What is a Money Manager?

Investing is a risky and time-consuming process that can either enhance financial stability or lead to significant debt if not managed properly. To avoid considerable losses, a detailed financial plan is a must.
However, developing an effective and beneficial investment strategy may require some assistance. Money managers, among others, offer investment advice, day-to-day trading, performance monitoring, and long-term planning services, ensuring that your portfolio is well-managed and not left in serious debt.
What is a money manager, and how do you choose one? Read on because selecting the right expert can significantly impact your financial situation.
Key Takeaways
- A money manager is responsible for handling financial assets for individuals or enterprises.
- Portfolio managers employ various strategies to meet client’s financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Money managers offer their services for a percentage or a commission-based fee.
- To become a financial manager, you should acquire a certain degree of education, as well as have a profound knowledge of the financial markets and relevant certification.
What is a Money Manager?
A money manager, or portfolio or investment manager, is a person or entity responsible for managing financial assets for individuals or institutional investors.
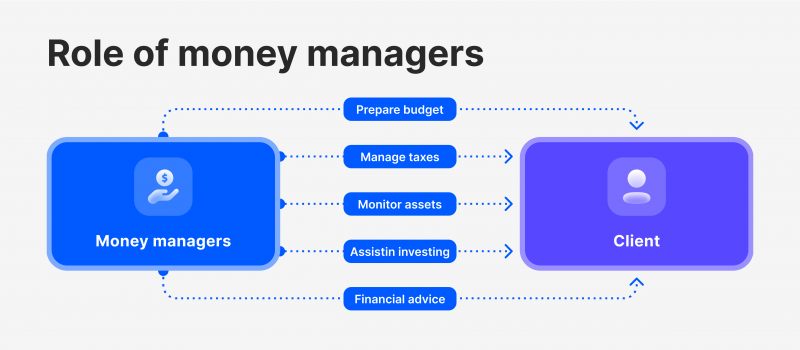
They assist clients in achieving financial goals by buying and selling securities, settling transactions, measuring performance, tracking expenses, creating budgets, managing taxes and reporting to regulators.
Their clients can have different goals, such as ensuring principal safety, maximising returns, or seeking value or growth investments.
A money manager in a corporation provides personalised advice, manages clients’ portfolios, and is responsible for choosing investments with their client’s best interests in mind. These managers may have access to areas of the capital markets that clients may not have.
Money managers handle portfolios for both individuals and organisations and can be found in traditional financial institutions, hedge funds, pension funds, private equity funds, or mutual funds.
Money managers use various portfolio management schemes to achieve their goals, depending on the type of fund or management style. For instance, mega-funds, like the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board, diversify asset classes like equities, fixed income, real estate, infrastructure, and private equity.
Those focused on increasing returns may invest in riskier assets. Retail money managers collaborate with clients to understand their goals and risk adversity, creating an investment portfolio. As economic data is released, money managers adjust their portfolios to suit their goals and client’s best interests, as they have a fiduciary responsibility.
Money managers are professionals with a CFA or degree in finance, accounting, economics, or business who analyse financial performance and make better decisions. They use their research skills, expertise, and experience to maximise client benefits.
Famous money managers include Warren Buffett, Benjamin Graham, Peter Lynch, and Sir John Templeton, while top investment management firms include Goldman Sachs, BlackRock, USB, Morgan Stanley, Vanguard Group, and J.P. Morgan & Co.
Types of Money Managers
Money managers have diverse expertise and specialities, with some common types including the following:
Financial Advisors
Financial advisors offer expert guidance on various financial matters, helping clients manage their finances, make informed decisions, and achieve their financial goals.
Mutual Fund Managers
Mutual fund managers manage mutual funds, which are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. They select securities, manage the portfolio, and ensure the fund meets its investment objectives.
Asset Managers
Asset managers, acting on behalf of institutions like pension funds, endowments, and foundations, manage investments to optimise returns and manage risk, utilising various asset classes like equities, fixed income, and alternative investments.
Alternative Asset Managers
Alternative asset managers are professionals who manage investments in different asset classes like real estate, private equity, and hedge funds.
Institutional Asset Managers
Institutional asset managers, acting on behalf of institutions like pension funds, endowments, and foundations, manage investment portfolios using their financial market expertise to optimise returns and manage risk for long-term investment goals.
Private Wealth Managers
Private wealth managers manage high-net-worth individuals’ finances, offering services like investment management, financial planning, tax planning, estate planning, and risk management.
Portfolio Managers
Portfolio managers manage investment portfolios, make decisions, and execute trades to achieve clients’ investment objectives. They collaborate with clients to understand their goals and risk tolerance, developing tailored investment strategies.
Investment Fund Managers
Investment fund managers manage mutual funds, ETFs, and hedge funds, making investment decisions on behalf of investors and managing the fund’s assets.
Hedge Fund Managers
Hedge fund managers manage investment vehicles that use various strategies like leverage and short-selling to generate high returns, typically charging performance-based fees.
What Does a Money Manager Do?
Money managers are responsible for developing investment strategies that align with client’s financial goals and risk tolerance, implementing and adjusting these strategies over time as market conditions change.
They also conduct research to identify investment opportunities and assess market trends, economic conditions, and other factors that may impact investment performance.

Money managers make investment decisions on behalf of their clients, using various techniques and tools to assess opportunities and manage risk. They regularly monitor investment performance and may adjust clients’ portfolios to optimise returns or mitigate risk.
They work closely with clients to understand their financial goals, provide regular performance updates, and advise on financial planning and other financial matters.
Portfolio managers must comply with regulations and industry standards set by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA). They may also manage operational and administrative tasks related to managing clients’ investments, such as maintaining records, processing transactions, and preparing reports.
Financial assistance managers offer clients various services, including budgeting, tax planning, asset monitoring, portfolio management, and currency trading. They monitor income expenses, save money, evaluate transactions, and file taxes.
They also provide personalised services for customers, supervise their holdings, and help investors maintain and diversify their portfolios. Additionally, they assist in assessing fluctuations and risks associated with foreign currency.
How Do Money Managers Get Paid?
Money managers offer money management services to clients for a fee, usually as a percentage of the account value, either by creating a customised portfolio or maintaining a set fund. The former is more common in retail banking, while the latter is more common in large-scale money management like mutual funds or hedge funds.
Compensation for money managers can vary, with some charging a one-time or periodic fee while others charge a commission-based fee, such as 20% of profits.
More commonly, money managers charge a fixed fee and a variable fee, such as the 2 and 20 fee structure, which combines a 2% fixed fee with a 20% commission. This structure may increase incentives to maximise investor returns and reduce moral risks.
Financial Advisor vs Money Manager
Financial advisors and money managers are complementary roles, but nevertheless, they have some distinctions.
Financial advisors, also known as wealth managers or investment advisors, understand clients’ financial needs and create detailed investment plans to help them achieve their goals.
A financial advisor should understand a client’s financial life, including investments, debt, and cash flow needs, as well as their goals. They should create a detailed investment plan, recommend money management strategies, and regularly review and adjust the plan to ensure they are best suited for the client’s individual plan.

Money managers, on the other hand, focus on managing the strategies in a portfolio, ensuring the portfolio’s success. Money managers should consistently meet expectations, such as managing investment portfolios aligned with investment objectives, managing risk appropriately, avoiding turnover, and operating transparently to maintain their reputation.
Why Hire a Money Manager?
Money managers are beneficial for non-professionals in capital markets and finance, as they help clients manage money effectively and reach their financial goals.
Despite the potential risks associated with investing in capital markets, money managers’ fiduciary responsibility ensures the money is in good hands, which also provides a sense of safety for clients.
Managing assets on your own can be time-consuming, especially for those with multiple investment accounts or a large portfolio. Money managers have advantages in investment choices due to their training and access to valuable information like analytical data, research reports, financial statements, and modelling software.
These professionals can make informed decisions that are unavailable for an average investor. Money managers can help investors understand how to effectively use their money to achieve financial goals, which is especially beneficial for those investors who have just started their journey in finance.

Hiring a personal money manager can be favourable for several reasons, such as the following:
1. Save Time on Planning
Clients can save time and effort by communicating personal goals to their corporate money manager, allowing them to plan their future finances without relying on income-based expenses.
2. Easier Tax Handling
Money managers assist individuals in filing taxes, which is crucial for companies as they pay significant taxes.
3. Advantages Over Brokers
Investment brokers charge commissions based on returns, making decisions in their best interest. Investment managers, on the other hand, charge fees independent of returns to maximise customer gains and provide other services.
4. Help in Investment Decisions
Through market-driven research, investment managers offer customers the best investment options like government securities, stocks, and cryptocurrencies, avoiding speculative activities.
How to Choose a Reliable Money Manager?
To select the best daily money manager, conduct thorough research consisting of figuring out manager type, studying suggested options and an interview involving a thorough understanding of each step and your financial needs.
1. Decide on The Manager Type
To choose the right money manager, assess your financial plan and investment portfolio. A certified daily money manager can assist with basic budgeting, estate planning, and investing for more robust planning.
2. Study The Suggested Options
To evaluate money managers, first determine your needs and preferences. After a background check, review their regulatory qualifications, experience, and previous client complaints.
Analyse their portfolio performance in recent years and whether they typically manage clients with similar financial backgrounds. It’s crucial to understand how they make their money, as not all money managers receive a percentage of their clients’ portfolios.
3. Interview
To choose a money manager, it’s essential to speak with a few potential options to understand their communication style, investment philosophy, risk tolerance, and demeanour.
It’s crucial to gauge their level of personalisation and service, as they may have different client-manager relationships. Money managers have different levels of autonomy over portfolios, so it’s essential to ensure they prioritise your needs and preferences.
How to Become a Money Manager?
To become an investment adviser, you must meet multiple criteria, including education, training, and work experience.
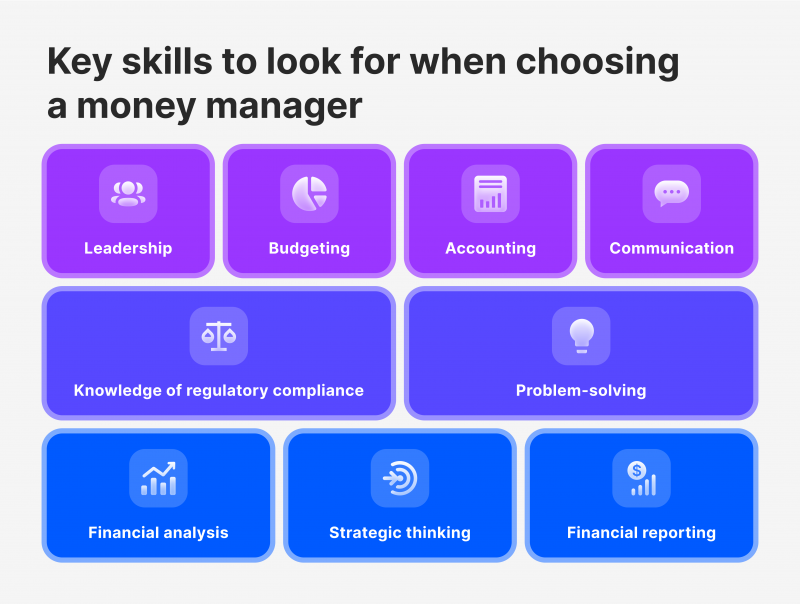
Portfolio managers require accounting skills to analyse and discuss financial reports with accountants and executives. They also need technical skills in data and financial technologies like QuickBooks, SAP, or Hyperion.
Quantitative skills enable them to review company and market financial data to identify risks and opportunities. Financial reporting ensures compliance with tax regulations and laws, and they create, review, and present financial reports to executives.
The abovementioned requirements and responsibilities require a profound knowledge and corresponding education in the field. Money managers typically hold a Bachelor’s Degree in Finance, Economics, Business, or a related field, with some employers preferring candidates with a Master’s Degree in Business Administration.
Good financial managers typically have years of experience in finance roles like investment analyst, financial planner, or portfolio manager and may also have related experience in accounting or risk management.
Certification is another crucial aspect of becoming a trustworthy money manager. Certified daily money managers often hold professional certifications like CFA or CFP, demonstrating expertise in financial analysis, investment management, and financial planning.

Besides professional knowledge and vast experience, investment managers must have good soft skills. They are responsible for clear communication, organisation, leadership, and attention to detail in their roles. They must present financial data clearly, analyse large amounts of information, lead consulting teams, and ensure legal compliance by correcting reporting, budgeting, and forecasting errors. They may also advance to executive leadership roles.
Money managers should stay informed about market trends, economic conditions, and industry regulations through continuing education and professional development opportunities like conferences and courses.
Final Takeaways
Choosing a money manager can be challenging due to the numerous titles and options available. A money manager specialises in managing investment portfolios and has a fiduciary duty to clients.
Understanding what is a money manager is crucial, especially for beginners, since picking a dependable manager can be tricky.
To become a portfolio manager, one should meet many criteria in terms of education and certification, develop good soft skills, and always stay updated on market conditions and trends.
FAQ
Should everyone have a money manager?
It depends. Money managers can manage independently if someone has a financial background, like a finance teacher or student, but it can be beneficial for those with limited time or seeking professional advice.
What obligations do I have as an investment manager?
As a financial manager, you’ll analyse financial data, tabulate data, report findings, evaluate market trends, oversee staff, and develop organisational budgets.
Why should I hire a money manager?
An asset manager can help manage your portfolio effectively, maximising its value without the stress or emotional rollercoaster that comes with it.
What are the average earnings of money managers?
Money managers offer professional services in accounting, financial management, taxation, and investment, earning an average of $95,445, with some experienced managers earning nearly $200,000.
Recommended articles
By clicking “Subscribe”, you agree to the Privacy Policy. The information you provide will not be disclosed or shared with others.
Our team will present the solution, demonstrate demo-cases, and provide a commercial offer







