What is Proprietary Trading, And How Does it Work?

The development of financial technology, digitalisation of financial markets and trading system automation made the industry more diverse and competitive. New trends are taking place more frequently, and new market participants are landing in this space to improve their financials.
Proprietary trading is gaining momentum and attention from key market players, multinational corporations and startups. This trend triggers high demand from brokers and traders to boost their businesses.
Let’s dive deeper into the proprietary trading definition, how it works and how to launch your platform.
Key Takeaways
- Proprietary trading involves a trader who invests in financial markets and shares profits with the broker.
- The firm sets trading challenges to ensure that only selected investors have access to institutional funds and resources.
- Prop brokers can earn from charging challenge participation entry fees, revenue sharing and classic brokerage service commissions.
- The deregulation of the market makes it highly desirable compared to hedge funds and traditional market makers.
Understanding Proprietary Trading
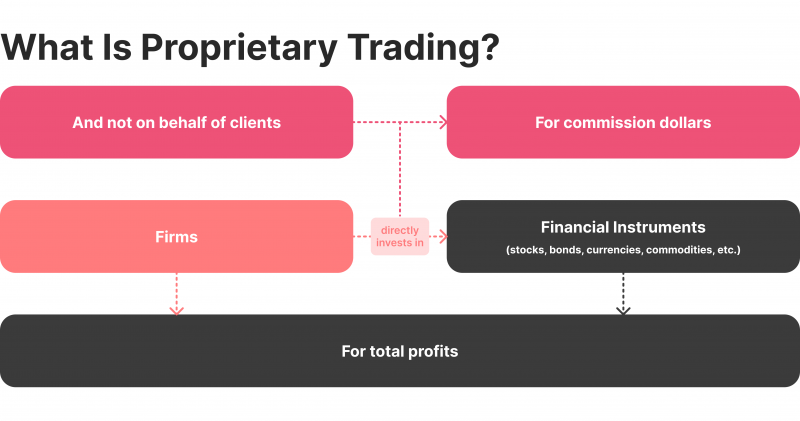
Proprietary trading refers to professional investors making market decisions on behalf of a firm to raise their wealth. They use the proprietary trading company’s software, technology and systems to explore the market, analyse opportunities and execute trading orders.
In exchange, proprietary traders earn from predetermined compensation models like commissions from returns, revenue sharing and other schemes. On the other hand, the company gains quick access to the financial market through experienced traders who have higher chances of success.
Brokers attract a wide range of potential investors, set trading challenges and award winners by offering in-house capabilities to improve their outcomes and ensure more returns.
Prop Traders vs Institutional Traders
Unlike ordinary traders employed by a brokerage firm, hedge fund or financial institutions, prop traders work on a contractual basis.
Institutional traders earn through a combination of fixed payouts and commissions, while proprietary traders earn through advanced return-sharing systems and bonuses from direct market earnings. Moreover, they can work simultaneously with multiple prop firms.
Industry Overview
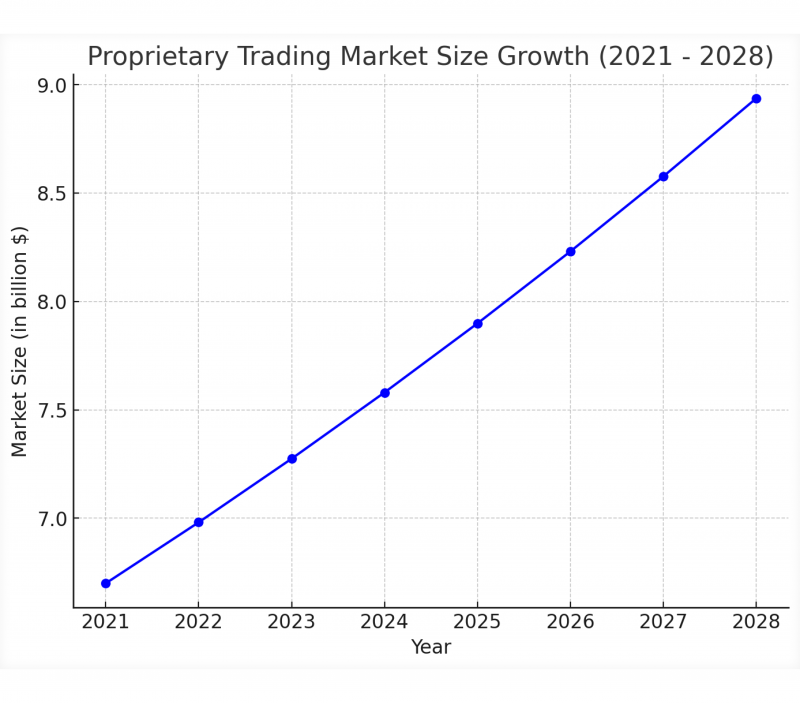
Proprietary trading is not a recent invention. It was introduced in the 1980s and gained huge popularity in the last couple of years. In 2020, the market value was estimated at $6.7 billion, which is expected to grow at 4.2% CAGR between 2021 and 2028. This means that the prop trading industry can potentially reach around $9 billion by 2028.
In the early 1980s, the emergence of investment bank systems and the modernisation of financial services triggered a rise in prop trading, which prevailed in leading banks like Morgan Stanley and Goldman Sachs.
In the 1990s, as more financial technology was poured into this space, such as derivatives contracts, high-frequency trading (HFT) and the rise of the internet, prop trading gained more significance and adoption.
Then, the 2000s was a peak period for proprietary trading. However, the financial crisis slowed down this trend and raised some scrutiny over this technology, attributing it to various banks’ collapse and threatening economic stability. In 2010, banks were prohibited from engaging in prop trading, which founded independent prop trading companies.
These trends picked up again after 2020 when markets faced surging volatility during the global pandemic. This increased the demand for HFT, algorithmic and prop trading.
The Volcker Rule was introduced in 2010 to limit banks’ risky trading activities, including prop trading. The former Fed chairman Paul Volcker introduced the rule as part of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act in 2010.
How Proprietary Trading Works?
After we explained what is proprietary trading, let’s dig deeper into its process and how such firms operate.
A prop firm trader signs up at a brokerage firm to take on some financial challenges. Once they pass the challenges successfully, they become eligible to trade on the brokerage’s behalf.
As such, selected investors trade using the company’s capital, software, matching engine, market access capabilities and liquidity features to execute market orders. Traders seek financial gain for themselves and the brokerage firm and share the realised gains through predetermined allocation systems.
This approach offers a win-win situation for both parties. Brokers ensure they trade through experienced investors with less marketing efforts and high earning potential. On the other hand, the prop trader earns a percentage of their trading activities, leveraging institutional capital and resources.
Core Elements for Operations
A prop trading platform may look similar to any brokerage software. However, there are key elements that you will find in any proprietary broker.
Prop Trading Firms
The prop firm can either be an ordinary brokerage platform with an extended arm into proprietary trading or an independent specialised entity.
Explore Deeper Industry Insights
Learn from experts shaping the future of financial services — get the latest strategies and trends.
The brokerage determines the trading markets, strategies, number of invited traders, challenges and allocated funds. Brokerage companies can minimise their marketing and hiring costs by attracting top-notch investors and engaging them in direct financial challenges.
Proprietary Trader
A financial expert registers at a prop firm, participating in multiple challenges before actively trading on the brokerage’s behalf. These Investors prefer reliable proprietary brokers to ensure safe payouts and low entry barriers.
Prop traders work independently for the firm without being directly employed by them. As such, they can work with multiple brokers if they ensure no conflicts of interest and manage to attain financial gains for themselves and the company.
Trading Challenges
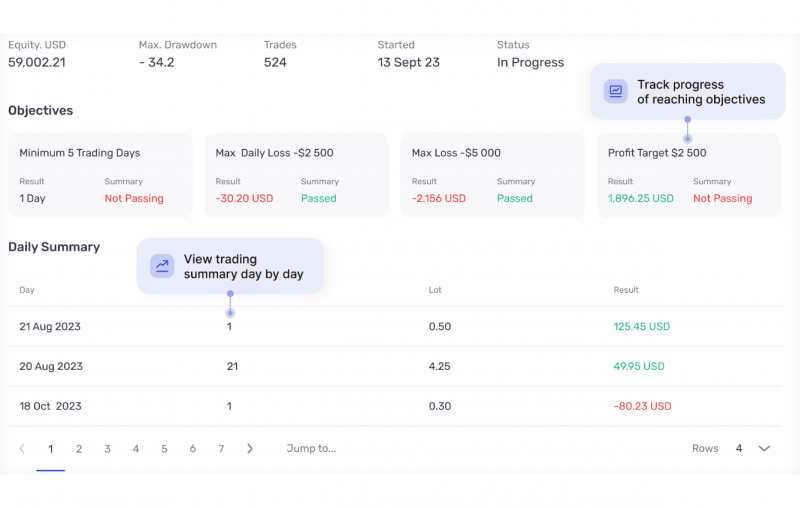
The prop firm creates trading challenges to ensure they hire the best and most qualified personnel. Such objectives may include achieving a particular return on investment, earning targets, profiting from margin accounts or more.
Financial institutions engage potential traders through challenges that can be adjusted according to their preferences, aligning with the business trading strategies and available asset classes.
It is worth noting that participating in these challenges entails paying specific fees that brokers determine. Qualified prop traders must pay to join and re-pay if they fail and want another attempt. This stream provides an income source for the prop trading firm.
Prop Software
The software is a key component, which is the technological means that enable brokers to create, customise and monitor potential prop traders during challenges.
The platform must offer a transparent working environment for challengers, prop traders who pass the test and revenue sharing. It is also connected to trading venues and servers that offer liquidity, market updates, newsfeeds and more.
Advantages and Disadvantages
There are multiple benefits and drawbacks to operating as a prop trading broker. You expand your business with new income-generating sources and integrate top traders into your platforms, but the uncertainty creates a fear factor. Let’s review these pros and cons.
Pros
- Exploring new income streams from challenges such as participation fees, revenue sharing, and trading activities.
- Maximising earnings as prop trading firms keep the trading returns rather than giving them to clients, like discount brokers.
- Freedom to utilise any automated or semi-automated approach without restrictions, such as algorithmic and copy trading.
- Leverage market opportunities through top-notch traders who are carefully tested and selected.
- The lack of regulations makes it more favourable for companies to launch and operate their proprietary trading firms.
Cons
- Trading with the company’s capital puts the institutional account at market exposure risk.
- Potential regulatory changes can massively impact the way prop firms operate and their potential growth.
- Reliance on independent traders creates a sense of uncertainty over outcomes and market volatility.
For Traders
If we look from the prop trader’s perspective, being able to work with autonomy and using the company’s assets, technologies, and capital are the most significant advantages. However, they face some challenges, such as upfront fees, instability, and increased pressure since they must report to and are held accountable in front of the prop broker.
Proprietary Trading Firms vs Hedge Funds
Hedge funds and proprietary trading might be similar in that they are two modes of financial services scrutinised during the 2008 financial crisis and faced different evolutions to become lucrative business ideas today.

However, they operate and offer revenues differently. A hedge fund is a financial institution using large-capital client funds to grow these funds. They execute global macro trading orders on behalf of companies and investment firms and earn significant trading commissions.
On the other hand, proprietary brokerage firms invest in the market using their money and accounts to grow their wealth. They are not answerable to any external client and operate through experienced prop traders.
Monetisation Strategies
Brokers usually gain from trading activities every time a trader opens or closes a market position, which is a fixed amount, proportional value or spread-based. However, prop traders have different revenue streams.
Revenue Sharing
One common method to monetise as a prop trading company is to split earnings with the prop investor. Both parties agree on a profit-sharing scheme, whether 40-60% or 50-50% split.
When traders are on probation as they complete the challenges, they might receive 20% to 30% of their returns. This share increases as they pass the test and become prop traders, getting 40% to 50%.
On the other hand, the prop firm earns between 50% to 80% of the trader’s activity, a solid income with minimum interference by the broker. The brokerage only provides trading capital, software and technology.
Challenges Fees
Another source of income for prop brokerage firms is the challenge participation price. The firm may set a $100 to $500 fee to enter and fulfil trading tasks, such as earning targets, ROI target rate or minimum loss target.
Higher-scale institutions that run prop trading desks may charge higher fees of up to $1,000, depending on the tools, capital, and markets provided.
Prop firms attract tens or hundreds of candidates who pay these fees to qualify as trading partners, creating a significant income. Moreover, when a participant fails the challenges, they can re-take them for additional fees, creating another income stream for the broker.
Opening Your Proprietary Trading Company
Launching your proprietary trading desk is an excellent way to capitalise on the rising trends and promising future of this invention. However, only with calculated steps and plans you can make. Here’s how you can start.
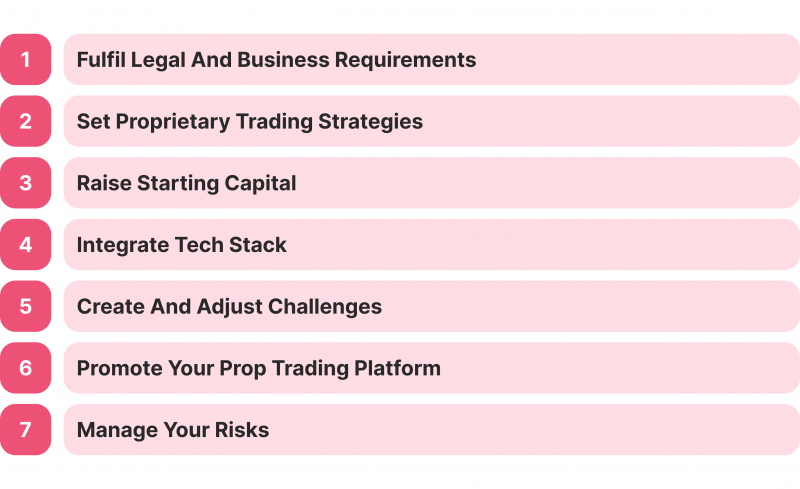
Fulfil Legal and Business Requirements
Currently, the market provides an excellent opportunity because there is no special license for proprietary trading. Obtaining a financial service provider or broker license can be enough to operate as a prop firm.
However, you must adhere to the regulations of your local regulator. For example, the FCA lays the foundation for brokerage and investment firms in the UK. At the same time, FINRA oversees the financial and trading activities of institutions in the US through a broker-dealer license.
Besides the legal aspect, prepare a business plan and state your goals, mission, and vision to create a shared sense of purpose across the organisation.
Set Proprietary Trading Strategies
When planning your business structure and mode of operation, determine your strategies. As such, define your target market, financial instruments, asset classes and other investing products.
Develop directions for your traders, including investing strategies, portfolio allocation, and goals to ensure that your profile grows in the desired market or niche.
For example, if institutional assets appeal to you, focus on stock and bond markets. You also need to source liquidity and provide seamless access to these venues to support your prop traders.
Raise Starting Capital
Identify your operational budget, whether you are using your own money, crowdfunding or raising capital from other sources. Having a compelling business plan is crucial to attracting angel investors and joint venturers to your business and raising significant starting capital.
Risk management plans, estimated earnings, return on investment, and balance sheets are crucial financial documents necessary to attract and raise funds.
Integrate Tech Stack
Your technological environment is vital in managing and operating your proprietary trading business. A reliable prop trading platform solution goes a long way in optimising your offerings, monitoring your performance and creating in-depth reports on your financials and operations.
Ensure that you can customise your trading challenges according to your preferences. This helps find traders that suit your goals and objectives.
A transparent platform also offers a fair overview for traders, where they can check the trading challenges beforehand, update their equities on time and report their earnings accurately to ensure fair competition.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Whether you engage in proprietary trading as an independent platform or as part of a larger brokerage company, it is crucial to find an easy-to-integrate solution that matches your software and offers broad access to asset classes and financial markets.
Create and Adjust Challenges
Set reasonable financial challenges that test the candidate traders’ adequacy and ability to create reliable returns from the financial market.
Most prop trading companies set up 4-5 objectives like the following:
- Profit targets that must be reached within a given budget and time.
- Maximum drawbacks that a trader can lose from the total capital.
- Daily loss limits on open positions on daily trading.
- Providing consistent average profits on a given number of days.
Promote Your Prop Trading Platform
Create a marketing strategy to spread the word about your brand. Even though prop traders lower client acquisition costs, lead generation and account management, you still need to promote your platform.
Take advantage of online forums where online traders and investors communicate, such as Telegram and Reddit. You can also promote your services through internet personalities and influencers to reach your target audience.
Improve your website’s and webpages’ visibility using search engine optimisation techniques to attract users from search engines and generate organic traffic.
Manage Your Risks
You must consider several risks when operating in proprietary trading, such as deregulation, uncertainty and dependence.
The lack of regulations opens the door for possible legal changes to prop trading, which can either inhibit or boost your business. The reliance on prop traders’ performance also raises uncontrollable risks as your profits rely on the investor’s intuition, analyses and decisions.
Moreover, the unpredictability of trading markets makes it impossible to have certain earning projections. Therefore, you must always prepare an emergency plan if the market goes sideways or swan events happen.
Conclusion
Proprietary trading involves independent professional investors who execute market orders, secure returns for a prop firm and share the revenue on a predetermined split scheme.
Candidate traders participate in various challenges to prove their capabilities. Once they complete the objectives, they become prop traders using the broker’s account, capital, software and technology.
This model offers income diversity for brokerage firms and ensures that only experienced individuals trade on their behalf. On the other hand, investors benefit from using the significant budget to leverage their positions and use advanced execution software and market access.