ABCs of Crypto ETFs: How Do They Work?

Since its introduction in the mid-1990s, ETFs have experienced meteoric growth in popularity. Their unique form combines the benefits of mutual funds with the adaptability and liquidity of individual equities, which may explain their rising popularity.
Unlike mutual funds, which can only be purchased and sold at the end of the trading day, ETFs may be traded on exchanges all day long, making them a good choice for long-term investors and active traders.
This adaptable financial tool has recently begun an intriguing venture into digital currencies, giving rise to crypto ETFs. These funds provide a streamlined method of investing in the unpredictable but potentially rewarding crypto market by tracking the values of one or more crypto assets. So, let’s discuss: what exactly are crypto exchange-traded funds?
Key Takeaways
- Crypto ETFs track cryptocurrency prices, allowing investment without direct ownership.
- Crypto ETFs function by creating and redeeming ETF shares based on cryptocurrency values.
- The benefits of crypto ETFs include accessibility, diversification, and trading flexibility.
- Offering crypto ETFs helps brokerages meet demand, diversify, and tap into the cryptocurrency market.
Basics of Crypto ETFs
Crypto ETFs are essentially investment vehicles that track the price of one or multiple digital currencies. These financial instruments allow investors to engage with the crypto industry without the need to directly buy, sell or securely store the crypto assets themselves.
This feature of crypto ETFs makes them especially appealing to traditional investors intrigued by cryptocurrencies’ high-reward potential but deterred by their volatility and the technical challenges associated with owning and managing them.
Crypto ETFs mimic the mechanisms of conventional ETFs, which usually track a specific index, sector, commodity, or asset. In the case of crypto ETFs, these could track a single cryptocurrency like BTC or ETH or a basket of multiple cryptocurrencies.
The objective of these ETFs is to mirror the performance of the tracked cryptocurrencies, giving investors exposure to their price movements without the need to hold the assets directly.
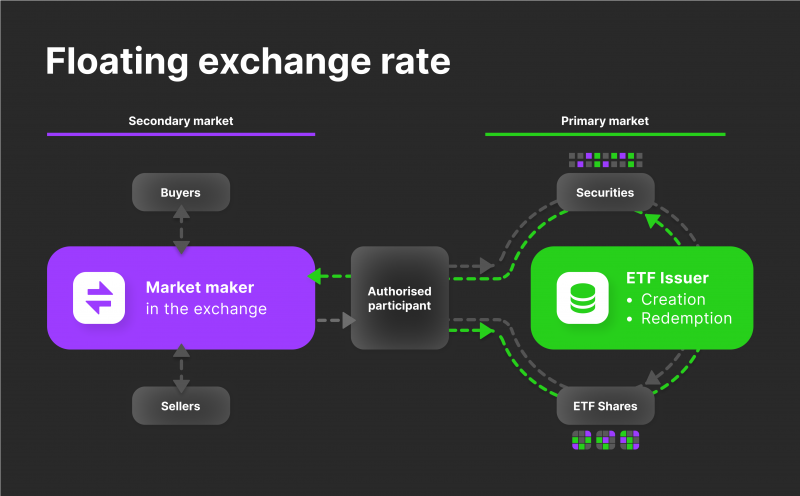
How Do Crypto ETFs Work, Exactly?
The creation and redemption procedure is fundamental to the operation of cryptocurrency ETFs since it keeps the ETF’s value in line with its underlying assets. To put it briefly, authorised participants (APs), often significant financial institutions, buy the underlying cryptocurrency and produce the ETF shares for a crypto ETF.
The APs purchase huge quantities of the applicable cryptocurrency and deposit them with the ETF provider. In exchange, the provider issues the APs shares in an ETF that may be traded on the stock market. The value of an ETF’s shares goes up and down in tandem with the cryptocurrency price it tracks.
To prevent the ETF share price from diverging too far from the value of the assets it follows, the APs will step in to arbitrate, either by purchasing additional cryptocurrency to produce more ETF shares (during periods of high demand) or by selling the underlying cryptocurrency (during periods of low demand).
Simply put, crypto ETFs allow investors to put their money to work in the cryptocurrency market without dealing with unfamiliar tools like digital wallets or cryptographic keys.
Benefits And Risks Of Trading Crypto ETFs
Every investment opportunity in an investment vehicle features its own distinct mix of pros and cons. In particular, the new market for crypto ETFs, which combines the unpredictability of cryptocurrencies with the structural elements of traditional ETFs, is a prime example of this phenomenon.
Benefits of Trading Crypto ETFs
Accessibility – Crypto ETFs bring cryptocurrencies into the conventional investment arena, making them easily accessible for everyday investors. For instance, you don’t have to learn about blockchain mechanics or store private keys or use a digital wallet. Crypto ETFs are traded on traditional stock exchanges, allowing anyone with a standard brokerage account to participate in the crypto market without dealing with the complexities of direct cryptocurrency ownership.
Affordability – Despite the regulatory ambiguity surrounding cryptocurrency ETFs, the following may interest crypto investors who already hold exchange-traded funds: ETFs, such as Proshares Bitcoin Strategy ETF, allow investors to gain exposure to a volatile asset class without breaking the bank.
Diversification – One of the advantages of crypto ETFs is the opportunity for diversification. A single crypto ETF exposes a specific cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, while a multiple crypto ETF tracks a basket of digital tokens or currencies. This is akin to investing in a technology-focused ETF versus a broader market ETF – the former might rise or fall based on the performance of a specific sector. At the same time, the latter provides broad exposure to several sectors, spreading the risk.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Liquidity – Crypto ETFs are traded on traditional stock exchanges, which means they can be bought and sold at any point during market hours. This kind of liquidity allows investors to react quickly to market changes. For example, if Bitcoin’s price starts to plummet, a Bitcoin ETF holder can promptly sell their shares to limit potential losses.
Risks of Trading Crypto ETFs
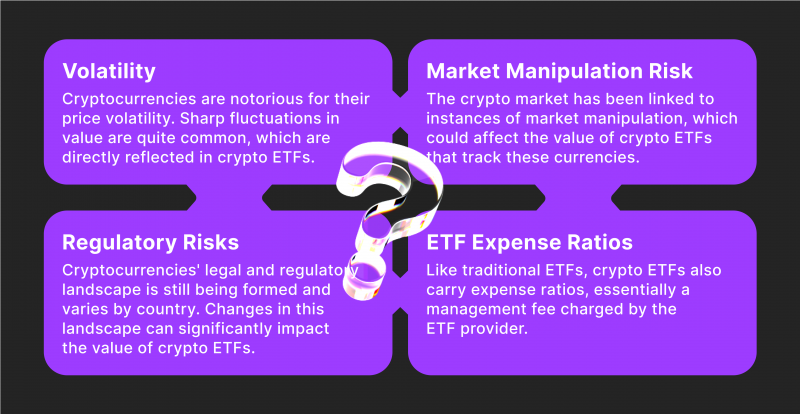
Volatility – Cryptocurrencies are notorious for their price volatility. Sharp fluctuations in value are quite common, which are directly reflected in crypto ETFs. To illustrate, in 2020, Bitcoin’s value experienced a steep drop, declining from nearly $10,000 to around $5,000 within a month. Such a drastic decrease would have similarly affected the value of any Bitcoin ETFs.
Regulatory Risks – Cryptocurrencies’ legal and regulatory landscape is still being formed and varies by country. Changes in this landscape can significantly impact the value of crypto ETFs. For instance, if a major economy like the U.S. or China imposes stricter regulations on cryptocurrencies, it could lead to a market-wide sell-off, reducing the value of crypto ETFs.
Market Manipulation Risk – The crypto market has been linked to instances of market manipulation, such as “pump-and-dump” schemes, where fraudsters inflate the price of a coin before selling off their holdings, causing the price to crash. This manipulative behaviour could adversely affect the value of crypto ETFs that track these currencies.
ETF Expense Ratios – Like traditional ETFs, crypto ETFs also carry expense ratios, essentially a management fee charged by the ETF provider. For instance, if an ETF has an expense ratio of 0.75%, you’ll pay $7.50 in annual fees for every $1,000 you invest. While this might seem small, these fees can significantly erode your potential earnings over time and with larger investments.

How To Trade Crypto ETFs
There are a number of ways to approach trading crypto ETFs based on your skill level, risk appetite, and personal preference.
ETF CFDs
Trading ETFs using contracts for difference (CFDs) is a common strategy. CFDs include selling or purchasing an asset with an agreement between a broker and a trader to settle any price fluctuations. Without purchasing the underlying asset, you may still profit from price fluctuations by trading ETFs using CFDs.
CFDs allow you to trade ETFs in both directions. If you anticipate an ETF’s price will rise, you can take a long position. Conversely, you can take a short position if you believe the price will fall.
ETF Options
ETF options trading is yet another avenue to explore. These derivative contracts, pegged to futures prices, let you take a position without committing to buying or selling the underlying asset when the contract matures. The striking price at which you agree to buy options contracts is based on the futures price.
If the futures price goes towards the strike price by the expiration date, you win, but if the futures price moves away from the strike price, you lose the premium you paid.
ETF Futures
Futures contracts also allow investors to bet on the price of an asset as of a future date. In contrast to CFDs and options, buyers of futures contracts must take physical possession of the underlying item or extend the contract’s expiration date.
Where Can You Buy Crypto ETFs?
Much like traditional ETFs, Crypto ETFs are listed and traded on established exchanges or brokerages. Therefore, the first step to investing in a crypto ETF is to have an account with a brokerage that provides access to the exchanges listing these ETFs.
Common brokerages like Charles Schwab, Fidelity, or TD Ameritrade are typical platforms investors use. Several online and app-based brokers like Robinhood and eToro have recently entered the fray, catering to the newer generation of investors.
Investing in a crypto ETF is quite straightforward once you’ve set up and funded your brokerage account. Simply use the platform’s search function to find the crypto ETF you want. This can be done by typing in the ETF’s ticker symbol, a unique series of letters representing each fund.
For example, if a Bitcoin ETF had a ticker symbol, ‘BTCF,’ you would search for this on your trading platform.
After locating the ETF, you can place an order to buy shares. The process is similar to buying shares of a common stock – you specify the number of shares you want to purchase and the price you’re willing to pay per share. Once your order matches with a seller, the transaction is executed, and the ETF shares are added to your portfolio.
Why Should Every Investment Firm Offer ETFs?
From a brokerage’s perspective, adding ETFs, including crypto ETFs, to their list of tradable assets can unlock many benefits.
First and foremost, ETFs meet growing investor demand. Investors seek modern, flexible, diversified investment vehicles as the financial market evolves. ETFs fit the bill perfectly, providing an efficient way to gain exposure to a broad range of asset classes – from stocks, bonds, and commodities to the more recent addition, cryptocurrencies. By offering ETFs, brokerages can adjust to this demand, attracting new clients and retaining the existing ones.
The potential for increased trading volumes is another compelling reason. Due to their intraday tradability and flexibility, ETFs often see high trading volumes. Greater trading activity can translate into more revenue for brokerages, particularly those that generate income from trading commissions.
Offering ETFs also helps to diversify the investment options on a brokerage’s platform. Diversification is not just a strategy for investors; it’s also vital for brokerages. By providing a wide range of ETFs – sector-based, index-based, commodity-based, and crypto-based – brokerages can ensure they fit varied investment preferences and strategies, thus broadening their client base.
The addition of crypto ETFs to the portfolio can also leverage the cryptocurrency boom. Despite its volatility, the crypto market has seen a dramatic surge in interest. Crypto ETFs allow brokerages to ride this wave, enabling their clients to engage with the crypto market in a more familiar and accessible way. This sets the brokerage apart from its competitors and potentially drives further client engagement.
Lastly, the ETF market’s growth trajectory makes it a lucrative field for brokerages to tap into. The global ETF market has been growing rapidly and is expected to continue its upward trend. Brokerages offering ETFs can benefit from this growth trend and establish themselves as forward-thinking firms.
How To Add ETFs To Your Investment Firm
Securing liquidity for the ETFs is a critical component of the process. Let’s discuss the detailed steps an investment firm needs to undertake to add ETFs to its platform.
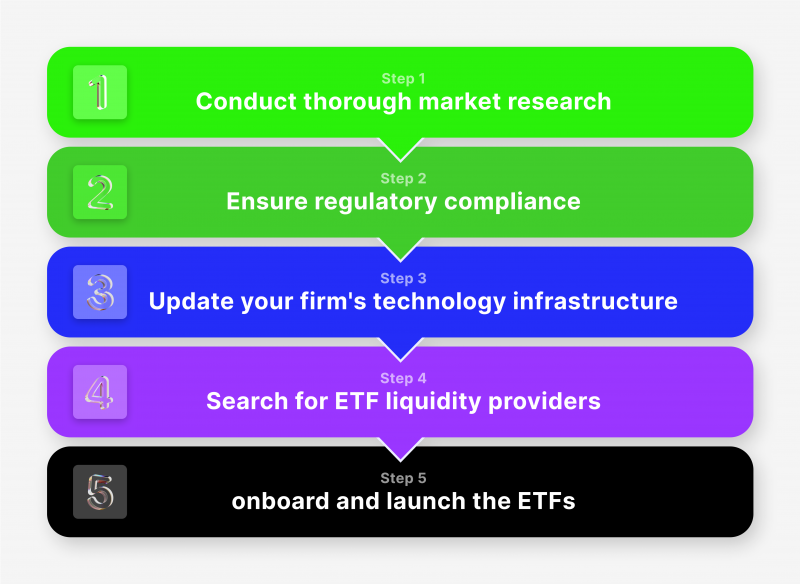
The first step is to conduct thorough market research. Understanding the current market demand for ETFs, identifying the types of ETFs investors are interested in, and assessing the competitive landscape are essential aspects of this research. This knowledge helps the firm decide which ETFs to add and can provide insight into potential marketing strategies.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Next, the firm needs to ensure regulatory compliance. Different jurisdictions have different rules regarding ETFs, and a firm must comply. This might involve obtaining necessary permissions or licenses, submitting documents to regulators, or adjusting the firm’s operations to meet regulatory standards.
The third step is to update the firm’s technology infrastructure. ETFs are traded throughout the day like stocks, so a brokerage’s trading platform must be capable of supporting intraday trading of these instruments. This might require software updates or a complete overhaul of the trading platform.
A critical part of the process is searching for ETF liquidity providers. Liquidity providers are essential for maintaining an orderly ETF market. They create and redeem ETF shares to ensure that the price of the ETF stays close to the value of its underlying assets.
They also provide the necessary capital to facilitate trade. Finding reliable liquidity providers is crucial, as it helps ensure the ETFs trade smoothly and transparently on the platform.
For instance, B2BROKER is the largest crypto ETF CFD liquidity provider on the market, offering comprehensive services beyond cryptocurrencies. Clients leveraging B2Broker’s services can facilitate trades for ETF CFDs from the biggest European, Asian, and American cryptocurrency exchanges. This expansive network makes them a key partner for investment firms looking to provide diverse ETF offerings.
The final step is onboarding and launching the ETFs. This involves adding the ETFs to the trading platform, updating the brokerage’s product lists, and training staff to handle customer queries about the new offerings. Launching a marketing campaign to inform existing and potential customers about the new ETF offerings is vital.
Final Takeaway
In the first quarter of 2023, crypto ETFs outperformed all other ETFs with extraordinary growth rates of 61.95% to 98.66%. With such a stellar track record, it’s clear why ETFs are the go-to investment vehicle for so many market participants.
Consequently, a thorough understanding of this investment vehicle and its specifics is required.
FAQ
Are ETFs and mutual funds the same?
No, ETFs and mutual funds are not the same. While they offer diversification and professional management, ETFs can be traded on exchanges like stocks throughout the day. At the same time, mutual funds are priced at the end of the trading day and allow buying or selling at the net asset value (NAV).
Where can I buy a crypto ETF?
You can buy a crypto ETF through brokerage platforms that offer access to the specific ETF. Ensure that the brokerage you choose supports the trading of crypto ETFs and follows their process to purchase the desired ETF.
Are ETFs safe?
ETFs carry risks, but they can be considered relatively safe investment options. They are regulated, provide diversification, and offer transparency.
How do I invest in Bitcoin through an ETF?
To invest in Bitcoin via an ETF, you must locate a BTC ETF on a recognised exchange. You may acquire shares of the BTC ETF by opening an account with a brokerage that allows trading in the ETF, depositing money into the account, and then placing a buy order. The ETF will follow the price of BTC, giving investors indirect exposure to the cryptocurrency’s growth without requiring them actually to purchase any bitcoins themselves.








