The Essential Role of a Crypto Market Maker in Market Liquidity
Articles


Liquidity is the force that keeps the whole financial system running smoothly. The proficiency to buy/sell assets quickly and efficiently is crucial for traders, investors, and the market as a whole. In this regard, market makers are the unsung heroes, ensuring that there is always a buyer for every seller and vice versa.
The function of crypto market makers is crucial in a world where digital assets are traded on a permanent basis. In this in-depth tutorial, you’ll learn about the significance of a crypto market maker, how this concept contributes to market liquidity and more.
Key Takeaways
- Market makers play a crucial role in maintaining liquidity in financial markets. They provide a continuous presence, reducing bid-ask spreads and enhancing market efficiency.
- Market makers facilitate liquidity by continuously offering buy and sell orders. Their use of advanced technology narrows bid-ask spreads, benefiting traders by allowing transactions at prices closer to the current market value.
- Market makers are essential for crypto exchanges, enhancing liquidity, stabilising prices, and promoting efficient trading.
- Various entities, including individuals, professional firms, exchanges, high-frequency traders, arbitrageurs, and institutional investors, act as market makers in the cryptocurrency space.
Market Makers: The Guardians of Liquidity
Market makers are specialised entities in the financial world tasked with the responsibility of ensuring sufficient liquidity and efficient trading volume. They stand ready to buy or sell assets at any given time under all market conditions. These liquidity providers can be individuals, financial institutions, or automated systems, all with a common goal: to facilitate the buying and selling of assets.

Market makers create a two-way market by quoting both a buying (bid) and selling (ask) price for an asset. This bid-ask spread represents their profit margin, but it also serves to narrow the market price difference between buyers and sellers. In doing so, market makers reduce the cost and risk for traders, making it easier for them to execute orders.
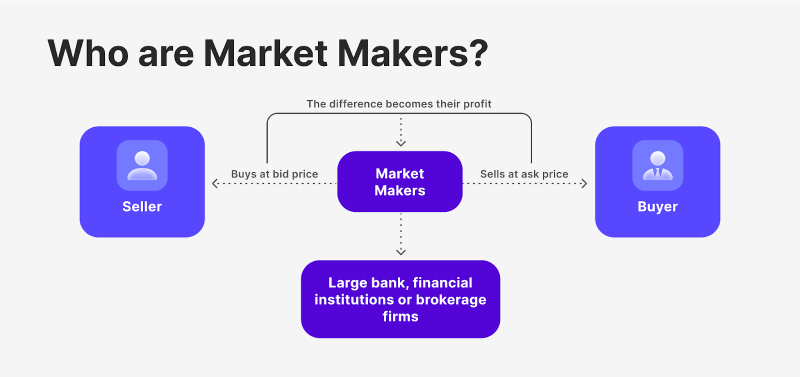
One key strategy employed by market makers is managing their order book. They maintain a balanced inventory of assets to meet the demands of buyers and sellers, minimising the impact of large buy or sell orders on the market. Additionally, market makers often utilise sophisticated algorithms and trading systems to automate their operations and respond swiftly to changing market dynamics.
In essence, market makers act as intermediaries that enhance market efficiency. Their ability to provide liquidity and narrow bid-ask spreads not only benefits individual traders but also fosters a more robust and resilient financial ecosystem. As they facilitate trading, market makers contribute to the overall stability of financial markets, allowing participants to execute transactions more efficiently and with reduced transaction costs.
What Do Market Maker Services Involve?
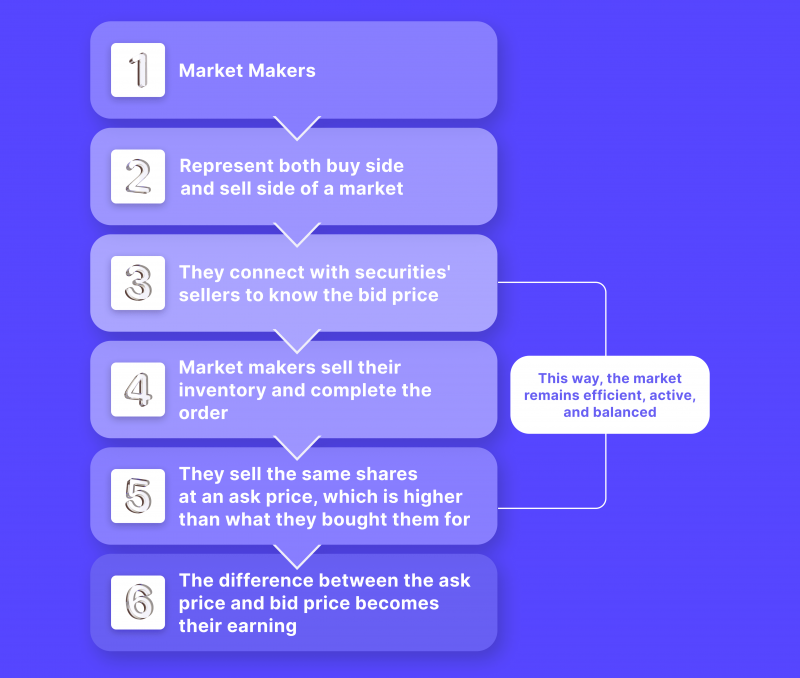
Market maker services encompass a range of activities:
- Price Continuity: Market makers ensure that asset prices remain consistent, lowering sudden fluctuations.
- Trade Continuity: They maintain a continuous presence in the market, facilitating real-time trading for institutions and traders.
- Flexibility and Coverage: Market makers offer flexibility in settlement options and a wide range of trading instruments.
- Intermediation: They connect buyers & sellers, identify opening prices, provide active quotations, and ensure market balance.
How Does Market Making Work in Crypto?
Cryptocurrency markets have gained tremendous popularity in recent years, and market makers have a significant presence in this space. Market making in crypto involves the same fundamental principles as traditional financial markets but with a few unique characteristics.
Crypto market making involves providing liquidity to digital asset markets by continuously offering buy and sell orders. This liquidity is essential for traders who want to enter or exit positions quickly and efficiently.
Crypto market makers reduce the bid-ask spread, ensuring that the difference between the buying and selling prices is minimal. They use advanced technology and algorithmic strategies to achieve their goal. The narrow spread is beneficial to traders because it allows them to transact at prices that are closer to the current market value of the asset.
The Need for Market Makers in Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Crypto exchanges are digital marketplaces where users trade various digital assets. These platforms are in need of market makers for several advantages:
Liquidity Management – Crypto market maker enhances the liquidity of digital coins, making it more effortless for traders to enter and exit positions. This liquidity ensures that trading pairs have sufficient depth.
Price Stability – Crypto market maker helps stabilise prices by narrowing the bid-ask spread. This reduces volatility and creates a more orderly market.
Efficient Trading – With crypto market makers in place, traders can execute their orders quickly and at competitive prices. This efficiency attracts more participants to the crypto markets.
Risk Mitigation – Advanced crypto market maker manages risk by using advanced trading strategies and technology. This risk management benefits the exchange and its users.
Types of Crypto Market Makers
In the context of the cryptocurrency market, there are several types of market makers:
- Individual Traders/Investors – Individuals who actively participate in cryptocurrency markets by placing limit orders on exchanges, aiming to profit from the bid-ask spread.
- Professional Market-Making Firms – Specialised firms that focus on market-making across various financial instruments, including cryptocurrencies. These firms often employ advanced trading algorithms and technology to automate their market-making activities.
- Crypto Exchanges – Some cryptocurrency exchanges act as market makers themselves. They provide liquidity by matching buy and sell orders on their platforms. In some cases, exchanges may use their own funds to facilitate trades and maintain liquidity.
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT) Firms – HFT firms use advanced algorithms and high-speed trading strategies to execute a large number of orders within fractions of a second. These firms often engage in market-making to profit from small price discrepancies.
- Arbitrageurs – Traders who engage in arbitrage by exploiting price differences between different exchanges or trading pairs. Arbitrageurs contribute to market efficiency by reducing price disparities across platforms.
- Algorithmic Market Makers – Traders and firms that employ sophisticated algorithmic strategies to make markets. These algorithms are designed to continuously adjust buy and sell prices based on market conditions, order book dynamics, and other relevant factors.
- Token Issuers/Projects – In the decentralised finance space, some projects and token issuers may act as market makers for their own tokens. They might provide liquidity to decentralised exchanges to ensure a liquid market for their assets.
- Institutional Investors – Traditional financial institutions, such as hedge funds and proprietary trading firms, may participate as market makers in the cryptocurrency space. Institutional market makers can bring substantial liquidity to the market.
- Crypto Funds – Investment funds dedicated to cryptocurrencies may engage in market-making as part of their trading strategy. These funds often have the resources and expertise to actively provide liquidity in the market.
Separately should be mentioned market maker brokers, intermediaries that connect traders with market makers. These brokers serve as a bridge between individual traders and the liquidity provided by market makers.
Market maker brokers play a crucial role in ensuring traders have access to liquid markets, especially in the crypto space. They offer trading platforms and access to various digital assets, making it easier for traders to execute their strategies.
How Do Market Makers Make Money?

Market makers employ a variety of trading strategies to provide liquidity and make profits. Some of these strategies include statistical arbitrage, order flow trading, and market-neutral strategies. These strategies aim to capitalise on market inefficiencies and price differentials.
Efficient trading strategies not only benefit market makers but also contribute to the overall health of the market by reducing volatility and providing market price stability.
Apart from this strategy, the market maker’s profit comes through various means:
- Exchange Commissions – Institutional market makers often receive commissions from exchanges for each completed transaction. This can be a significant source of revenue.
- Turnover Earnings and Bid-Ask Spread – Market makers profit from the difference between the buying and selling costs of assets. They can handle a high volume of orders, making this spread lucrative.
- Opening Their Own Trading Positions – Market makers use their knowledge of market data and analysis to open profitable positions. This unique insight gives them an edge in the market.
Are Market Makers Manipulating?
Market makers are perceived as manipulative by some because of certain practices they engage in that may be interpreted as attempting to influence or manipulate market prices. It’s essential to note that not all market makers engage in manipulative activities, and their role is generally crucial for market liquidity and efficiency. However, some factors contribute to the perception of market makers as manipulative.
Bid-Ask Spread Manipulation
Market makers profit from the bid-ask spread, the difference between the buying (bid) and selling (ask) prices. Some critics argue that market makers widen spreads intentionally to maximise their profits. This can be perceived as manipulating the prices, especially in less liquid markets.
Quote Stuffing
Market makers may engage in quote stuffing, a practice where they flood the market with a large number of orders that they have no intention of executing. This can create a false impression of market demand or supply, influencing other traders’ decisions and potentially manipulating prices.
Front-Running
Front-running involves a market maker executing orders on a security for its own account while taking advantage of advanced knowledge of pending orders from its customers. This can create a perception of unfair advantages and manipulation, as market makers may exploit their position for personal gain.
Information Asymmetry
Market makers often have access to more information than individual retail traders. This information advantage can be perceived as manipulative, especially if market makers use proprietary information to make trading decisions ahead of the broader market.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
Some market makers engage in high-frequency trading, using complex algorithms to execute a large number of orders at extremely high speeds. Critics argue that this can create market instability and may be perceived as manipulative, particularly during periods of market stress.
Lack of Transparency
The opaque nature of some market-making activities, such as the use of dark pools and over-the-counter (OTC) markets, can contribute to the perception of manipulation. Lack of transparency may lead to suspicions about the fairness of market maker practices.
It’s important to realise that market makers operate within regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines. Their primary function is to provide liquidity by consistently offering buying and selling prices, which contributes to stable markets. However, it’s crucial for regulators to monitor market maker activities to prevent any abuse or manipulative behaviour that could harm the market.
Final Remarks
Crypto market makers are the driving force behind the efficiency and liquidity of digital asset markets. They ensure the smooth flow of transactions and play a vital role in sustaining market stability. Their functions, advantages, and disadvantages are crucial for realising how financial markets operate in the digital age.
FAQ
What is the best crypto pair for market making?
The Bitcoin and Tether pair (BTC/USDT) remains one of the most popular choices for both inexperienced and advanced traders due to the stability of USDT and the prominence of Bitcoin.
What do market makers do?
A market maker participates in the market at all times, buying securities from sellers and selling securities to buyers. Market makers provide liquidity, which ensures investors can trade quickly and at a fair buying and selling price in all conditions.
How do market makers make money?
Market makers employ various strategies such as statistical arbitrage, order flow trading, and market-neutral strategies. They also earn commissions from exchanges and profit from bid-ask spreads. Additionally, they can open profitable trading positions.














