What Is Arbitrage Trading? Detailed Guide

The current state of trading in all kinds of financial assets is conditioned by the high demand for innovative crypto technologies and, as a consequence, the utilisation of their potential to profit from highly volatile markets.
At the same time, there are highly efficient systems for analysing and aggregating price divergences of assets between certain markets, allowing you to make money from them. Such systems are called arbitrage systems and are widely used today compared to their counterparts.
This article will explain what arbitrage trading is, what varieties of it exist, and what reasons are fundamental for its use in practice.
Key Takeaways
- Arbitrage trading signifies the ability of market players to exploit price differentiation between markets with reduced risk by sequentially buying low and selling high.
- Technologies like algorithmic, high-frequency, and AI are important for spotting and accomplishing arbitrage matches in real-time.
- Arbitrage trading improves market efficiency, corrects price anomalies, and provides liquidity across global markets.
What Does Arbitrage Trading Stand For?
Arbitrage trading is a market-making concept that involves purchasing and selling identical or related instruments in dissimilar markets concurrently to exploit price divergences. The core idea is to impose on short-lasting inefficiencies by buying low in one market and selling high in another, capturing the difference as profit.
At its core, arbitrage trading is centred on price differentials for specific segments of the market. A multitude of causes, such as shifts in supply and demand, transaction costs, exchange rates, or time zones, can dictate these price gaps.
For example, the price of a stock might differ between two exchanges because of varying trading volumes or differing regional economic news. Arbitrage traders, often using sophisticated technology, act quickly to exploit these differences before the markets adjust and the price discrepancy disappears.
Arbitrage trading is considered a low-risk strategy because the purchase and sale of the asset happen simultaneously or within a very short window of time, minimising exposure to market volatility. The profits in arbitrage trades are typically small per transaction, but when executed at high volumes or with HFT calculations, these profits can accumulate significantly.
Michael Lewis’s 2014 book “Flash Boys” highlighted how high-frequency traders profited from latency arbitrage by exploiting microsecond speed advantages, sparking debates about fairness in financial markets.
The Role of Technology in Arbitrage Trading
Technology has become the backbone of arbitrage trading, transforming the way traders identify, execute, and manage their trades. Manual arbitrage is nearly impossible in modern financial markets, where prices move in milliseconds.
Traders rely on advanced technologies such as algorithmic trading, HFT, and AI to stay competitive and capture fleeting opportunities. Technology’s speed, precision, and automation have made arbitrage trading more efficient and accessible than ever before.
Here are some of the technologies that are currently having the greatest impact on the development of arbitrage trading within different capital markets:
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading, often called algo-trading, involves using pre-programmed computer algorithms to generate trades based on specific market conditions. These systems can scan multiple exchanges simultaneously, identify price variances, and carry out trades within fractions of a second. This is critical in arbitrage trading, where opportunities arise and disappear in a very short time frame.
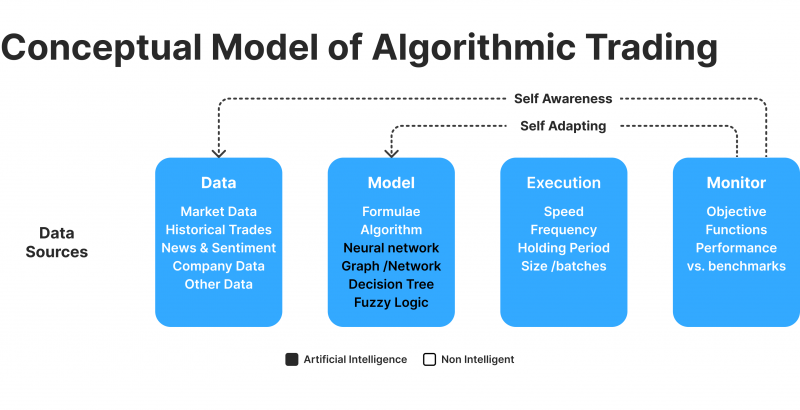
With algorithmic trading, arbitrage traders can concomitantly monitor multiple markets, asset classes, or currencies. Logic can automatically place trades without human intervention, ensuring that trades are executed at the optimal time.
Additionally, these systems can be programmed to account for transaction costs and fees, helping traders maintain profitability despite small price imbalances.
High-Frequency Trading
HFT is a subset of algorithmic trading that takes arbitrage to another level by executing dozens of orders within microseconds. It firms use cutting-edge technology and infrastructure, such as co-location servers, to minimise latency (when sending orders to the exchange). This speed advantage allows HFT traders to exploit even the smallest price deviations before the rest of the market catches up.
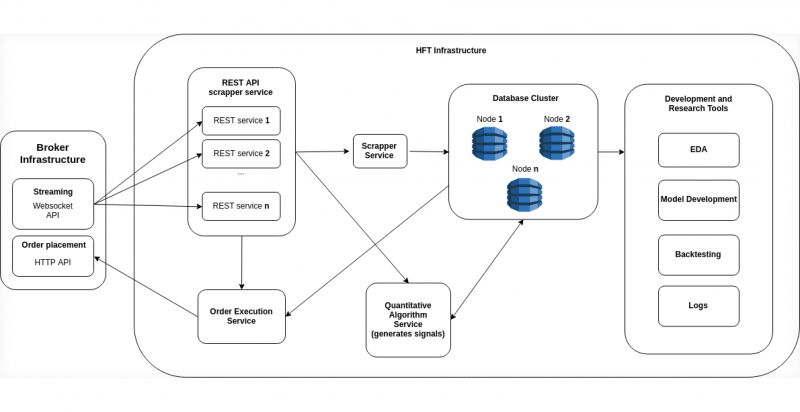
In arbitrage trading, HFT is particularly effective in markets with high liquidity and volatility, such as stock, Forex, or cryptocurrency markets. For example, its neural networks can quickly identify price differences between two stock exchanges, execute the buy and sell orders instantly, and lock in a profit before other traders notice the opportunity.
Automated Trading Systems and Bots
Furthermore, a key contemporary tool in arbitrage trading is computer-generated trading models or trading robots. These bots continuously monitor different exchanges, identify arbitrage opportunities, and execute trades without human intervention. Automated systems are essential in fast-moving markets, where human traders would struggle to keep up with price changes.
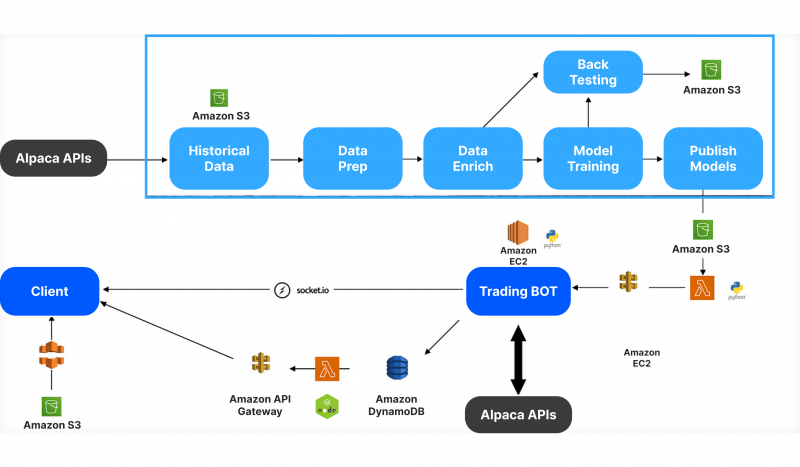
For instance, cryptocurrency traders often use arbitrage bots to exploit price dissimilarities between exchanges, such as Binance, Kraken, or Coinbase. These bots can operate 24/7, scanning a number of markets for potential deals and executing trades instantly. In the highly fragmented and volatile world of cryptocurrencies, where prices vary significantly between platforms, automated bots are an essential tool for arbitrage deals.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The rise of AI and machine learning (ML) has added another layer of sophistication to arbitrage trading. AI-driven systems can process large amounts of historical and real-time data to detect patterns or anomalies that may indicate future arbitrage opportunities. By analysing factors such as trading volume, order book depth, and market sentiment, AI programs can predict when price mismatches are likely to occur and execute trades proactively.
Machine learning models can also refine trading strategies over time, adapting to changing market conditions and learning from past trades to enhance performance. This allows arbitrage traders to stay ahead of the market by continuously refining their approach, even as traditional arbitrage opportunities become scarcer.
Market Scanners and Analytical Tools
In addition to automated trading systems, arbitrage traders rely on market scanners and analytical tools to identify and evaluate potential opportunities. These tools allow traders to set parameters, such as price thresholds or market scenarios, and receive alerts when an arbitrage opportunity arises. Some scanners are even integrated with trading platforms, enabling one-click execution of trades once the opportunity is detected.
Many of these tools use real-time data feeds and sophisticated analytics to track multiple markets or asset pairs, ensuring that traders can react quickly to price movements. With the help of advanced analytics, arbitrage traders can better assess the viability of a trade, factoring in variables such as liquidity, volatility, and transaction costs.
Blockchain and Smart Contracts
In the evolving landscape of cryptocurrency markets, blockchain technology and smart contracts are playing a growing role in arbitrage trading. Smart contracts allow for the automatic execution of trades when certain conditions are met, removing the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of human error. This is particularly valuable in DeFi sphere, where arbitrage traders can exploit efficiency gaps both in decentralised and centralised exchanges.
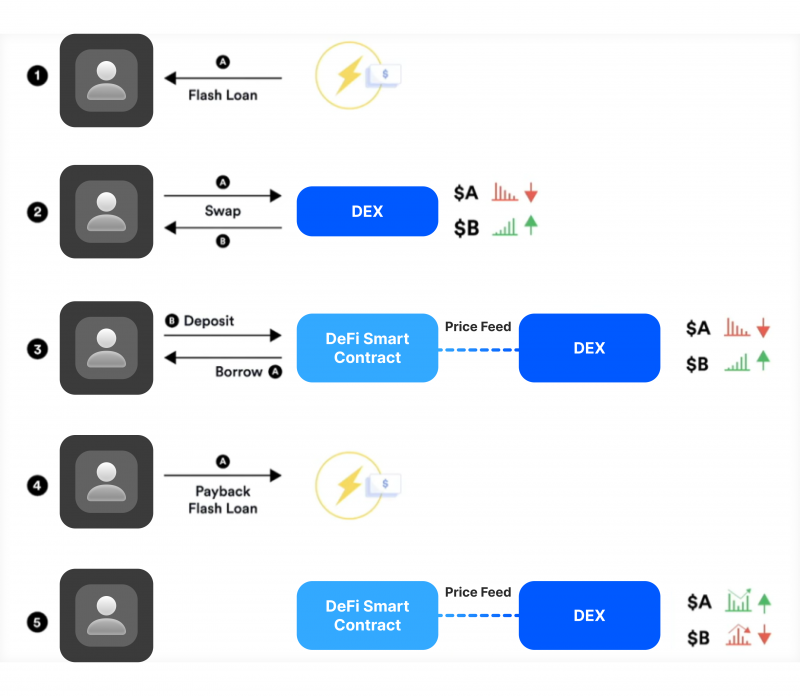
For example, in DeFi arbitrage, a trader can write a smart contract that automatically swaps one cryptocurrency for another when a specific price discrepancy is detected. Using blockchain and smart contracts ensures that trades are transparent, secure, and executed precisely as programmed.
Basic Types of Arbitrage Trading
Today, technological development in the field of arbitrage trading has become a catalyst for the creation and practical application of various forms of this strategy, among which we can highlight the following, which have found the greatest popularity among the participants of trading in the capital markets:
Pure Arbitrage
Pure arbitrage is the most straightforward and classical form of arbitrage trading. It extends to buying and selling the same asset simultaneously in two markets to profit from price inaccuracies. The trader purchases the asset in the market where it is undervalued and sells it in the market where it is overvalued.
Suppose a stock trades at $100 on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) but $102 on the London Stock Exchange (LSE). A trader can buy the stock in New York and immediately sell it in London, capturing the $2 difference as profit. This process occurs almost instantaneously to reduce the risk of price movements.
This form of arbitrage is identified as a low-risk endeavor because it deals with taking possession of contemporaneous transactions, limiting exposure to market volatility.
Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage (or “stat arb”) is a more advanced, quantitative form that uses mathematical models and statistical techniques to identify price discrepancies between correlated assets. It involves analysing historical price data and predicting short-term price divergences. Traders then bet on the price relationships between these assets returning to normal.
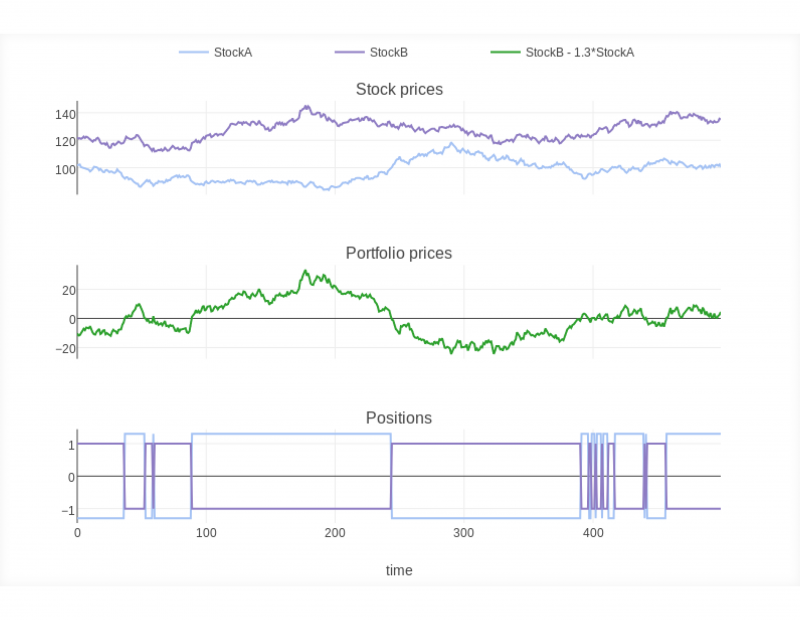
Suppose two stocks have historically moved together (like stocks from the same industry). In that case, a trader may use statistical arbitrage to predict that if one stock becomes temporarily mispriced relative to the other, their prices will eventually converge. The trader can go long (buy) the undervalued stock and short (sell) the overvalued one to profit from this reversion.
Such arbitrage is driven by data and can involve hundreds of assets, making it scalable and ideal for large hedge funds and institutional traders. However, it requires sophisticated tools and significant computing power.
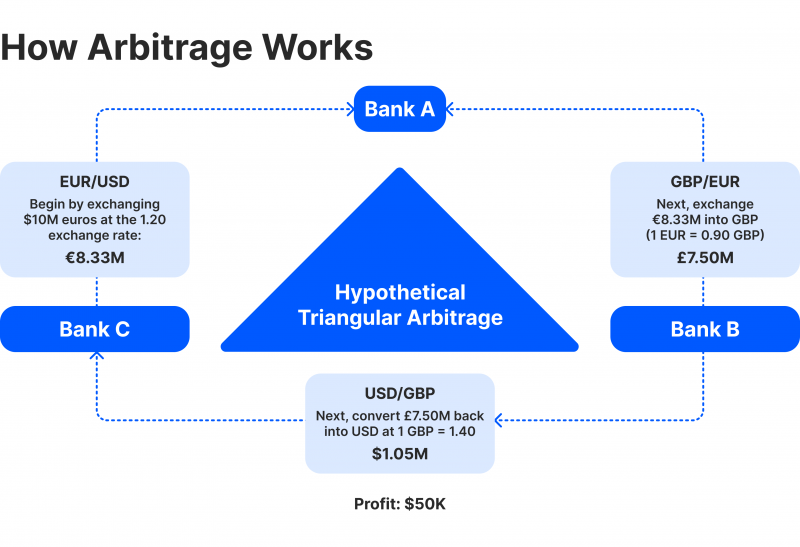
Triangular Arbitrage
Triangular arbitrage is a type of arbitrage commonly used in the foreign exchange (Forex) market. It exploits price imbalances between three currencies by executing a series of trades that convert one currency into another and back into the original currency. The goal is to profit from inconsistencies in exchange rates.
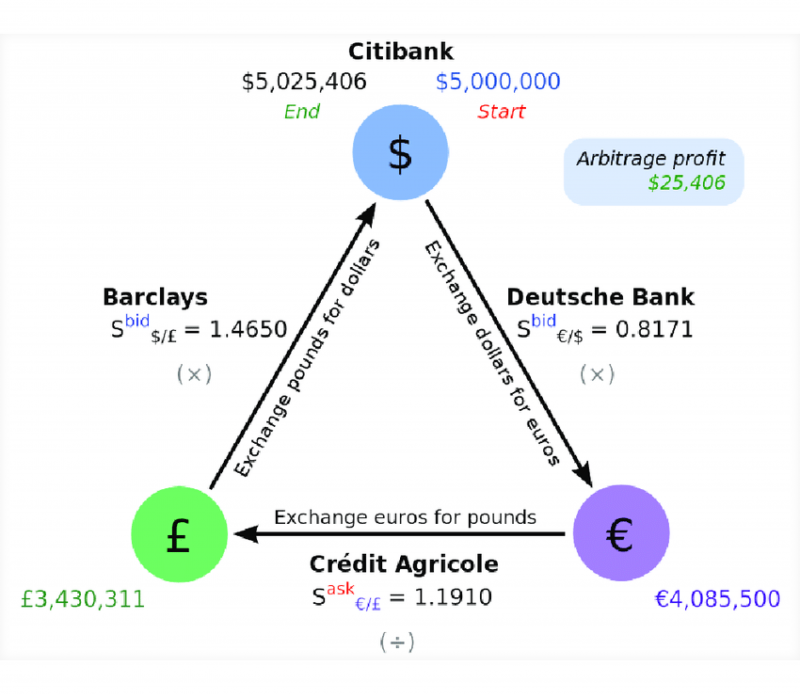
Suppose the exchange rate between USD, EUR, and GBP is misaligned. A trader could convert USD to EUR, EUR to GBP and GBP back to USD. If the exchange rates are mispriced, the trader will end up with more USD than they initially started, capturing the difference as profit.
Triangular arbitrage can be highly profitable in currency markets because exchange rates fluctuate continuously. However, the opportunities are usually short-lived, and fast execution is crucial.
Merger Arbitrage
Merger arbitrage, or risk arbitrage, refers to trading stocks of entities entailed in mergers or acquisitions. Traders typically buy the stock of the target company (the company being acquired) and short the acquiring company’s stock. This strategy is based on the expectation that the target company’s stock price will rise as the deal closes, while the acquiring company’s stock may decline due to acquisition costs.
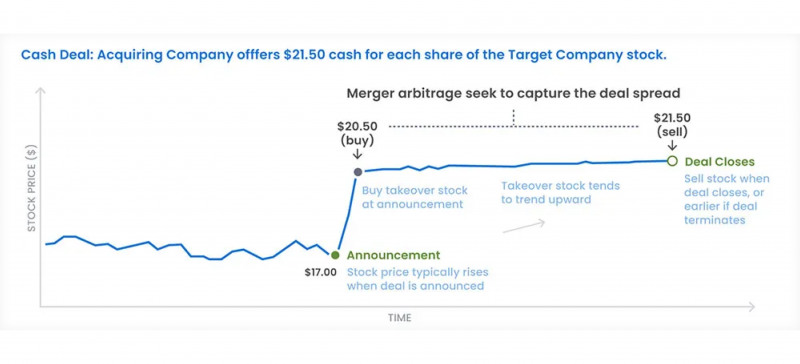
If Company A announces plans to acquire Company B for $50 per share, but Company B’s stock currently trades at $48, a merger arbitrage trader may buy Company B’s stock. The assumption is that once the acquisition is completed, Company B’s stock will rise to $50, allowing the trader to profit from the $2 per share difference.
Merger arbitrage can yield significant returns, but it carries risks, particularly if the merger or acquisition fails, causing the target company’s stock price to drop.
Covered Interest Arbitrage
Covered interest arbitrage focuses on put to good account of interest rate differentials between two countries while using a forward contract to hedge exchange rate risk. This type of arbitrage is often used in the forex market when a trader notices a discrepancy between interest rates and the forward exchange rates of two currencies.
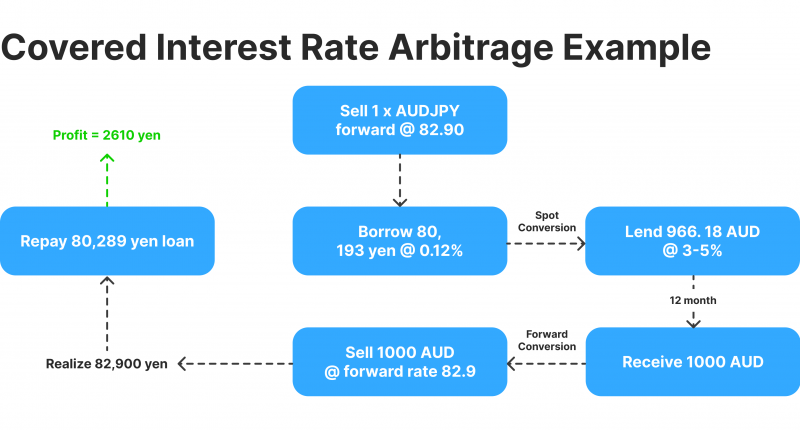
Suppose the interest rate in the U.S. is 2%, while the interest rate in Japan is 1%. A trader can borrow money in Japan at a lower interest rate, convert the Japanese yen to U.S. dollars, and invest in U.S. assets at a higher interest rate. To mitigate exchange rate risk, the trader enters into a forward contract to exchange the dollars back to yen at a predetermined rate when the investment matures.
Covered interest arbitrage allows traders to lock in risk-free profits based on differences in interest rates, with minimal exposure to currency risk due to using forward contracts.
Crypto Arbitrage
Crypto arbitrage trading is similar to traditional arbitrage but occurs in cryptocurrency markets, which are less regulated and more fragmented than traditional markets. Price variations between different cryptocurrency exchanges are more common in response to fluctuations in liquidity, market participants, and regional demand.
Bitcoin might be trading at $40,000 on one exchange and $40,200 on another. A trader can buy Bitcoin on the lower-priced exchange and sell it on the higher-priced one, profiting from the $200 difference. Cryptocurrency arbitrage can be performed across centralised or decentralised exchanges.
The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, which creates frequent possibilities for arbitrage traders. However, challenges such as transaction fees, withdrawal limits, and exchange delays can reduce profitability.
Regulatory Arbitrage
Regulatory arbitrage refers to taking advantage of regulatory environment divergences in distinct regions or countries. Traders or firms may engage in arbitrage by structuring transactions or locating their businesses in areas with more favourable regulations to reduce costs or increase profits.
A company might decide to establish its operations in a country with lower tax rates or more lenient financial regulations, allowing it to operate at a lower cost and gain a competitive advantage over companies in stricter jurisdictions.
Regulatory arbitrage can lead to substantial cost savings for businesses, but it carries the risk of regulatory changes or legal challenges if regulators close the loopholes being exploited.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
What Are The Reasons to Implement Arbitrage Trading?
Arbitrage strategy is a modern way of extracting micro profits due to the divergence in prices of similar trading tools within different exchanges and capital markets. This practice, being a popular risk hedging tool, is widely used due to the following reasons:
Market Efficiency
Arbitrage trading plays a crucial role in improving market effectiveness. By tapping into price variances inherent in markets or lending instruments, arbitrageurs help align prices in specific markets. This assures that the same asset or commodity is priced similarly regardless of where it’s traded, contributing to overall price accuracy and fairness in the market.
Liquidity Provision
Arbitrage deals provide liquidity to markets by engaging in combined buying and selling activities. Their actions increase trading volume, which makes it easier for other market participants to buy or sell assets without drastically affecting prices. More liquidity generally leads to more stable and smoother market conditions.
Risk-Free Profits
One of the most attractive features of arbitrage is the possibility of near-risk-free profits. Since arbitrage entails the one-time acquisition and selling of the same asset in divergent markets, the trader is not susceptible to market risk like speculative traders. This is why arbitrage is often referred to as a low-risk trading strategy, although it is subject to performance and liquidity risks.
Correction of Market Anomalies
Arbitrage helps correct pricing anomalies in financial markets. If security is priced differently across markets, arbitrageurs will quickly buy the undervalued security and sell the overvalued one, bringing prices back to equilibrium. This rapid adjustment helps eliminate imperfections and ensures that markets remain competitive.
Encourages Global Market Integration
Arbitrage typically occurs in entirely isolated geographical markets, which fosters integration between them. As traders capture price swings across markets, they connect global financial systems, making capital and assets flow more smoothly. This integration benefits international trade, investment, and economic collaboration.
Reduction of Systemic Risk
In certain markets, particularly in currency and commodity markets, arbitrage can help reduce systemic risks by aligning prices across borders and minimising disparities. This price alignment lessens the likelihood of large-scale market distortions that could lead to instability or crises in interconnected markets.
Faster Market Adjustments
Arbitrage ensures that prices adjust quickly to new information or events. As arbitrageurs act on price deviations, they drive prices to reflect valid values in real-time, ensuring that markets stay responsive and reflective of actual conditions. This makes price discovery more accurate and timely.
Multifaceted Trading Approaches
Arbitrage can be applied in various forms (e.g., statistical, convertible arbitrage or merger), countenancing traders to modify their decisions. This diversity offers multiple avenues for traders to benefit from arbitrage potential with regard to certain asset forms and markets, intensifying the appeal of arbitrage as a versatile trading approach.
Conclusion
Arbitrage trading remains a cornerstone of financial markets, providing critical functions like improving market efficiency, ensuring liquidity, and reducing systemic risks. While technological enhancements like algo-trading and AI have transformed the ecosystem of arbitrage-based trading, making it faster and more efficient, the core principle of exploiting price variability remains unchanged.
As global markets become more integrated, and with the rise of emerging sectors like cryptos and decentralised finance, arbitrage opportunities continue to evolve. However, the strategy’s reliance on rapid deployment and low-risk results makes it an indispensable tool for traders and market stability alike.
FAQ
What is arbitrage trading?
Arbitrage trading is a market-making technique that comprises concomitantly acquiring and dumping the same or equivalent valuables in diversified markets to make a buck from price gaps.
Why is arbitrage considered low-risk?
Arbitrage is low-risk due to the concomitant buying and selling of assets, which minimises market exposure. However, factors like transaction costs and liquidity constraints can impact profitability.
Is arbitrage trading legal?
Yes, it is legal in most markets as it enhances efficiency, though some types, like HFT, may face specific regulations depending on the market.
Can arbitrage trading be performed autonomously?
Many arbitrage traders use autonomous systems, bots, and predictive models to quickly scan markets, spot price gaps, and perform trades without human intervention.







