How to Obtain a Forex License in 2023?
Articles


Forex is an international financial market founded in 1976, where currencies are exchanged. Forex plays a crucial role in the functioning of the global economy and in ensuring the exchange of capital between different countries. Forex trading involves central banks of different countries, companies conducting international business, commercial banks, brokers, investors and traders (speculators).
One of the most essential standards for evaluation for Forex traders when choosing a Forex broker is the broker’s status, whether it has the appropriate license, and what regulatory body it is regulated by. Brokers who operate without regulation do so at their own discretion and put their clients’ funds at risk.
Foreign exchange activity is regulated by many organizations in different countries. Some Forex brokers obtain a local license in an offshore jurisdiction, while others receive a license in a reputable jurisdiction, for example, in the EU or the United States. Getting such a license can take quite a long time because Forex regulators delve deeply into the essence of a Forex broker’s business and the financial condition of the company, as well as carefully examine the past experience of the director and other key figures in the company.
This article will shed some light on Forex licensing and its importance for brokers. We will also cover what categories of Forex licenses exist and what financial bodies help regulate Forex brokers. In the end, you’ll learn how to get a Forex license to start your own broker.
What is Forex License and Why Is It Important For Forex Broker’s Operation?
Today’s international currency market is a financial system with thousands of regular participants. A certain group of these participants is called Forex brokers, who act as intermediaries between private traders/investors and the interbank market. Forex brokers are very popular on the market, but a brokerage company has no legal right to process traders’ transactions without having a Forex license. Traders avoid brokerage companies that do not have a Forex license because the activities of such companies are considered illegal and unsafe. In addition, such a brokerage company can raise many questions from the regulatory authorities. If a broker wants to avoid having problems with the regulators or losing potential clients, he should obtain a Forex license.
The Forex market has no centralized regulator. That is, no single international body or organization would control all aspects of market participants’ activity. Strictly speaking, there can not be such a regulator because the foreign exchange market is based on the independence of operations and the providers of these operations concerning each other. But the activity of some players in the Forex market is still controlled; the brokers are controlled too. The algorithms of control over the brokers are constantly developing and evolving, and there are local regulators for individual countries and international ones.
Today all brokers aspire to get a license which is the guarantor of their clients’ safety. Such licenses are issued by different financial commissions, which check the legality of the broker’s work, audit it, and then monitor it after the license is issued. That is, a Forex broker needs a license to be able to confirm the legality of its actions, as well as to confirm that it actually places the trades of its traders at the interbank market and has obligations to them.
Categories of Forex Licenses
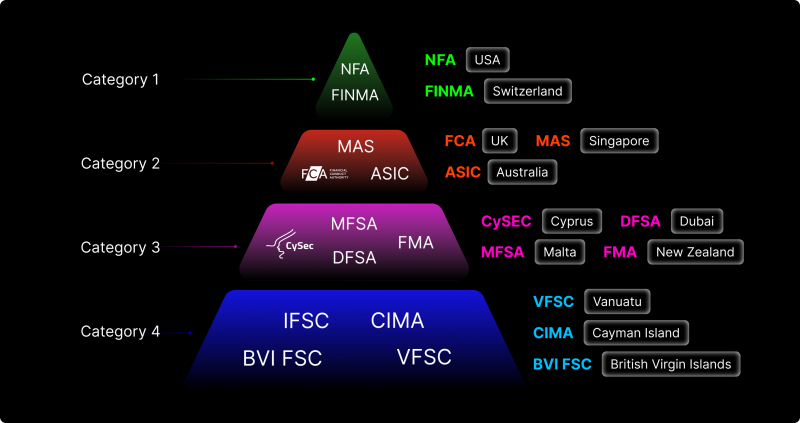
Forex broker license — a universal document that guarantees the reliability of a Forex brokerage company, but in spite of its universality, Forex licenses are divided into several categories, described below.
1. Category A (Main Market)
The U.S. license is considered quite prestigious and provides access to the world’s largest foreign exchange market. The jurisdictions of the main market are the United States of America and Switzerland. To get a license in these states, you need to prove that you own $20 million in free access, not counting client funds.
American brokers are required to file many reports and are subject to unexpected regulatory inspections at any time. The minimum violations of the rules lead to huge fines, up to suspension of work. In Switzerland, Forex brokers are subject to total monitoring. However, local licensees are considered reliable partners, proving this through unconditional compliance and the existence of significant warranty obligations.
2. Category B (Universal Jurisdictions)
The universal jurisdictions are Australia and Great Britain. Here the licensing rules are a little less strict. The UK FCA license is very prestigious and highly valued all over the world. The qualifications and experience of employees and directors must be proven, and they must reside in the UK. To obtain a license in Australia, entrepreneurs set up a firm and confirm that they are financially qualified to run the business.
Obtaining a license can cost about $30,000 to $60,000. And in this case, requires the physical presence of a broker’s representative to process the paperwork. It is also necessary to have about $100,000 of capital from customer deposits. If Forex transactions are made “in-house” and not offered to third parties, at least $1 million in cash is required. If third parties are used for transactions, only $100,000 of capital is needed.
3. Category C (Popular Jurisdictions)
Cyprus, Malta, New Zealand, and others: these states also require a physical office for licensing, but there are no reporting rules as in the previous categories. The main feature of firms licensed in these jurisdictions is access to cooperation and interaction with the European space without restrictions.
4. Category D (Offshore Regulators)
Belize, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Vanuatu. These jurisdictions have favorable foreign exchange market conditions, tax rates, and minimal required documentation packages. Besides, an offshore Forex license does not require a preliminary audit. The license is issued based on submitted documentation. However, opening a bank account and connecting the business to the payment system is more complicated. Regulatory pressure with stricter rules may force the country to introduce additional restrictions or new regulations. The main offshore firms are located on islands. The cost of an offshore Forex license here is also several times lower than in the previous categories.
The speed of setting up a company in these states is a significant advantage. Registration of the company takes just a few days; the approval takes from one month for Vanuatu or Cape Verde, and on average from 3 to 4 months for Belize and BVI, after submission of all necessary documents. A considerable advantage is that it is much easier to set up a bank account if you have a license in the British Virgin Islands or Belize. Several banks can also open a corporate account for a Forex company without a license.
Main Types of Financial Regulators Licensing in the Forex Industry
The activity of brokers is controlled by organizations called regulators. The regulator can be local (competent public authorities) or international (independent financial commissions). Regulators perform three types of actions in relation to the Forex broker: check it for compliance with the requirements of the license issuance, monitor compliance with these requirements in the course of the broker’s work, and withdraw the license if the broker violates the requirements.
The main task of the regulator, which gives a broker the license, is to prevent situations when the broker will not be able to fulfill its obligations to the traders. The regulator carries out legal protection of traders and investors in disputable situations, considers their complaints, and carries out checks on the broker. The regulator also undertakes periodic audits of the broker’s activities in order to detect discrepancies with the requirements of the license. It is also necessary to emphasize that brokerage activity is not obligatory for licensing in some countries. That is, a broker can simply register as a legal entity providing some financial services and actually work around the world through the Internet. Of course, this does not mean that such a broker is unreliable or even a fraudster. In this case, traders and investors do not get any guarantees when working with such a broker.
Below is a list of some of the most popular regulators whose activities constitute the legal basis of the Forex market to date.
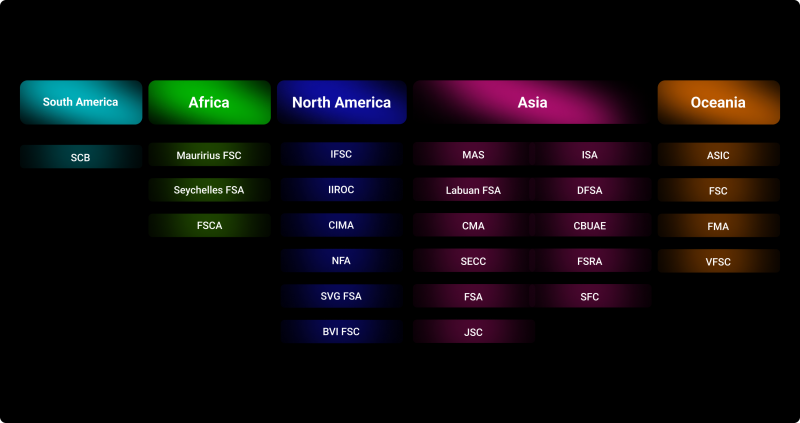
- CySEC – Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission
The Commission is the state regulator in the Republic of Cyprus and is one of the most prominent and essential regulators for Forex brokers and dealing centers that provide services in international financial markets. Cyprus is a full member of the European Union, which gives the CySEC all the powers of the European Forex regulator combined with attractive economic conditions for brokers. Many Forex brokers prefer registering in Cyprus and getting a license from this regulator. The CySEC issues licenses for European financial markets and supervises the activities of the brokerage and investment firms licensed by it.
- FSA – Financial Services Authority
This regulator is the central body supervising the financial services market in the U.K. The main purpose of the regulator is to protect consumers of financial services and ensure stability in the industry, as well as to maintain healthy competition among service providers in the financial markets. FSA regulates more than 70,000 financial institutions, ensuring that they comply with prudential risk management standards to reduce the potential harm to the industry as a whole and to individual investors. The FSA reports to the U.K. Treasury, but the department is an independent organization and is not funded by the government.
- NFA – National Futures Association
The Association is an independent financial watchdog whose purpose is to protect U.S. futures and commodity markets from abuse by financial institutions. Membership in the Association is mandatory for any financial institution providing futures exchange and trading services in the United States. NFA ensures investor protection and guarantees equal rights and opportunities for all market participants. The regulator has the right to impose sanctions and penalties of varying severity on violators of business regulations, depending on the amount of damage or potential damage resulting from the activities of financial institutions.
- CBR – Central Bank of the Russian Federation
This financial regulator is a special public and legal institution with the exclusive right to issue money and organize circulation. In cooperation with the Government of the Russian Federation, the CBR develops and implements the unified state monetary policy, licenses banking institutions, and has the right to withdraw from banks that do not operate following the regulations and rules. The primary purpose of the CBR activities is to protect and ensure the stability of the Russian Ruble, develop and strengthen the banking sector, and ensure the effective and uninterrupted functioning of the payment system.
- FSC – Financial Services Commission
The Commission is the regulator of the non-banking financial services sector and business. The regulator promotes the development, efficiency, and transparency of financial institutions and regulates the activities of brokerage firms registered in Mauritius. The FSC is developing measures and rules aimed at increasing the transparency of financial institutions, as well as exploring new opportunities for the financial services sector. The FSC is empowered to license companies that meet the requirements of financial safety, security, and transparency. The Commission’s main task is to take measures to prevent abuses in the investment business and financial fraud in brokerage services.
It should be noted that the number of regulators in the Forex market is much more and all help to regulate the legal and regulatory framework in the industry.
How to Obtain a Forex License? – Ultimate Guide
Now that you know what a Forex license is and why it is important when carrying out activities related to the Forex market, as well as what kinds of licenses and regulators exist in this area, it is time to find out how to get a Forex license to start your own broker.
1. Selecting the Regulator
Choosing a regulator is the first and most important step in obtaining a Forex license. The choice of the regulator determines what markets you will be able to operate in. To date, there are many different bodies regulating the Forex industry, and each of them has its own requirements for the issuance of licenses and launching a Forex business. Determine the market you would like to serve as a broker and carefully study the requirements and regulations of the regulatory body of the market you want to be present in.
2. Company Registration
Company registration is the first step that will lay the foundation for your future Forex business. This procedure is carried out in several stages and includes many nuances. First of all, you should choose the name of your Forex company and decide on the platform which traders will use for trading. Some of the most popular solutions in this regard are the MT4 and MT5 platforms, as well as cTrader. You will also need to take care in choosing a liquidity provider; also, don’t forget to beta test all of your systems before you launch your brokerage and create a website that can be used not only on PC but also on other devices.
3. Preparation of Corporate Documents
After registering a company, you have official documents regulating the rights and obligations of the legal entity registered in accordance with the laws of the country where you are opening your business. These documents are needed to confirm the status of the legal entity itself or for legally significant actions: for example, to open a bank account in another country, to close a deal with a partner, to conduct an audit in another jurisdiction, etc. Some of the documents you may need are: articles of incorporation, articles of association, registration card, tax residency certificate, and list of beneficiaries.
4. Payment of State Duties
The state fee is a special payment for many public services. For example, when applying to a court, getting married, obtaining a passport, or buying real estate. One such payment is the state duty for registering a legal entity (in our case, a brokerage company), and there are several essential nuances when paying it. The fee for registering a legal entity is charged for consideration of the founders’ documents. Again, depending on the state where you are located, the amount of the state duty will vary significantly, so before submitting the documents, it is recommended to read the information on payment of the duty on the relevant websites.
5. Opening of Corporate Bank Account
Opening a corporate bank account has become an indispensable condition within the framework of modern business. A corporate account is a bank account that is opened by legal entities for the payment of bills and routine control of financial accruals; it is also necessary for various commercial activities. Before opening a corporate account, study all offers from banks in the country where you have decided to open a Forex business, as you are interested in the most favorable conditions of its service by the bank.
6. Connection of Merchant Account for Bank Card Processing
Processing is an automatic technology of electronic funds transfers from buyer to seller (in our case, from trader to broker). It is built on software that can function thanks to the power of electronic banking. Through this software, payments made with bank cards and e-wallets are verified and processed and, as a result, these transactions can be accepted or rejected.
Almost all brokerage companies work with payment processing through VISA, MasterCard, and American Express. In some cases, it is also possible to find payment methods through various electronic wallets and other electronic payment systems.
7. Completion and Submission of Forex License Application Form to the Relevant Regulator
After completing all the previous steps, it’s time to prepare a special application for a Forex license. As a rule, this stage is the easiest because, if all the above requirements are met, the completed application with all the necessary information about the brokerage company is submitted to the regulatory authority and considered within a set period of time. After the receipt of the license, you can officially start the brokerage activity on the Forex market.
Conclusion
A Forex broker’s license to provide traders with access to the foreign exchange market is a document that indicates the company’s solvency and seriousness. Having obtained a Forex license in one of the countries listed in the article, you will be able to conduct trading activities with currency pairs and other financial assets. As a rule, getting a Forex license without professional help is not easy in any country. Therefore, enlist the help of experienced specialists and professionals in the field of jurisprudence which can help you apply for a license correctly, execute documents in accordance with the legal requirements of a particular country, and monitor and edit the entire process.
Seeking answers or advice?
Share your queries in the form for personalized assistance