Inverse ETFs: How to Make Profits From Declines

Amidst the unexpected market movements this year, one asset class emerged as the golden medium between risk and return, delivering a satisfactory earning without taking unpredictable challenges.
ETFs have always been known as a great portfolio diversification element to offset investment risks. However, inverse ETFs take things a step further and offer excellent hedging capabilities to make earnings on market declines.
Investing in inverse exchange-traded funds can be more challenging, but during economic stagnation, they are your go-to option trading tools. So, what are inverse ETFs? Are they more profitable? Let’s explore!
Key Takeaways
- Inverse exchange-traded funds are financial instruments that track the opposite price performance of stocks and indices.
- Inverse ETFs are suitable for day trading and hedging against risky long positions.
- Future short selling and inverse ETFs are similar, but inverse equities are more straightforward to comprehend and invest in.
Understanding Inverse ETFs
Let’s briefly explain what ETFs are. An exchange-traded fund is a financial basket collecting one or multiple tradeable securities, reflecting the underlying benchmark or the asset price performance in the ETF value.
For example, a Bitcoin ETF mimics the spot Bitcoin market price without actually owning the BTC coin, whereas the Inverse ETF’s value increases as the BTC price grows and vice versa. This approach makes it faster to trade in a specific market or asset.
Inverse ETFs reflect the counter-price performance of the underlying asset. These instruments offer an inverse exposure to market declines, which can be described similarly to shorting stocks.

How Do Inverse ETFs Work?
In an inverse Bitcoin ETF, when the coin price decreases, the inverse BTC ETF increases in value. Similarly, if the coin value surges, the ETF value decreases. The Inverse futures contracts formula is as follows:

Suppose the Bitcoin entry price was $62,000, and the exit price was $69,000. Calculating the ETF future value for 1 BTC would go like this:
Profit = 1 x (1/62000 – 1/69000)
Profit = 1 x (0.00001613 – 0.00001449) ⇒ 1 x 0.00000164 = 0.00000164.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
As such, to earn from inverse BTC/USD futures contracts, investors would execute long (buy) orders to benefit from the associated increase against the USD and earn 0.00000164 BTC.
Are Inverse ETFs Better Than Linear ETFs?
Inverse exchange-traded funds can be lucrative in volatile markets, where assets move up and down constantly, delivering returns on both sides of the trade.
Therefore, Inverse Bitcoin ETFs can be profitable, given the high volatility levels of the crypto market and the price rallies created by Bitcoin bulls and bears.
Inverse ETFs offer excellent hedging tools, allowing investors to offset risky positions by taking the counterpart side of the trade. Moreover, they enable traders to gain from declining ETF instruments and capitalise on market meltdowns.
In January 2024, the SEC approved the spot Bitcoin ETF, increasing the inflow of inverse BTC ETFs benefiting from the crypto market volatility.
Pros and Cons of Inverse ETFs
Line inverse ETFs gained a significant lift after introducing crypto ETFs in spot and future Bitcoin and Ethereum assets. This expansion saw more investors favouring risky assets that deliver sufficient returns during price decreases.
However, there are several challenges to these instruments. Let’s review the advantages and disadvantages of inverse ETFs.
Advantages
- Inverse ETFs offer a hassle-free alternative to short-selling that comes with various restrictions and taxing procedures.
- Traders use inverse exchange funds to hedge against risky long market orders and minimise damages from unpredictable changes.
- Capitalising on market declines using inverse ETFs is more affordable than through hedge funds or short-sellers.
- Leveraged inverse ETFs can boost the trader’s potential income during market declines, especially in highly volatile assets.
Disadvantages
- Inverse ETFs are highly risky, and volatile markets can experience sharp price corrections that can liquidate the trading position.
- Futures contracts counterparty arises if the financial derivatives seller fails to fulfil their obligations and deliver the underlying asset.
- This niche market has less demand and participants than conventional ETFs, increasing liquidity risks.
How to Trade Inverse ETFs
Inverse exchange-traded funds are less common than standard ETFs and other securities. However, they are becoming more popular when coupled with Bitcoin and crypto assets.
Therefore, you must find a reliable brokerage firm that offers inverse ETFs and ensures sustainable liquidity streams that provide sufficient volumes on both sides of market fluctuations.
Check the range of products and financial instruments provided by the broker, and engage in a variety of standard, leveraged and inverse ETFs to diversify your chances. You can also combine selected technical indicators to support your decision-making, such as:
- MACD: Track trends and predict future prices to make the right entry.
- Fear and greed index: Track market sentiments and make decisions based on overall market behaviour.
- RSI: Monitor overbuying and overselling points to predict price corrections and surges and make the right trading decision.
Top-Performing Inverse ETFs
Investing in the right inverse exchange funds is vital because these assets can hold significant liquidity and market risks. Therefore, you must find an investment firm offering a wide variety of ETFs, including the inverse ETFs listed below.
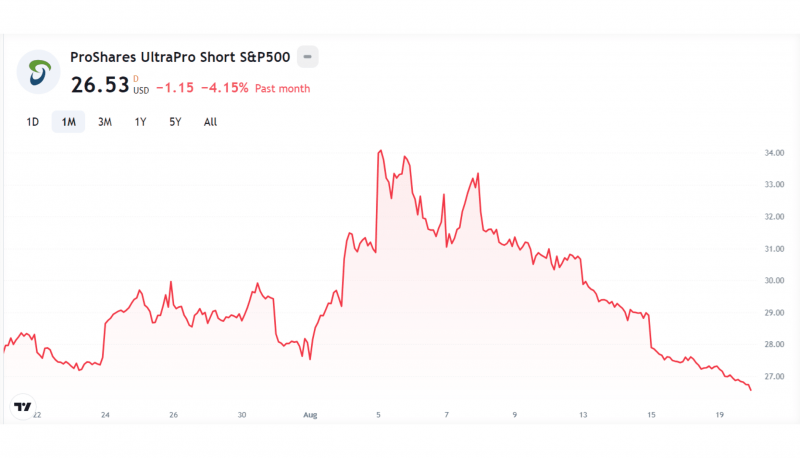
ProShares UltraPro Short S&P500 (SPXU)
This is a 3x leveraged short-term inverse ETF tracking the inverse price of the S&P500 index. It is described as a very aggressive fund because it offers three-time short selling of the best-performing stocks in US markets, where traders earn on S&P500 market declines.
This ETF peaked in the first week of August 2024, reaching $34 before dropping under $27 in the following weeks. However, as stock exchanges continue to move unexpectedly, this inverse ETF can provide lucrative returns.
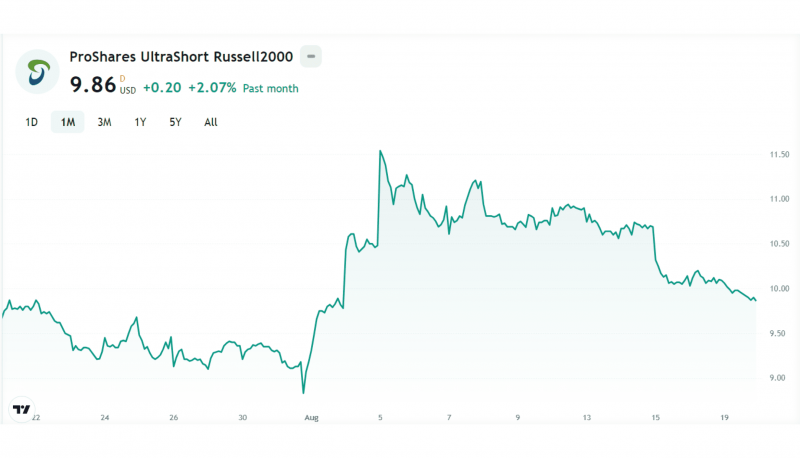
ProShares UltraShort Russell2000 (TWM)
The Russell2000 index tracks the smallest 2,000 small US public firms in the original Russel 3000 index in a market cap-weighted approach. The ProShares UltraShort Russell2000 includes small companies in different industries and is suitable for day trading strategies.
It is a 2x leveraged inverse ETF, offering 200% on daily market declines of the underlying index. The ProShares UltraShort Russell2000 was one of the best inverse ETFs in August 2024, reaching $11 in the first five days, or 30% in a few days.
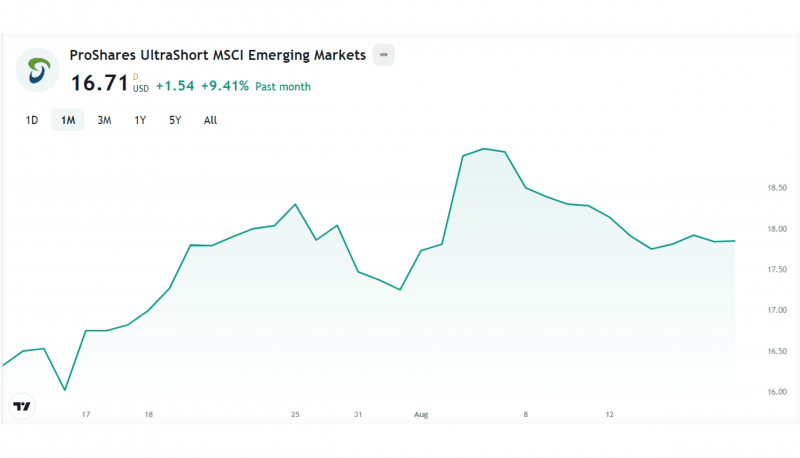
ProShares UltraShort MSCI Emerging Markets (EEV)
This ETF tracks the performance of stocks in emerging markets, such as Brazil, China, Egypt, Kuwait, Mexico, Qatar, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, and the United Arab Emirates. It offers 200% leverage on daily market declines of 1,400+ mid and large-cap stocks in 24 nations.
The ProShares UltraShort MSCI Emerging Markets inverse leveraged ETFs is a short-term security suitable for day trading, allowing investors to capitalise on daily unpredictability and declines.
This inverse exchange fund is performing significantly better in August 2024 than in the few previous months, reaching $20 per share for the first time in four months.
Inverse ETFs vs Short Selling: What’s The Difference?
Both trading strategies serve the same purpose. However, inverse ETFs are easier to comprehend as they simply track the opposite price performance of the current market value. Inverse means showing negative price action when the actual market moves positively and positive price action when the actual market moves negatively.
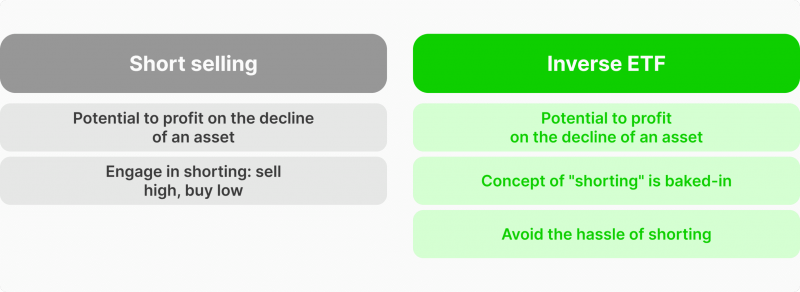
This approach is a day-to-day trading method, and it is easier to open and close positions, making this investment strategy suitable for day traders.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
On the other hand, short-selling, in essence, is a more complex concept to understand. It requires borrowing from shareholders and selling the underlying security, then re-buying them again when prices drop and returning them to the original owner. In this transaction, the short-seller earns from the price difference between borrowing and returning.
However, this three-way operation may entail premium fees and counterparty risks. The one benefit to future short selling is that investors can keep the position for more than one day.
Conclusion
Inverse ETFs are financial instruments that track the market performance of one or multiple equities and reflect the opposite value in the fund value. For example, Inverse Bitcoin ETFs show a decline when the coin price increases and the ETF value grows when the price drops.
Investing in inverse indices is similar to short selling. However, it is less complex for new traders and is mainly designed for day traders and short-term investment strategies.