commodities to indices. While futures trading offers significant profit potential, the strategies you employ can make all the difference.
In this article, we’ll explore some of the best futures market trading strategies for both beginners and professionals. These strategies are crafted for different skill levels, allowing traders to develop from basic understanding to advanced execution.
Key Takeaways
- Futures trading strategies vary in complexity, with options suitable for both beginners and experienced traders.
- Effective risk management is crucial in futures trading for long-term success.
- Backtesting and developing a comprehensive trading plan is fundamental for any futures trader.
- Utilising tools such as a futures trading simulator and being mindful of futures trading hours can significantly optimise performance and decision-making in the futures market.
Best Futures Trading Strategies for Beginners
In futures trading, success can mean significant profits, but mistakes can be extremely costly. That’s why it’s so important to have a strategy in place before you begin trading. If you are a newcomer to this field, consider these more or less easier strategies.
Adaptive Trend Following
Adaptive trend following is an excellent starting point for beginners in futures trading. This strategy involves identifying the momentum of established stock market trends. Unlike rigid trend-following methods, the adaptive approach allows traders to adjust their positions as market conditions change.
Key components:
- Use moving averages or the Average Directional Index (ADX) to identify trends
- Adjust position sizes based on trend strength
- Set trailing stop-losses to protect profits.
For beginners, the beauty of adaptive trend following lies in its simplicity and flexibility. It removes the pressure of perfectly timing market entries and exits, allowing novice traders to focus on larger market movements.
The Pullback Strategy
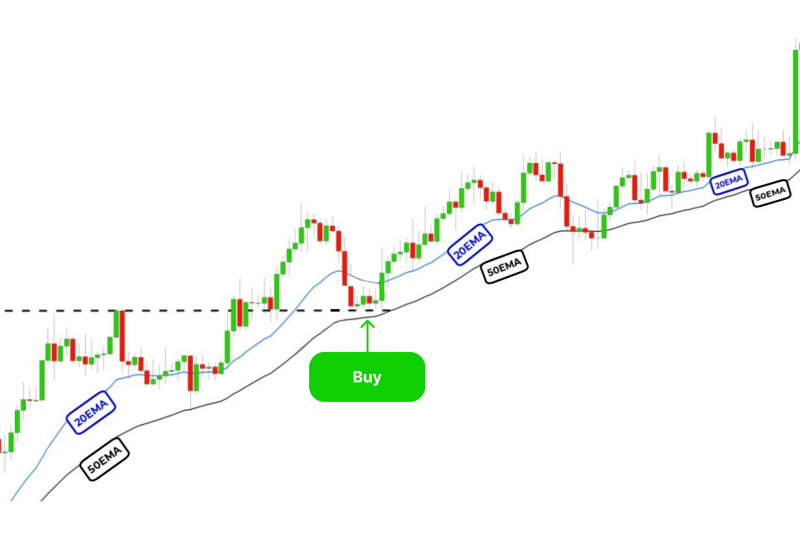
The pullback strategy is another beginner-friendly approach that capitalises on short-term price retracements within a larger trend. This method requires patience and a good eye for identifying support and resistance levels.
How it works:
- Identify the overall market trend
- Wait for a price pullback to a support or resistance level
- Enter a trade in the direction of the primary trend when the pullback shows signs of reversing
Tools like Fibonacci retracement levels and the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can help beginners spot potential pullback opportunities. This strategy teaches new traders the importance of timing and helps them avoid chasing prices at unfavourable levels.
Breakout Trading Strategy
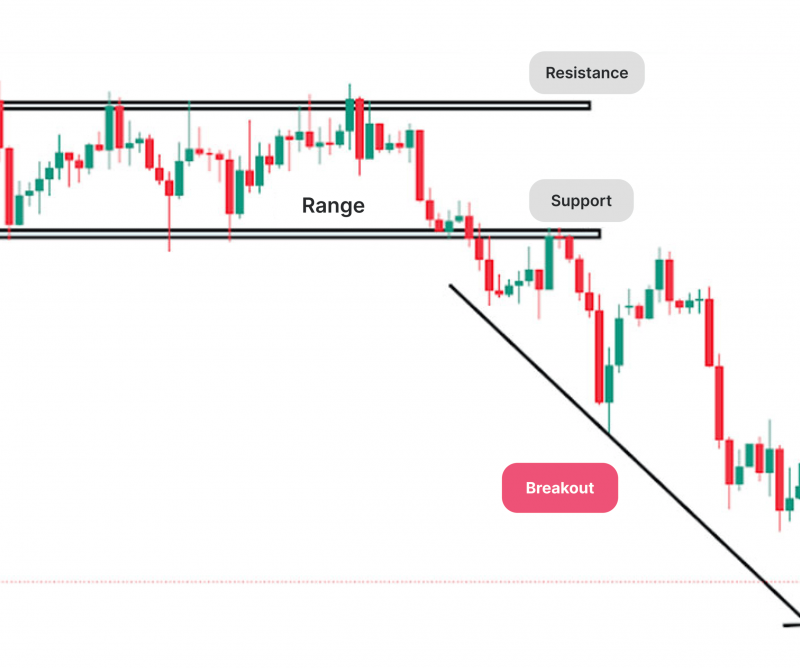
Breakout trading is a popular strategy aiming to capture profits from significant price movements when the market breaks through established support or resistance levels. This approach is particularly suited for beginners due to its clear entry and exit points.
Steps to implement:
- Identify key support and resistance levels on charts
- Set up alerts for potential breakouts
- Enter trades when the price convincingly breaks through these levels
- Place stop-loss orders just beyond the breakout point to manage risk
For beginners, the challenge lies in identifying these breakouts correctly. Tools such as Bollinger Bands, volume indicators, or price patterns like triangles and flags can help traders spot potential breakouts.
When a breakout occurs with high volume, it’s often a strong confirmation that the price will continue in the breakout direction. Timing is crucial with this strategy, so traders must be ready to enter the market swiftly after a breakout happens.
Simple Moving Average (SMA) Crossover Strategy
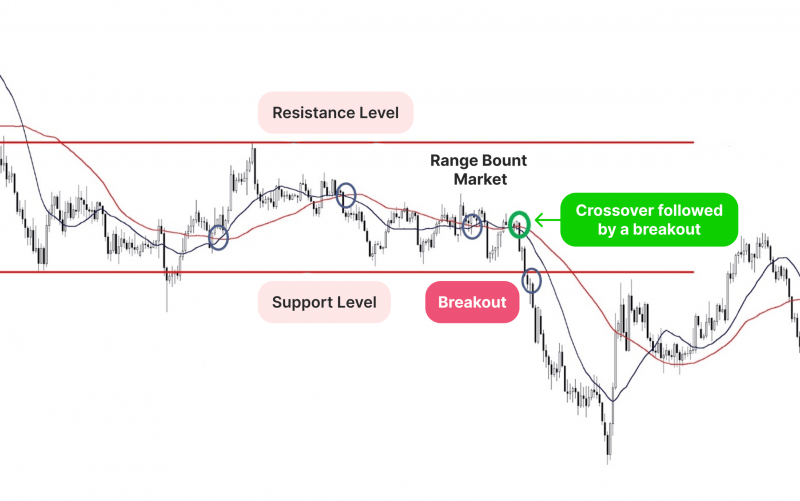
The SMA crossover strategy is a straightforward yet effective method for beginners to identify potential trend changes in futures markets. This approach uses two moving averages – typically a shorter-term and a longer-term average – to generate buy and sell signals.
How to use it:
- Plot two SMAs on your chart (e.g., 50-day and 200-day)
- Buy when the shorter-term SMA crosses above the longer-term SMA
- Sell when the shorter-term SMA crosses below the longer-term SMA
This strategy helps beginners filter out market noise and focus on significant trend shifts. However, it’s important to note that SMA crossovers can lag behind price action, so combining this with other indicators can improve its effectiveness.
Range Trading Strategy
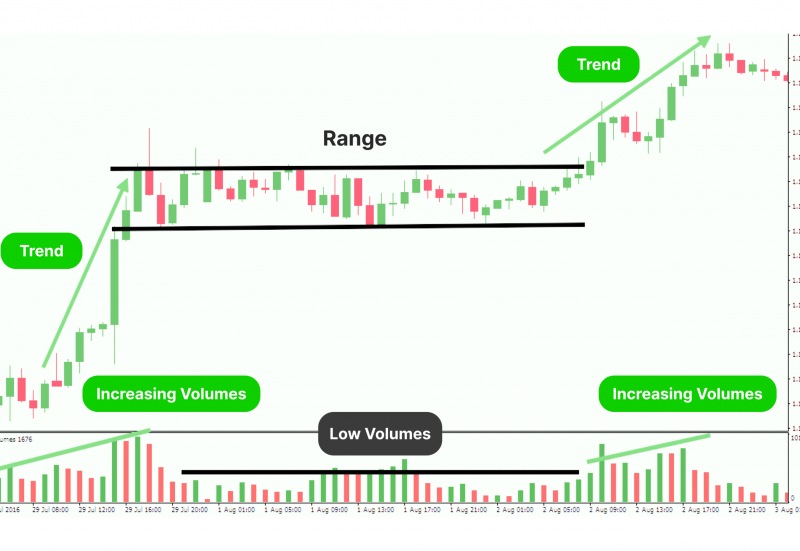
Range trading is an excellent strategy for beginners to practice in less volatile market conditions. This approach involves identifying price ranges where a futures contract tends to bounce between support and resistance levels.
Key steps:
- Identify a trading range using horizontal support and resistance lines
- Buy near support levels and sell near resistance levels
- Set stop-loss orders just outside the range to limit potential losses
Range trading teaches beginners the importance of patience and discipline in futures trading. It’s beneficial in sideways markets where trend-following strategies may be less effective.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Beginners can use technical tools like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to confirm overbought and oversold conditions, which helps determine optimal entry and exit points within a range. By buying at the support level and selling at the resistance level, traders can generate profits in a relatively low-risk environment.
However, being aware of potential breakouts that could invalidate the range, resulting in a sharp move outside the expected boundaries, is crucial.
Advanced Futures Trading Strategies for Professionals
Now, let’s explore more complicated strategies that require more experience and knowledge for successful utilisation.
Spread Trading Strategy
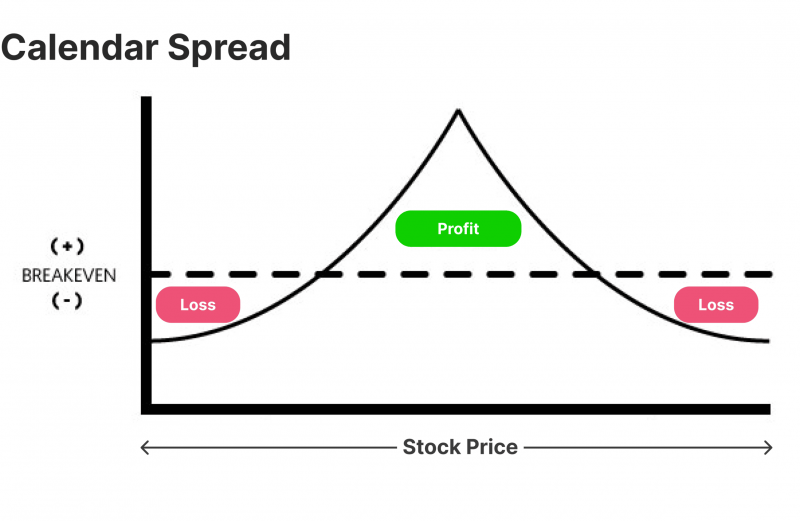
Spread trading is a more advanced strategy involving simultaneously buying and selling related futures contracts to profit from the price differential. This approach is popular among professional traders due to its potential for reduced risk compared to outright futures positions. Additionally, margin requirements for spread trades are often lower, allowing for more efficient capital use.
Types of spreads:
- Calendar spreads: Trading the same commodity with different delivery months
- Inter-commodity spreads: Trading related but different commodities
- Inter-market spreads: Trading the same commodity on different exchanges
Professional traders use spread trading to capitalise on market inefficiencies and to hedge against overall market movements. This strategy is widely used in commodity markets where seasonal changes can cause price fluctuations.
Success in spread trading requires a deep understanding of market relationships and factors affecting relative values between contracts.
Quantitative Order Flow Analysis
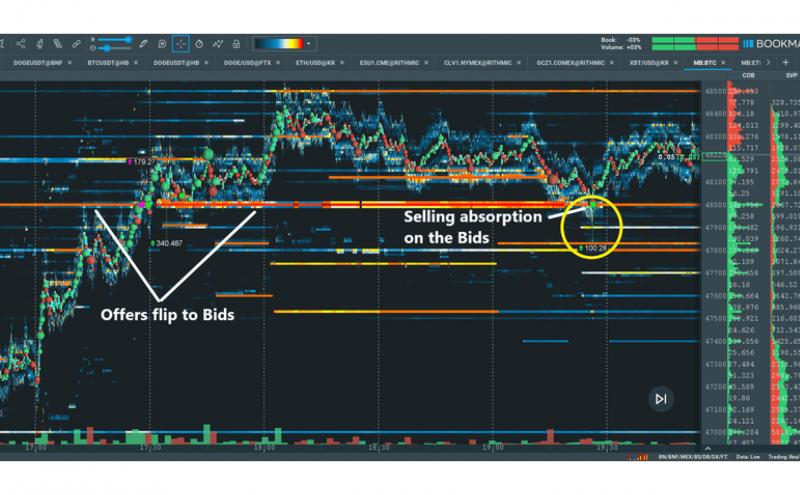
Quantitative order flow analysis is a sophisticated strategy involving real-time market data to predict future price movements. This approach is compelling in futures markets, where large institutional orders can significantly impact prices.
Key components:
- Analyse market depth and transaction volumes
- Identify patterns in order flow that may indicate future price direction
- Use advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to process data
Professional traders employing this strategy often use specialised software and high-frequency trading tools to gain an edge in fast-moving markets. The ability to interpret order flow data quickly can provide valuable insights into market sentiment and potential price movements before they’re reflected in the broader market.
Volatility Harvesting
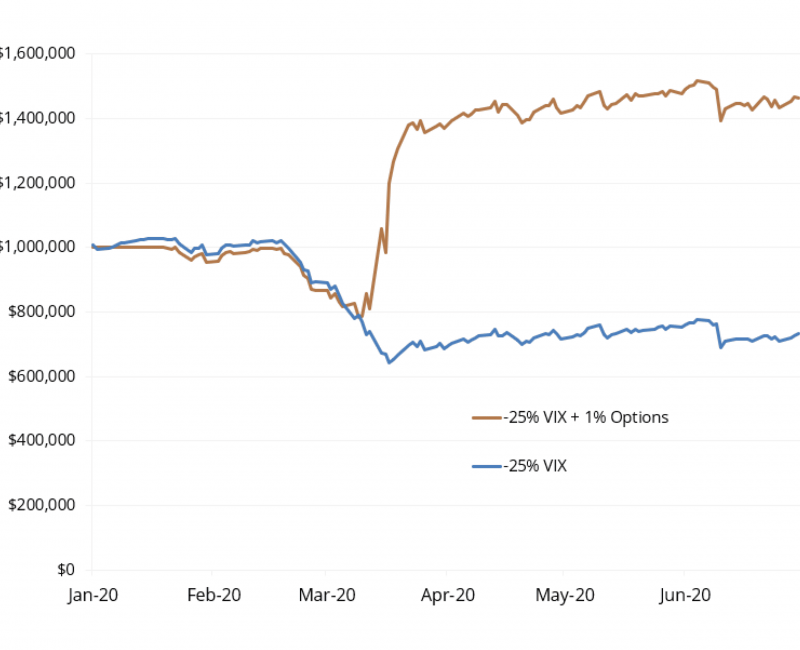
Volatility harvesting is an advanced strategy that aims to profit from price fluctuations regardless of market direction. This approach is particularly relevant in 2024’s uncertain economic climate, where markets are experiencing increased volatility due to factors like geopolitical tensions and shifting monetary policies.
Implementation techniques:
- Use options strategies like straddles or strangles to profit from volatility
- Employ mean reversion strategies during periods of extreme price movements
- Utilise volatility indicators like the VIX to time entries and exits
Professional traders using volatility harvesting strategies must have a strong understanding of options pricing and risk management techniques to overcome the complexities of this approach.
Precision News Trading
News trading has always been a part of futures markets, but professional traders are taking it to new heights with precision timing and advanced analytics. This strategy involves making rapid trading decisions based on economic releases, corporate announcements, and global events that can impact futures prices.
Key elements:
- Develop a system for quickly processing and analysing news releases
- Use algorithmic trading to execute trades immediately upon news release
- Incorporate sentiment analysis of social media and news sources
Success in precision news trading requires quick reflexes and a deep understanding of how different types of news impact various futures markets. Professional traders often use specialised news feeds and low-latency trading infrastructure to gain a competitive edge.
Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage, or “stat arb,” is a complex strategy that uses mathematical models to identify pricing inefficiencies across multiple related futures contracts. Quantitative traders and hedge funds favour this approach due to its potential for consistent, low-risk returns.
How it works:
- Develop statistical models to identify historical price relationships between futures contracts
- Detect temporary deviations from these relationships
- Execute trades to profit from the expectation that prices will revert to their statistical norms
Successful implementation of statistical arbitrage requires advanced mathematical skills, powerful computing resources, and the ability to process vast amounts of market data in real time. Professional traders using this strategy often employ teams of quantitative analysts and data scientists to develop and refine their models.
The strategies employed by Richard Dennis, Paul Tudor Jones, John Henry, Ed Seykota, and Larry Williams have set them apart as some of the most successful futures traders in history.
Backtesting and Optimising Your Futures Strategy
Regardless of your experience level, backtesting is crucial in validating any futures trading strategy. This process involves applying your trading rules to historical market data to assess how your strategy would have performed in the past.
Steps for effective backtesting:
- Gather reliable historical data for your chosen futures markets
- Define clear rules for your trading strategy, including entry and exit criteria
- Use backtesting software to simulate your strategy on past market data
- Analyse performance metrics such as win rate, profit factor, and maximum drawdown
- Refine your strategy based on backtesting results
Incorporating tools like futures trading simulators can dramatically improve your success in the futures market. These tools are invaluable for both beginners looking to test basic strategies and professionals experimenting with advanced techniques.
Understanding futures trading hours is also essential to optimise the timing of your trades. The global futures market operates nearly 24/7, but liquidity and volatility vary depending on the time of day. Traders must consider these fluctuations when planning their entry and exit points.
But keep in mind that past performance doesn’t guarantee future results. Market conditions change, and strategies that worked well in the past may not be as effective in current or future markets. Use backtesting as a tool to refine your approach, but always be prepared to adapt to changing market conditions.
Developing a Futures Trading Plan
A comprehensive trading plan is essential for both beginners and professionals in futures trading. Your plan should outline your trading goals, risk tolerance, and specific strategies you’ll employ in various market conditions.
Key components of a futures trading plan:
- Define your financial goals and risk tolerance
- Specify markets where and why you’ll trade futures
- Outline your chosen trading strategies and the conditions for using each
- Set clear rules for position sizing and risk management
- Establish a routine for market analysis and trade execution
- Create a system for tracking and reviewing your trading performance
Your trading plan should be a living document that evolves as you gain experience and market conditions change. Regularly review and update your plan to ensure it remains aligned with your goals and the current market environment.
Risk Management
Effective risk management is crucial in futures trading due to the leveraged nature of these markets. Both beginners and professionals must implement robust risk management practices to protect their capital and ensure long-term success.
Essential risk management techniques:
- Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on each trade
- Implement proper position sizing based on your account balance and risk tolerance
- Diversify your futures portfolio across different markets and strategies
- Regularly monitor and adjust your positions based on changing market conditions
- Use options strategies to hedge your futures positions when appropriate
Remember that no risk management system is perfect, and there’s always the potential for losses in futures trading. Be prepared for worst-case scenarios and never risk more capital than you can afford to lose.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One of the most common mistakes in futures trading is over-leverage, where traders take on too much exposure with too little capital. This can lead to significant losses if the market moves against the position. Beginners, in particular, often underestimate the risk of leverage and overextend themselves, leading to rapid losses.
Another common mistake is emotional trading, where decisions are driven by fear or greed instead of a well-thought-out strategy. Emotional trading often leads to impulsive decisions, such as exiting trades too early or chasing after losing trades, which can minimise profits and increase losses.
Finally, failing to plan is a widespread error affecting new and experienced traders. A well-developed trading plan, which includes entry and exit points, stop-loss levels, and position sizes, is critical for maintaining discipline and avoiding rash decisions in the heat of the moment. When applied consistently, risk management is a safeguard that prevents these common mistakes from collapsing a trader’s success.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Advanced Tools and Resources for Future Traders
Choosing the right trading platform is critical for both beginners and professionals in futures trading, as it can greatly impact the efficiency and success of your trading.
Beginners should look for platforms that offer a user-friendly interface, educational resources, and tools like paper trading to practice without risking real money. Platforms like TradingView are excellent choices for beginners because they offer intuitive designs, a wide range of charting tools, and access to futures markets.
For more experienced traders, advanced platforms such as MetaTrader 5 provide professional-grade features like custom algorithmic trading, sophisticated charting tools, and access to global futures exchanges. These platforms also support advanced order types, automated strategies, and extensive backtesting capabilities, allowing seasoned traders to refine and implement complex trading strategies rapidly.
Additionally, many professional platforms integrate with APIs and third-party tools to execute high-frequency trades or perform real-time market analysis.
Market News and Data Feeds
Real-time market data and news feeds are essential for futures traders, as market-moving events can happen quickly, leading to significant price shifts. Access to live data allows traders to react to news and economic events as they unfold, which is crucial in fast-moving futures markets.
Services like Bloomberg Terminal, Reuters Eikon, and CQG provide professionals with real-time data feeds, detailed economic reports, and access to breaking news across various sectors, including commodities, equities, and global events.
For beginners, platforms like Yahoo Finance or Trading Economics offer free or affordable access to economic calendars, news, and basic real-time quotes. Traders can also use tools such as the Commitments of Traders (COT) report, which tracks the positions of large market participants and can offer insights into the sentiment behind futures markets.
Keeping up-to-date with geopolitical events, supply and demand fluctuations, and government policies is crucial for making informed futures trades, as these factors can dramatically influence price movements.
Education and Mentorship
Both new and experienced traders benefit significantly from continuous education, as futures markets are complex and constantly evolving. Beginners should enrol in online courses covering trading futures basics, risk management, and common strategies. Platforms like Investopedia Academy, Udemy, and Coursera offer comprehensive futures trading courses covering foundational and advanced topics.
Trading forums and communities like Elite Trader or Futures.io allow traders to share ideas, strategies, and insights. These forums are valuable for traders looking to learn from others’ experiences or get feedback on their trading approaches. Additionally, subscribing to newsletters from reputable futures traders or firms can provide regular market updates and strategy tips.
For those seeking more structured guidance, mentorship programs offer personalised advice and strategies from experienced traders. Mentorship allows traders to receive feedback on their performance, fine-tune their strategies, and gain deeper insights into market behaviour. Having a mentor who can offer practical insights and tailored advice is invaluable, particularly for intermediate and advanced traders looking to refine their skills or transition to more complex futures trading techniques like arbitrage or spread trading.
Conclusion
The best futures trading strategies for 2024 combine time-tested techniques with innovative approaches that adapt to evolving market conditions. Whether you’re a beginner starting with simple trend-following strategies or a professional employing advanced quantitative methods, success in trading futures requires continuous learning, disciplined execution, and robust risk management.
As you explore these strategies, remember there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to futures trading. Experiment with different techniques, backtest rigorously and develop a trading plan that aligns with your goals and risk tolerance. With dedication and the right approach, both beginners and professionals can find success in futures trading.
FAQ
How do interest rates affect futures?
Interest rate futures prices move inversely to interest rates. Investors can speculate on the direction of interest rates with interest rate futures or use the contracts to hedge against rate changes.
Which are the most profitable futures trading strategies?
Breakout trading, Pullback strategy, trend following, News trading, Long trading, Range trading, Order flow trading, Scalping, Swing trading, Spread trading, and Day trading.
What are trading strategies for futures?
There are three futures trading plans: Long: Buy futures and profit when the prices increase. Short: Sell futures contracts and profit when the prices decrease. Spread: Simultaneously buy different futures contracts and profit when the relative futures price difference widens (or narrows).
What is crude oil WTI futures?
WTI (West Texas Intermediate, a US light sweet crude oil blend) futures provide direct crude oil exposure and are the most efficient way to trade oil after a sharp rise in US crude oil production.