How to Build a Crypto Wallet for Business: From Planning to Deployment

A growing share of companies now integrates digital assets into payments, treasury flows, and trading workflows. This move is driven by market demand; a recent Kraken survey found that 55% of Americans believe crypto has practical, real-world uses, which signals rising expectations for businesses operating in this space.
A crypto wallet becomes core infrastructure once an organization moves beyond experimentation. It governs how assets are stored and monitored, completely shaping the firm’s security posture and compliance framework.
This guide gives you a path on how to build a crypto wallet for business. The following sections detail how each choice impacts your long-term operational stability and capacity for growth.
Key Takeaways
- Business crypto wallets require institutional-grade features, including multi-user permissions, advanced key management, and integrated audit trails.
- Core infrastructure must include integrated KYC/AML modules and real-time transaction monitoring to meet regulatory standards.
- Choosing between custodial and non-custodial models depends on your firm's liability appetite and licensing status.
- White-label solutions significantly reduce time-to-market compared to custom development.
What Is a Crypto Wallet for Business?
A crypto wallet for business is enterprise software for managing digital assets. It safeguards private keys, processes transactions, and maintains controlled access to multiple blockchain networks.
While a retail user manages a single key, an organization oversees many accounts linked to permissions and use cases. This creates a need for security layers that support both internal oversight and external regulatory expectations.
Because businesses handle higher volumes, their wallets must accommodate throughput that personal wallets never face. Some organizations process thousands of on-chain actions per day across multiple networks, which requires predictable performance and clear separation between operational funds and long-term reserves.
A business wallet needs to align with regulatory frameworks. In regions such as the EU and the United States, companies handling digital assets must demonstrate verifiable record-keeping, identity screening, and internal-control procedures. A wallet with built-in compliance modules reduces that burden and creates a foundation that supports future licensing or banking relationships.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Why Businesses Need a Secure Crypto Wallet
Implementing a dedicated crypto wallet addresses fundamental needs in today's financial landscape. It provides the necessary infrastructure to engage with digital asset markets securely and at scale. State Street reports that 66% of institutional investors plan to increase their digital asset allocations within five years, signaling rising expectations for enterprise-grade infrastructure.
A robust and secure cryptocurrency wallet greatly improves the efficiency of business operations. Instead of routing actions through scattered tools, teams work within a single, governed environment, reducing manual review time and helping departments coordinate decisions on transfers and approvals.
Moreover, a strong wallet directly supports revenue generation by giving startups a reliable way to receive and move assets. When transfers settle without disruption, firms introduce new services faster and support higher transaction volumes without restructuring their processes.
Companies that demonstrate consistent control over their Bitcoin operations gain an edge when forming partnerships or pursuing regulated markets. A well-governed custody layer often becomes a prerequisite for banking integrations or enterprise contracts.
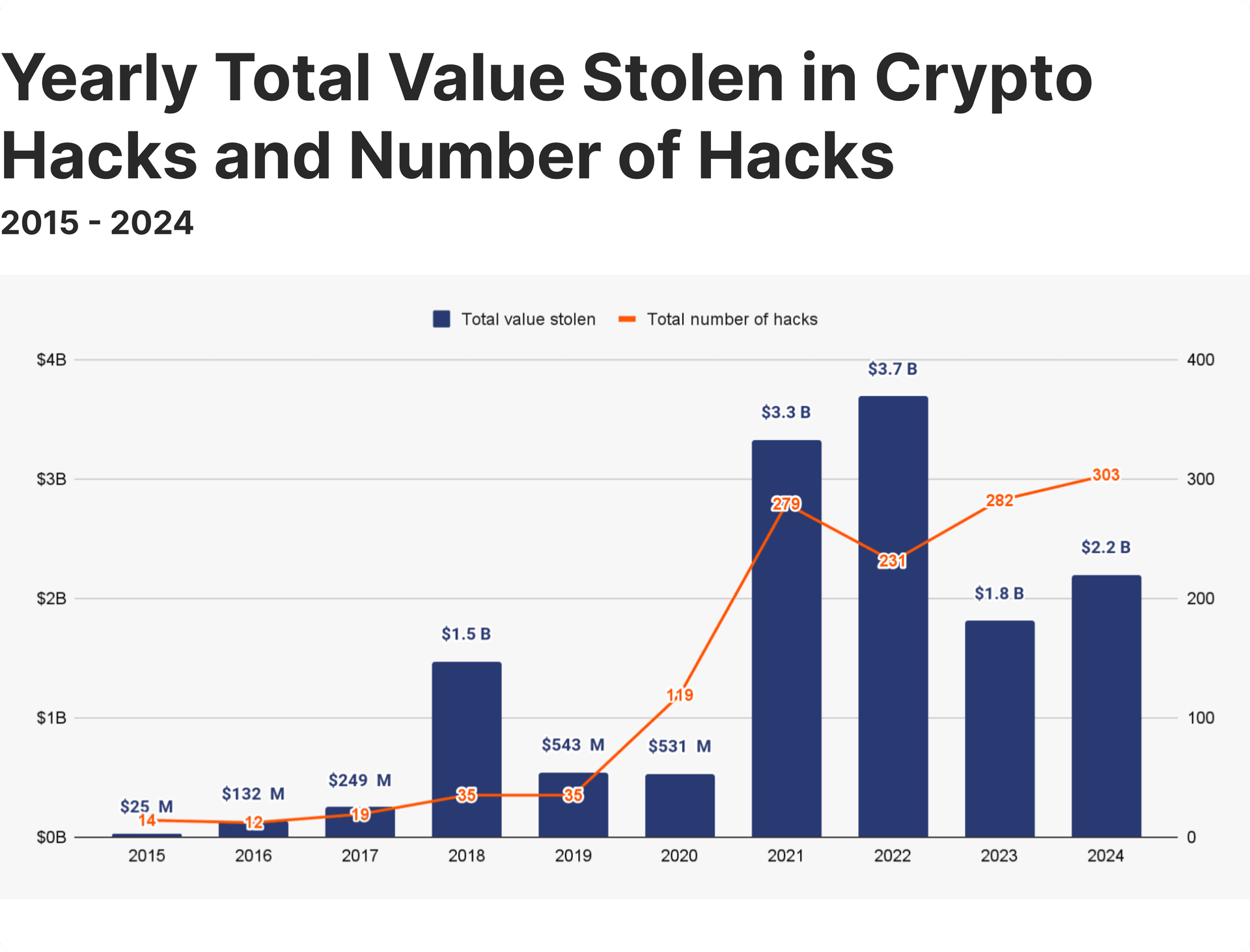
Chainalysis reports that illicit cryptocurrency activity reached $40.9B in 2024, with a considerable share tied to compromised keys and weak internal safeguards. A business wallet with structured access controls and hardened key-management practices lowers this exposure and gives clients confidence that assets remain protected.
Importantly, a mature wallet helps with regulatory alignment. It records activity in a format auditors can review and applies identity checks where required. Integrated monitoring tools that support AML and travel-rule workflows greatly assist businesses in their workflow, reducing risks of compliance failures as global oversight increases.
Types of Crypto Wallets: Custodial, Non-Custodial, Hot, Cold
A business wallet must fit the operating model of your organization. Clarity at this stage prevents costly redesigns as transaction volume grows.
Custodial Wallets
A custodial wallet means your business holds and manages the client's private keys. This centralized model is familiar to users of a traditional cryptocurrency exchange like Coinbase or Binance. Clients trade direct responsibility for convenience, relying on your platform for account recovery and security.
This approach requires specific financial licenses in most jurisdictions, because your company assumes legal liability for safeguarding client assets. Operational costs include implementing bank-level security audits, maintaining proof of reserves, and carrying substantial insurance policies. This model is ideal for regulated brokerages seeking to offer a managed experience.
Non-Custodial Wallets
Non-custodial wallets ensure clients retain exclusive control of their private keys. Your platform provides a user-friendly interface for blockchain interaction without ever accessing the actual funds. This design philosophy aligns with decentralization principles and user sovereignty.
Your business avoids the direct regulatory burden of asset custody, focusing instead on software reliability and user education. Support requests shift from password resets to transaction troubleshooting. This model is typical for DeFi protocol front-ends, certain payment processors, dApps and platforms emphasizing user privacy and control.
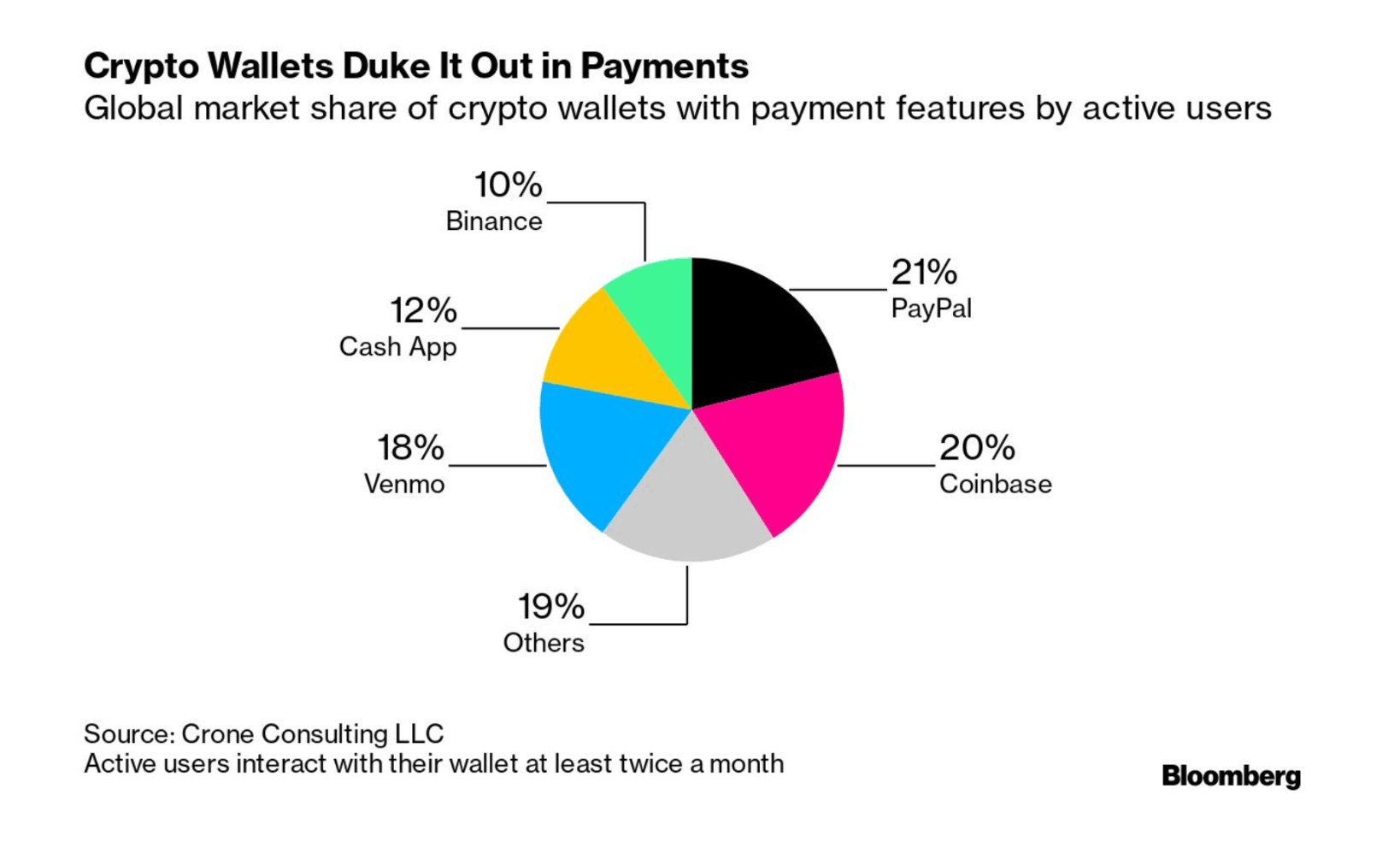
Hot Wallets
Hot or software wallets operate with an active internet connection to facilitate immediate transactions. They are the operational workhorses for real-time activities like processing customer withdrawals or executing trades. They often come in the form of a mobile app for iOS and Android or a browser extension. Beginners in the crypto space start their crypto journey using these wallets.
Their constant connectivity presents an attack surface that requires robust isolation and monitoring. Industry security standards mandate that only a small percentage of total assets, necessary for daily liquidity, remain in hot storage. Regular automated sweeps move excess funds to more secure cold storage.
Examples: MetaMask, Exodus, Zengo.
Cold Wallets
Cold or hardware wallets store cryptographic keys completely offline, eliminating remote network-based threats. They secure the majority of the company and client capital, along with master backup keys. Access requires physical procedures and multiple authorized personnel.
These systems often utilize hardware security modules (HSMs) in high-security data centers or dedicated air-gapped computers. The transfer of funds from cold storage involves manual, multi-step verification processes, creating intentional latency that is incompatible with high-frequency operations but essential for long-term asset preservation.
Examples: Trezor, Ledger, SafePal, paper wallets.
Essential Features for an Enterprise Grade Wallet
An enterprise wallet shapes how your business moves funds and connects to markets. The key features below decide whether your wallet can support real growth instead of creating operational drag.
Multi-Currency Support
A business-grade wallet must handle several blockchains and token standards without turning daily work into a support ticket queue. When teams manage BTC, ETH, stablecoins, and tokenized assets in one environment, treasury decisions become faster and audits stay clear.
Implementation typically uses a hierarchical deterministic framework. This method derives all cryptographic keys from a single secure seed, simplifying backup while organizing assets across different ledgers. The system must also manage protocol-specific requirements autonomously, such as allocating funds for transaction fees on the Ethereum network.
Fiat On/Off-Ramp Integrations
If you plan to serve real clients, you need clean bridges between cryptocurrency balances and bank money. That means integrations with payment rails (SWIFT, SEPA, or Faster Payments), plus reliable card and payout partners.
Well-designed ramps reduce abandonment across your funnel. Clients fund trading or payment activity in their domestic currency and see funds reflected in crypto immediately, with clear status updates instead of opaque “processing” states.
Advanced Key Management
Institutional security measures depart from single-key models. Multi-Party Computation distributes the signing authority for a transaction across several independent parties. Each party holds a unique key share, and a predefined quorum must collaborate to authorize any movement of funds.
Hardware Security Modules provide physical protection for cryptographic material. These certified devices perform all sensitive operations within their tamper-resistant environment. Regulated entities often mandate HSMs validated to specific standards like FIPS 140-2 Level 3 for storing master keys.
User Roles and Permissions
Role-based access control keeps daily operations disciplined. Each action ties to a named profile, which gives you clean accountability when auditors review flows.
A simple structure might include:
- Viewer: sees balances and reports
- Operator: prepares withdrawals and approves low-risk tasks
- Approver: signs high-value movements and changes limits
These controls integrate with existing corporate authentication systems. Every action taken within the wallet platform is irrevocably logged with the user’s identity.
Transaction Monitoring Tools
Real-time monitoring protects your wallet from misuse and keeps regulators informed. Screening engines score each transaction against risk rules, geography, and behavioral patterns, then raise alerts when something falls outside expected behavior. Teams can investigate cases before value leaves your environment.
This monitoring generates the detailed reporting required by regulators. It documents the company's proactive efforts to identify and deter illicit activity, forming a key component of the annual audit. The software's rulesets are updated regularly to counter evolving money laundering techniques.
Regulatory Compliance Modules
Legal adherence is built into the transaction workflow. Identity verification occurs at account creation by cross-referencing user data with official databases and watchlists. This process continues throughout the client lifecycle as ongoing due diligence.
For cross-border transfers, the system enforces the Travel Rule. It securely packages the required sender and recipient information, transmitting it to the counterparty vault before the transaction settles. This requires the wallet to support emerging technical standards for data sharing between virtual asset service providers.
How to Create Crypto Wallet Infrastructure Step by Step
Developing institutional wallet infrastructure follows a disciplined sequence. This process transforms strategic requirements into a live, secure system, prioritizing risk management at each transition.
Step 1: Define Objectives and Requirements
Start with a short requirements document instead of jumping into vendors. Write down what you want the wallet to do in year one and what volume you expect in year three. This anchors every later decision in clear business goals.
Early alignment with legal and compliance teams is essential to capture licensing needs and jurisdictional restrictions. Translate goals into measurable requirements. Examples include peak transactions per second, maximum approval time for large payouts, and recovery time objectives for outages. These numbers guide capacity planning and frame discussions with any external provider.
Step 2: Choose Blockchain Networks
Select protocols based on your commercial logic and technical demands. On Ethereum, average transaction fees can spike above a few dollars during busy periods, while layer-2 networks or alternative L1 chains often settle activity at a lower cost.
Assess each network against four filters:
- Fee stability for your most common transaction sizes
- Confirmation time that matches your user promises
- Ecosystem depth for DeFi, tokens, and tooling
- Regulatory signals in your key regions
Document why you select each chain and how it serves a specific use case, such as spot trading, payments, or tokenized deposits.
Step 3: Integrated Infrastructure Solutions
Once you know what you want to support, decide how much of the stack you will build yourself. Many firms now combine in-house logic with integrated infrastructure to shorten delivery without losing control of risk policies.
Third-party providers, including B2BROKER, deliver audited wallet core infrastructure. Such solutions include direct connectivity to institutional liquidity and payment networks. This approach is particularly effective for businesses seeking a faster deployment cycle or those requiring a proven compliance framework.
An integrated wallet solutions fit best when you:
- Need to go live within weeks
- Operate without a large internal engineering group
- Plan to add trading, payments, or exchange functionality on the same stack
You keep ownership of client relationships, branding, and business logic, while the provider handles the rest. For many brokers and fintech platforms, this balance delivers enterprise-grade stability without a multi-year build.
Step 4: Integrate Security and Encryption
Security features implementation must be comprehensive. Network layers require enterprise firewalls and DDoS protection. Application code needs regular review by specialized audit firms. All sensitive data, including backups and logs, must remain encrypted.
Deploy and configure the multi-signature key management system according to strict internal policies. Enforce separation of duties for transaction authorization, two-factor authentication, biometric authentication, and more. Manage all operational secrets, such as API credentials, through a dedicated service to eliminate exposure in application code.
Step 5: Implement Front End for User Access
The interface determines how well clients and internal teams use your wallet. Design separate views for retail users, operations staff, and compliance officers so each group sees only what they need to work effectively.
Key requirements include:
- Ease of use across desktop and mobile wallets
- Clear transaction history with timestamps and identifiers
- Accessible flows that accommodate different languages and regions
Integrate real-time updates using websockets or similar technology so balances and status changes refresh without manual reloads, especially during busy trading or payout windows.
Step 6: Conduct Multi-Phase Testing
An e-commerce business wallet must pass several layers of testing. Start with unit and integration tests that validate every function in isolation and then as part of full payment and withdrawal journeys.
Add security-focused checks that cover access control, input handling, and common vulnerabilities listed by OWASP. Load tests should stress key flows until you understand behavior at and beyond your expected peak volume.
Close with user acceptance testing that involves operations, support, and compliance teams. Their feedback will uncover workflow friction and missing controls that pure technical testing never reveals.
Step 7: Roll Out Gradually and Monitor
Begin with an internal pilot, then a small client cohort under clear limits on volume and asset types. Document entry and exit criteria for every rollout phase before you start.
Set up dashboards for error rates, confirmation times, and failed crypto transactions. A structured incident playbook ensures your team reacts quickly to any anomaly during the first months in production.
Skip the Dev Cycle, Launch Faster
Deploy a fully audited, white-label solution with fiat ramps and liquidity access in weeks.
Security Compliance and Risk Management
Effective wallet security operates on multiple distinct layers. Every layer should safeguard digital currencies while ensuring continuous compliance with international regulations.
Adhering to Recognized Standards
Independent security certifications provide validated benchmarks. Achieving SOC 2 Type II compliance proves operational controls for data security are consistently effective. An ISO 27001 certification demonstrates a functioning Information Security Management System with formal risk management protocols.
Hardware security modules often require FIPS 140-2 validation for core cryptographic operations. These certifications are mandatory for securing partnerships with banks and for obtaining licenses in major financial jurisdictions.
Regional Compliance Imperatives
Legal requirements are dictated by operational geography. In the United States, FinCEN mandates Money Services Business registration alongside a customized Anti-Money Laundering program. The EU Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation standardizes custody and governance rules for wallet services.
Singapore's regulatory regime under the Payment Services Act emphasizes anti-money laundering controls. The UK Financial Conduct Authority enforces specific standards for financial crime prevention. Firms typically appoint a dedicated Money Laundering Reporting Officer and undergo annual external audits. Specialized insurance for crime and professional liability offers a necessary financial safeguard for custody operations.
Technology Stack and Blockchain Integration
A wallet's technical foundation dictates its operational limits and capacity for growth. The chosen stack must ensure transaction reliability, maintain security, and allow for integration with evolving financial systems.
APIs and SDKs
APIs enable the core functionality of a wallet. They connect the system to blockchain technology for balance checks and transaction submission. External market data feeds integrate via API to provide real-time valuations for portfolio reporting.
Compliance providers use these interfaces to screen transactions and client addresses. Banking and payment partners supply SDKs that handle fiat currency deposits and withdrawals. These connections consolidate operations, allowing asset and data flows between the wallet and specialized external platforms.
Server Infrastructure
Professional wallet backends require resilient cloud architecture. Platforms like AWS or Google Cloud provide the necessary scalability and geographic distribution.
This setup uses load balancers to manage user traffic and containerization for consistent service deployment. A securely configured virtual private cloud isolates the network. The infrastructure must maintain consistent performance during periods of high transaction volume.
Smart Contract and Node Providers
Reliable blockchain connectivity is non-negotiable. The choice here is between managing proprietary node infrastructure and subscribing to a specialized provider. Operating your own nodes offers full control and data privacy but demands dedicated engineering resources for maintenance and upgrades.
Managed services like Infura or QuickNode deliver node access without operational overhead. They offer high availability and handle protocol updates. A common strategy employs a primary managed service for reliability while maintaining a private node for critical backup functions and custom data queries.
Centralize Control Over Wallet Operations
Integrate your wallet with B2CORE to streamline user onboarding, KYC checks, and real-time transaction monitoring in one dashboard.
Testing, Deployment, and Ongoing Maintenance
Your wallet's reliability depends on validation that extends beyond standard software checks. Before launch, engage a specialized security firm to conduct penetration testing focused on your key storage and transaction authorization logic. Simulate extreme user load to verify the infrastructure maintains stability during market surges.
Deploy the system using a blue-green strategy: direct live traffic to the new environment while keeping the previous version immediately available for rollback. Implement comprehensive monitoring from the first day to track transaction latency, system errors, and security alerts.
Maintenance is an ongoing operational discipline. Your team must schedule regular updates for security patches and prepare for mandatory blockchain protocol upgrades. Performance optimization becomes necessary as transaction volume increases. A formal incident response procedure ensures swift action during any operational disruption.
Cost Factors and Timelines
Building enterprise wallet infrastructure requires a clear financial commitment. Initial development cost for a secure, compliant MVP typically requires an investment between $100,000 and $500,000. The final cost depends directly on the complexity of your chosen custody model and regulatory integrations.
Annual infrastructure costs for cloud services and node providers usually range from $15,000 to $50,000. Third-party security audits and compliance consultations represent a critical one-time expense, often costing $50,000 to $100,000. Plan for annual maintenance and support costs at 15-20% of your initial development budget.
A functional MVP demands 6 to 9 months of app development time. Reaching a full production deployment with all banking and liquidity integrations typically extends the timeline to 12-18 months.
Choosing a Development Partner vs White Label Solutions
Your choice between custom crypto wallet development and a white-label solution defines your project's roadmap. Commission a custom build if your business model depends on unique, proprietary functionality not available on the market. This path offers maximum control but requires a dedicated internal technical team to manage the complex lifecycle.
A white-label solution delivers an operational digital wallet in weeks. It converts large upfront capital expenditure into a predictable operational cost. This approach is optimal for businesses that need to deploy quickly and prefer to rely on a specialist provider for core security updates and compliance maintenance.
Launch Your Crypto Wallet with Confidence with B2BROKER
How to build a crypto wallet for business? Developing a custom solution in-house demands vast resources and time, while opting for an unproven provider introduces security and compliance risks. You need a reliable path that ensures security and accelerates your time to market.
All-In-One CRM & Back Office for Brokers and Exchanges
Fully Customisable Trader’s Room with Modular Features
Built-In IB Module, KYC, Payment Integrations, and Reporting Tools
Intuitive Interface that Boosts Client Engagement

B2BROKER brings over a decade of regulated expertise to the table. We hold more than ten financial licenses worldwide and support over five hundred institutional clients. Our company facilitates access to specialized technology partners that deliver complete, production-ready infrastructure.
For enterprise custody and payment processing, we work with B2BINPAY. This solution provides secure, multi-currency wallet technology with built-in compliance and fiat gateways. Your team can monitor all treasury and transaction activity through our B2CORE back-office platform, which unifies control over liquidity, client accounts, and reporting.
Book a personalized demo with our specialists to see the platform in action. We will analyze your specific operational workflow and help you form a clear, actionable roadmap for a secure and compliant launch.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions about Building a Crypto Wallet for Business
- How does crypto wallet regulatory compliance vary by region?
Regulations differ by jurisdiction, requiring specific KYC/AML integrations to meet local standards like MiCA (EU) or MSB rules (US).
- Can an LLC own and operate a business Bitcoin wallet?
Yes, corporate entities can operate wallets as business assets, provided they meet all licensing, tax, and AML reporting obligations.
- How much does it cost to build a crypto wallet?
Custom enterprise builds typically range from $100,000 to $500,000 due to security audits and complexity, while white-label solutions significantly reduce this cost.
- How long does it take to develop a crypto wallet app?
Custom development generally takes 9 to 18 months to reach a secure production state. White-label solutions can deploy fully audited infrastructure in just a few weeks.







