What Are Smart Contracts?

The invention of Blockchain and cryptocurrencies has taken the financial world by storm. For hundreds of years, Fiat currencies offered a flawed but necessary support for the liquidity of global commerce. However, the Crypto emergence has put Fiat’s dominance in question. Seemingly overnight, the world got introduced to an upgraded version of money that eliminated Fiat’s shortcomings.
From increased speed and lower fees to flagship security, Crypto alleviated the most significant downsides of traditional currencies. But how exactly does Crypto manage to offer such better terms? Today we will discuss one of the core technological concepts that make the Crypto world tick – Smart contracts.
Key Takeaways
- Smart contracts (SCs) are virtual agreements written and executed with a line of code. The mentioned code includes the contract terms that will be carried out ideally once triggered.
- SCs cannot be reversed or tampered with in any form or fashion, offering a heightened sense of security compared to conventional contracts.
Let’s Define the Smart Contract
Smart contracts represent advanced and secured versions of traditional contracts, designed and executed automatically without human intervention.
These aptly named contracts follow the pre-determined “if” statements and execute them flawlessly, without the possibility of reversal or changing of the established contract terms.
Smart Contracts: A practical example
Imagine a simple contract paying employees their monthly salary if they are present on their job post during the entire month. In the case of a traditional contract, the employer is responsible for honoring this agreement without exceptions.
However, in practice, many companies might pay unpaid salaries belatedly and, in a few cases, not at all. On the other hand, if the same contract is written in the form of a smart contract, there is no room for variance or delay. In this case, if the smart contract receives the information that a given employee honored their part of the agreement, the money will be distributed automatically without any chance of delay.
Core Benefits of Smart Contracts
Forget the human error factor
Additionally, SCs are not susceptible to human error since an automated command executes the pre-determined agreement. As a result, our diligent employee will receive the money promised during the contract’s inception.
Minimal Paperwork
Finally, the most attractive feature of SCs is that they require no extra paperwork or prolonged bureaucracy to be executed. If the code receives appropriate proof of prerequisite actions, such as full-month attendance, the contract will be honored instantly. No delays and no uncertainties are involved.
The essential nature of smart contracts
The above-discussed example perfectly conveys the importance of smart contracts. Unlike the traditional method, they are intrinsically immutable, immune to tampering, and error-free. Any party involved with the smart contract can be assured that their intelligent contract agreement will be honored without any exceptions.
It is important to note that technical issues sometimes prevent SCs from functioning perfectly, as with every other piece of software. However, SC developers have designed several safeguards to avoid malfunction or reverse faulty executions through additional smart contracts.
Key Takeaways
- Smart contracts eliminate the need for third party involvement on the Crypto market.
- With this milestone, smart contracts enable Crypto users to transact swiftly and without excessive fees.
How Smart Contracts Power Crypto
While smart contracts have practical applications in almost every field of business, they have been particularly indispensable for the Crypto landscape. Due to Crypto’s decentralized and anonymous nature, the trading parties need a solid initiative to continue their operations without the fear of fraud, theft, or simply being left high and dry.
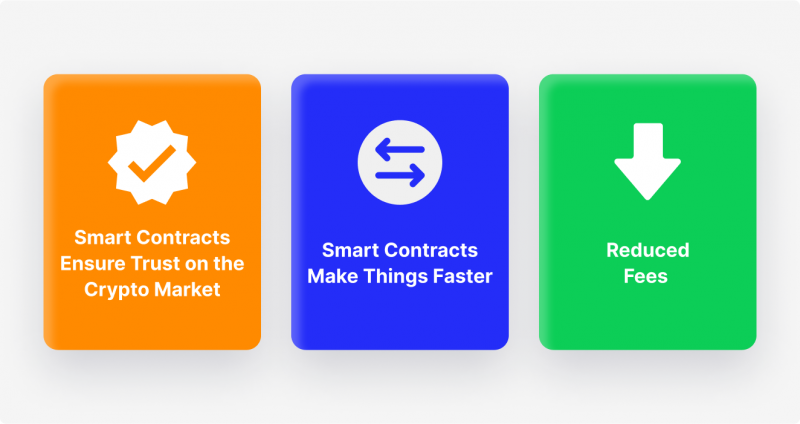
Smart Contracts Ensure Trust on the Crypto Market
That is where SCs come into play, ensuring that completely anonymous two parties can transact with Crypto and be sure that the agreement will be honored perfectly. Any reputable and trusted Crypto exchange platform utilizes smart contracts as a foundation for their trading activities. With this technology, platform participants are guaranteed to receive their funds back as the SC distributes the traded amounts simultaneously to trading parties.
Explore Deeper Industry Insights
Learn from experts shaping the future of financial services — get the latest strategies and trends.
Smart Contracts Make Things Faster
With traditional currency trading and general transactions, we have numerous red tape procedures clogging the process. Regarding international transfers, Fiat currency has to go through several national banks, all requiring specific paperwork. These relatively swift procedures stack up to several days, or even weeks in some cases, making cross-border Fiat transactions lengthy and often harmful for business dealings.
After all, most business opportunities have strict windows that could disappear in hours, and Fiat transactions can’t accommodate this sensitive timing. Conversely, smart contracts enable Crypto transactions to go through in several minutes, as no extra parties prolong the process.
Once the protocol is satisfied and the triggering event has transpired, Crypto is instantly distributed to respective parties—no more lengthy journeys through several financial institutions that stack up to unreasonable periods.
Reduced Fees
One of the most attractive qualities of smart contracts is their inherently low costs. SCs eradicate the necessity of involving numerous financial institutions in a simple money transfer. Aside from saving time, this contributes to significantly reduced fees. The reason for this is simple – the aforementioned financial institutions require a certain fee for their involvement in international money transfers.
While an individual fee might be small, numerous transfers accumulate transaction fees from four or more financial third parties. As a result, we have a significant cost on our hands. With smart contracts, we can say goodbye to the aggregation of transaction costs in such a fashion. Now, you only have to account for the inherent transfer fees payable to the Crypto platform itself.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
While we have already covered the basics of smart contracts, let us delve deeper into how exactly these automated protocols simplify the lives of Crypto traders. First off, SCs require a platform to operate on. Before any coding occurs, you must select the best-suited platform for your specific needs. In this case, there are no apparent answers – some platforms offer various functionality and speed, while others prioritize smaller costs. And with this, let us examine the practical expenses of smart contracts – the gas fees.
The Cost of Smart Contracts
It is widely known that Blockchain runs on the Turing principle of Cryptography. This concept of executing a command through every single node in a given system makes the Crypto transactions completely secure and uncrackable. However, this process requires significant computing power to run every single time. Thus, Crypto platforms like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others have introduced gas fees to make this process manageable and financially feasible.
These transactional costs are called gas fees, and they directly make all the operations on Blockchain happen. Smart contracts are no exception, requiring gas fees to be executed. This variable is a prime factor to consider when deciding on a platform for SCs. Various Blockchain platforms utilize different methodologies to run the Encryption protocol. These methodologies require considerable computational power, leading to differing gas fees.
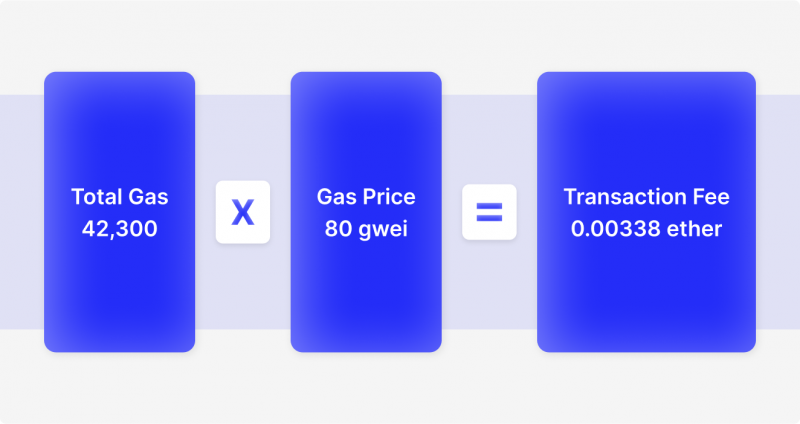
Gas fees are calculated fairly simply on each platform – We must identify the amount of gas used on a single, smart contract execution. Then we multiply this figure by the gas price of a single unit, and we receive the total transaction fee:
Coding the Smart Contract
Now, we have reached the most sensitive and complicated part of smart contract creation. Writing the SC consists of two major aspects: setting all relevant conditions of the agreement and writing the execution command. Once a developer has received clear instructions on what terms need to be honored, they code these conditions into the smart contract using an “IF” statement methodology.
The “If” command considers all selected prerequisites to executing the smart contract and only triggers once every milestone has been flagged as complete. Now, you might have formulated a logical question – How will a smart contract know if a practical condition that happened outside of the SC’s local network has been fulfilled? We’re glad you asked.
How Oracles Feed Data to Smart Contracts From Outside
Now, it is no secret that Blockchain networks are highly secluded ecosystems. They are completely cut off from outside digital powers to maintain their decentralized and secure nature. While this is excellent news for the safety of involved parties, it creates an inherent problem for smart contracts. After all, smart contracts require data to ensure that their built-in terms have been honored.
This is where oracles enter the scene and save the day! Oracles represent the lines of code that connect the on-chain smart contracts with the outside world, providing the essential data needed to carry out the virtual contracts.
The invention of oracles was initially problematic, as they were centralized by nature and posed significant cyber threats to respective exchange platforms. However, decentralized oracles were soon introduced to the Crypto world. They utilize numerous reputable data sources and aggregate them into a single data storage. This way, even if malicious attackers can access a single source, they will not have a green light to enter the entire platform.
Looking to Create a Smart Contract?
Smart contracts require several building blocks to function seamlessly. Firstly, we need a robust base platform to execute smart contracts swiftly, efficiently, and without faults.

Choose the right platform for your goals
As of 2023, Ethereum still prevails as the champion of smart contract platforms, offering the most advanced ecosystem and built-in tools supporting various smart contract features. However, Ethereum also has hefty gas fees that could weigh heavily on the limited budgets.
On the contrary, the Binance platform offers slightly lower fees but has yet to catch up with Ethereum’s robust smart contract ecosystem. So, selecting the right platform to run potential SCs is a tricky trade-off that needs to be carefully analyzed.
Analyze the terms of contract diligently
Considering all relevant contract terms might not seem like a big deal, but it is crucial to creating a proper smart contract. Since SCs are immutable and irreversible, creating faulty or inaccurate terms could lead to severe potential losses. Once the “If” statement code is triggered by the prerequisite conditions, where there’s no going back – the execution will commence immediately.
Even a tiny mistake here could cause a lot of damage, and in numerous cases, involved parties have created an opposing smart contract that would reverse the first deal and enable them to try again. However, not all parties may agree to change the agreed-upon terms if the transaction is in their favor.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
For example, if a particular party received funds with SC that they did not yet deserve, they might refuse to return the asset to the rightful owner. In some cases, concerned parties have been able to reclaim the lost funds, but with varying success. It’s important to remember that SCs are often not considered legally binding contracts.
In case of disagreements, you might be at the mercy of your counterparty without the law on your side. So, flawlessly executing smart contracts depends on their complexity. Some agreements include numerous variables as prerequisites, and it’s vital to code them into your SC statement without confusion.
Deploy and audit your smart contract
After you identify, analyze, and write all the necessary conditions and respective outcomes into your SC code, it’s time to deploy your creation on the platform of your choice. Deployment is a simple operation and won’t cause any major headaches if your code is well-optimized and error-free. The hard part here is comprehensively testing your SC for various bugs and technical problems.
After all, SCs have complete access to the funds of various parties, and even a minor malfunction could lead to material losses. Thus, it would be best to ensure that your custom SC code functions as intended, accessing all the right data feeds and executing the correct protocols.
It is unwise to take any chances here, since there have been numerous cases of dramatic failure with SC executions. In order to gain trust of your counterparties, you need to rigorously test your SCs and assure all involved participants that it’s safe to conduct business.
In summary
SCs are one of the most useful digital breakthroughs of recent years, not just for the Crypto market but for global business. They enable completely unrelated parties to transact without outside involvement and with complete transparency. SCs raise the level of trust in the Crypto market and ensure that the anonymity of its participants doesn’t pose a threat to honoring the digital contracts.
However, smart contracts are far from being perfect. They have obvious limitations and inherent dangers. SCs are not legally binding. They also have technical issues that could endanger the entire network. SCs also have limited access to the off-chain data, limiting their functionality and value to global commerce. So, if you want to create your own smart contracts and execute deals without needing third parties, we implore you to explore the pros and cons of this fascinating technology deeply.
FAQ
What are smart contracts?
SCs are automated commands written in the form of an “if” statement code. They include the terms and outcomes of the contract. Once the terms have been satisfied, the smart contract automatically honors the contract and distributes the determined outcomes to involved parties.
What are the main challenges faced by smart contracts?
SCs are limited by nature. They require the help of Oracle protocols to receive off-chain data. This process is highly complex to maintain the security of a given on-chain platform. SCs are also not considered to be legally binding. Their irreversible nature can also pose threats since even flawed agreements will be carried out without a chance of reversal.
Is Eth a smart contract?
While Ethereum is not a smart contract, it is a decentralized platform that utilizes SCs as the means of interaction and trading. Every time a transaction is carried out on the Eth platform, smart contracts ensure that both parties instantly receive their promised funds, and there is no need to involve outside parties in the transaction.
What is an NFT smart contract?
SCs are a vital part of NFTs with any utility whatsoever. With the help of SCs, developers can equip Non-fungible tokens with various utilities or even tie them to different commodities.
Can SCs work without blockchain?
A blockchain network is necessary to have a fully-fledged smart contract. The essential part of SCs is to be executed instantly without requiring third parties. Blockchain technology enables SCs to achieve that through its decentralized chains.
Recommended articles
Recent news