Understanding Grid Trading: Purpose, Pros & Cons

Electronic trading, in all its complexity and comprehensiveness, is a complex process of interacting with financial markets to make profits with the help of different trading strategies, each with its advantages, disadvantages and peculiarities.
At the same time, among a large number of such strategies, the so-called grid strategy is particularly popular and widely used in highly volatile markets.
This article will explain to you what grid trading is, why it is so popular, what advantages and disadvantages it has, and what the main types are divided into.
Key Takeaways
- Grid trading involves strategically placing buy and sell orders around a central price point at predefined intervals.
- For trend trading, buy orders are placed at intervals above the central price, while sell orders are positioned below it, allowing profits to be captured as the market moves directionally.
- For range trading, buy orders are set at intervals below the central price, and sell orders are placed above it, enabling traders to profit from price fluctuations within a specific range.
What is Grid Trading?
Grid trading is a systematic strategy that begins with issuing buy and sell orders at regular price periods, creating a “grid” of trades. It is designed to take advantage of market volatility by generating profits from price fluctuations, regardless of the market’s overall direction. The strategy is widely used in markets such as Forex, cryptocurrencies, and equities.
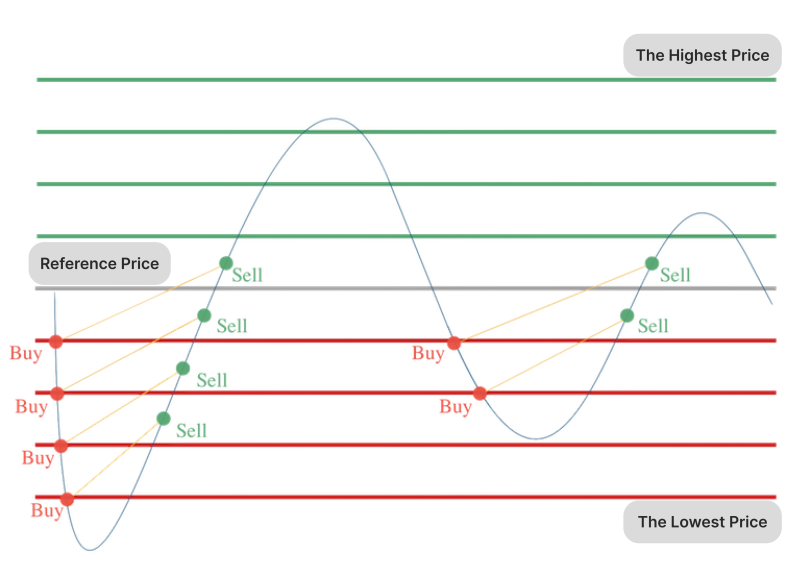
Grid trading establishes a range within which an asset is expected to move, divided into multiple price levels or intervals. Buy orders are placed at levels below the current market price, while sell orders are placed above it.
As the price fluctuates, orders are executed when the market hits these predefined levels, capturing profits from both upward and downward movements.
For example, in a grid with $10 intervals, a buy order might trigger at $50, and the corresponding sell order would activate at $60, capturing a $10 profit.
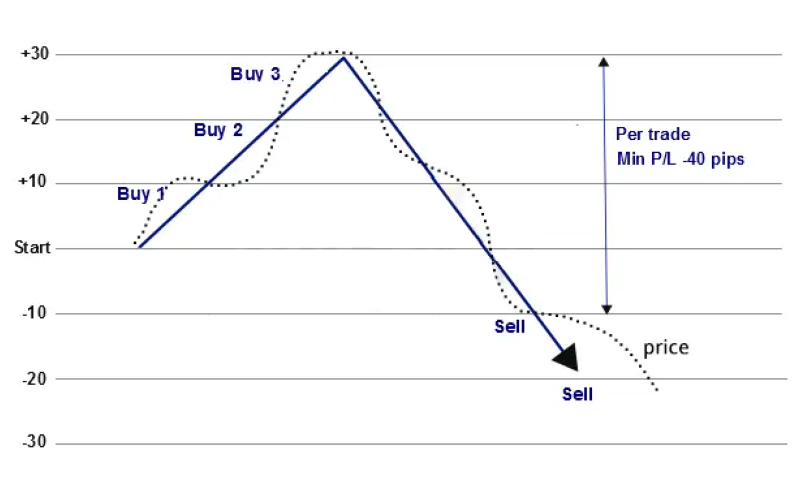
This approach thrives on market volatility, where prices frequently oscillate within a specific range. This method allows traders to benefit from price swings without needing to predict the market’s direction. Unlike trend-following strategies, grid trading focuses on price patterns and levels, making it ideal for range-bound markets.
There are two main approaches to setting up a grid: the arithmetic grid and the geometric grid.
Why Grid Trading is Popular?
Grid trading’s appeal lies in its simplicity and versatility. Unlike strategies requiring in-depth market analysis or complex indicators, grid trading relies on a straightforward setup of price levels and intervals. This makes it an attractive option for traders seeking a systematic approach that minimises emotional decision-making.
Furthermore, its adaptability to various market conditions, from range-bound to trending markets, broadens its usability across different asset classes like Forex, cryptocurrencies, and stocks.
Additionally, grid trading provides a degree of risk management, as each trade is executed at predefined levels, ensuring that positions are systematically opened and closed without excessive exposure. This disciplined approach can help traders mitigate losses while capturing consistent profits from market volatility.
Types of Grid Trading Strategies
Grid trading strategies are diverse and can be tailored to different market conditions and trader preferences. Each type serves a specific purpose, allowing traders to align their approach with the prevailing market environment and their objectives.

Neutral Grid Trading
Neutral grid trading is the most common type of grid strategy. It operates on the assumption that the market will oscillate within a predefined range without a strong directional trend.
This strategy places buy and sell orders above and below a reference price, aiming to profit from the continuous fluctuations within the grid. Neutral grid trading is suitable for range-bound markets where prices move sideways with consistent volatility.
Bullish Grid Trading
Bullish grid trading is designed for upward-trending markets. It focuses on placing buy orders at lower levels to accumulate the asset and sell orders at higher levels to lock in profits as prices rise. This strategy works under the assumption that the market will generally move upwards, making it ideal for scenarios where a sustained uptrend is expected.
Bearish Grid Trading
Bearish grid trading is tailored for downward-trending markets. It places sell orders at higher levels to capitalise on price drops and buy orders at lower levels to reduce losses when the market reverses. This strategy is used when traders anticipate a prolonged downtrend and want to profit from falling prices while managing their positions effectively.
Dynamic Grid Trading
Dynamic grid trading adjusts the grid range and intervals in real time based on market conditions. Unlike static grids, which remain fixed, dynamic grids respond to significant market movements or changes in volatility.
This strategy allows traders to adapt their grids to current market behaviour, ensuring continued relevance and profitability even as conditions evolve.
Inverse Grid Trading
Inverse grid trading operates on the assumption that the market will reverse after hitting extreme price levels. It places buy orders above the current price and sell orders below it, contrary to the traditional grid setup.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
This strategy aims to capitalise on reversals rather than trends, making it suitable for markets with frequent corrections or false breakouts.
Adaptive Grid Trading
Adaptive grid trading combines the principles of static and dynamic grids. It allows traders to adjust grid parameters manually or automatically in response to market conditions. By incorporating technical indicators or market signals, adaptive grids aim to optimise trade execution and improve profitability. This strategy is versatile and can be applied across a variety of market environments.
High-Frequency Grid Trading
High-frequency grid trading focuses on capturing small price movements by using narrow intervals between orders. This strategy is best suited for highly liquid markets with frequent price changes.
It generates a large number of trades, relying on volume to accumulate profits over time. High-frequency grid trading often requires automation due to its speed and intensity.
Advantages of Grid Trading Strategy
Grid trading is a popular strategy due to its systematic and straightforward approach to capturing profits in volatile markets. Below are the key advantages of using grid trading:
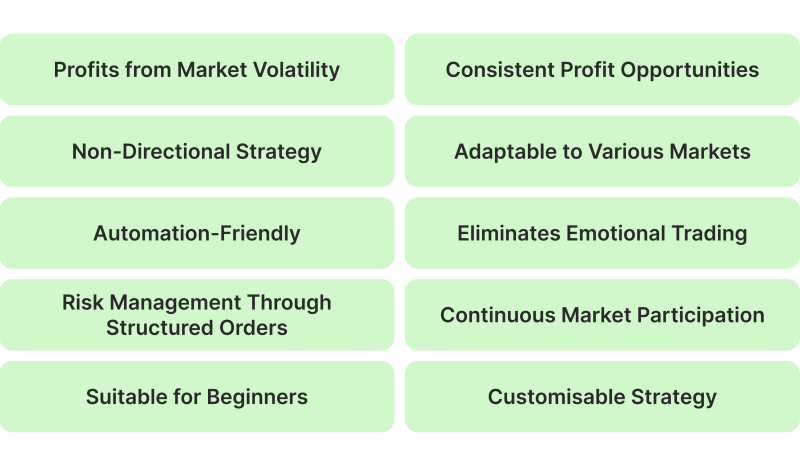
Profits from Market Volatility
Grid trading thrives in markets where prices fluctuate frequently within a range. The strategy captures small price movements multiple times by placing buy and sell orders at regular intervals. This approach works particularly well in volatile markets, as each price swing presents a new opportunity for profit.
For example, if the price of an asset oscillates between $100 and $120, grid trading can generate consistent profits by buying at $100 and selling at $110 or $120 and repeating this cycle as long as the price stays within the range.
Non-Directional Strategy
Unlike trend-following strategies, grid trading does not require traders to predict whether the market will increase or decrease. It focuses solely on exploiting price fluctuations within a set range. This makes it especially effective in range-bound markets where prices move sideways.
Even during uncertain or choppy market conditions, grid trading can still generate profits by capturing small movements in either direction, eliminating the need for complex market forecasts.
Automation-Friendly
Grid trading is particularly well-suited for automation, as it relies on systematically executing predefined orders. Trading bots or algorithms can be programmed to handle all aspects of the strategy, from placing buy and sell orders to adjusting grid parameters based on market conditions.
Automation ensures consistent execution, reduces human error, and allows traders to take advantage of opportunities 24/7. This is especially useful for markets like cryptocurrencies, which operate continuously without closing hours.
Risk Management Through Structured Orders
Grid trading inherently incorporates a level of risk management by structuring buy and sell orders at predefined levels. Traders can specify a range within which trades occur, ensuring they do not overextend their positions.
For example, if a trader sets a grid between $90 and $110, they limit their exposure to price movements outside this range. Additionally, predefined exit points (take-profit and stop-loss levels) ensure trades are closed systematically, reducing the risk of significant losses during unexpected market movements.
Suitable for Beginners
The simplicity of grid trading makes it an attractive option for novice traders. Unlike strategies that require extensive knowledge of technical analysis, indicators, or market trends, grid trading focuses on straightforward price levels and intervals.
Beginners can use trading bots or user-friendly platforms to set up their grids, allowing them to participate in the market without needing advanced skills. Many platforms also provide tutorials or demo accounts to help new traders understand how the strategy works.
Consistent Profit Opportunities
Grid trading generates profits from small price movements, which can accumulate over time to create significant returns. This consistency is particularly advantageous in highly liquid markets like Forex or cryptocurrencies, where price fluctuations occur frequently.
For example, in a volatile market, even slight price changes of 1% or 2% can be captured multiple times within a day, leading to steady gains. Over time, these small profits compound, providing a stable income stream for traders.
Adaptable to Various Markets
One of the strengths of grid trading is its adaptability. It can be applied to different asset classes, including Forex, cryptocurrencies, stocks, and commodities. Each market has unique characteristics, such as volatility levels and trading hours, but grid trading can be customised to suit these conditions.
For instance, smaller grid intervals may be used in Forex trading, where currency pairs often fluctuate within narrow ranges. In more volatile cryptocurrency markets, wider intervals may be more effective.
Eliminates Emotional Trading
Grid trading relies on predefined rules and parameters, removing the emotional aspect of trading decisions. Emotional trading, driven by fear or greed, often leads to impulsive decisions that result in losses.
By sticking to a systematic approach, grid trading ensures that trades are executed based on logic and strategy, not emotions. For example, traders won’t be tempted to chase a trend or panic during a price drop, as the system operates independently of human bias.
Continuous Market Participation
Grid trading ensures that traders remain active in the market without needing to monitor price movements constantly. This is particularly beneficial in markets that operate 24/7, such as cryptocurrencies. Once the grid is set up, the system automatically places and executes orders as the market fluctuates.
For example, suppose a trader sets a grid in a cryptocurrency pair. In that case, the bot will continue trading even while the trader is asleep, ensuring no opportunity is missed due to time constraints.
Customisable Strategy
Grid trading offers significant flexibility, allowing traders to customise parameters based on their preferences and market conditions. Traders can define:
Grid range: The upper and lower price limits for the strategy.
Price intervals: The distance between each buy and sell order.
Order size: The amount invested in each trade.
For example, a trader expecting high volatility might set wider intervals and larger order sizes. In comparison, a trader in a stable market might use narrower intervals to capture frequent, small movements. This adaptability ensures the strategy can be tailored to individual goals and risk tolerance.
Disadvantages of Grid Trading Strategy
Despite its systematic and structured approach, grid trading has several disadvantages that traders must consider before implementing it.
One of the main drawbacks is its reliance on market volatility. Grid trading performs best when markets experience frequent price fluctuations within a defined range.
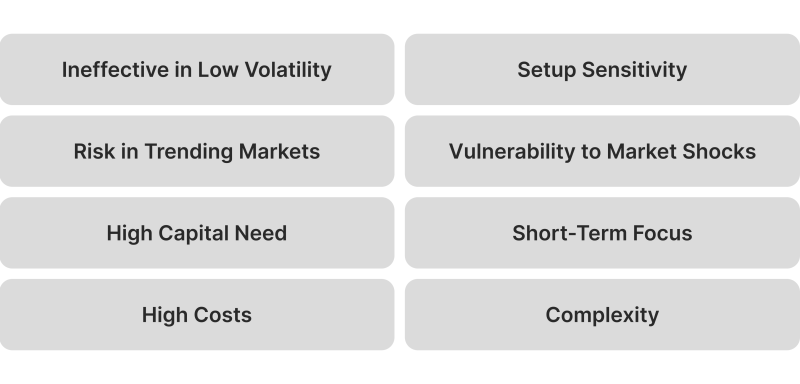
Another challenge with grid trading is its vulnerability to trending markets. The strategy is designed to capture profits from price movements within a range, making it less effective when markets exhibit directional solid trends.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
In such cases, traders may encounter significant losses if their grid parameters do not account for breakouts or prolonged trends, as the system may continue placing orders that go against the prevailing market direction.
Grid trading also requires substantial capital to maintain multiple open positions simultaneously. As price fluctuations activate buy and sell orders, the demand for capital increases, particularly in volatile markets.
Traders must ensure adequate funds to sustain their grid without over-leveraging their accounts. This high capital requirement can limit the accessibility of the strategy, especially for those with smaller trading balances.
The high-frequency nature of grid trading can result in increased transaction costs. Every executed trade incurs fees, spreads, and potential slippage, which can significantly reduce overall profitability.
For traders operating in markets with narrow price intervals or frequent trades, these costs can accumulate rapidly, diminishing the returns from the strategy.
Additionally, the success of grid trading depends heavily on accurate parameter settings. Poorly configured grids, such as those with intervals that are too wide or too narrow, can lead to inefficiencies.
Traders may miss profitable opportunities or execute too many trades with minimal gains, undermining the strategy’s effectiveness. Regular adjustments and monitoring are often required to ensure the grid remains aligned with current market conditions.
Final Remarks
Grid trading is a versatile and systematic strategy that allows traders to capitalise on market volatility by setting buy and sell orders at predefined intervals. Its appeal lies in its simplicity, adaptability, and potential to generate consistent profits in various market scenarios.
Whether in Forex, cryptocurrencies, or equities, grid trading provides a structured approach that minimises emotional decision-making and enhances trading efficiency.
However, like any trading strategy, grid trading comes with its challenges. Its reliance on market volatility, susceptibility to trending markets, and high capital requirements highlight the importance of careful planning, precise parameter settings, and robust risk management.
While automation can mitigate some of these challenges, traders must continuously monitor and adapt their strategy to meet changing market conditions.
FAQ
Why is grid trading popular?
Grid trading is popular because of its simplicity, automation potential, and adaptability across different markets.
Can grid trading be automated?
Yes, grid bots trading is highly compatible with automation. Trading bots can execute orders based on predefined grid parameters, reducing manual effort, minimising human error, and enabling continuous trading in 24/7 markets like cryptocurrencies.
What markets are suitable for grid trading?
Grid trading is commonly used in Forex, cryptocurrencies, and equities. It is most effective in volatile markets with frequent price movements and range-bound conditions.







