Choosing Regulation for Forex Broker Licence: Pros & Cons

Thanks to the development of the Forex industry, there are numerous Forex brokers with distinct business models today, which, despite the differences, offer the same service — the opportunity for users to try their hand at trading currency pairs and other trading instruments. However, in order to successfully provide services to its clients, a broker must have an appropriate license for its activities, the obtaining of which, as a rule, begins with the choice of the regulatory body.
This article will explain what a Forex license is and why it is essential for the work of a broker. In addition, you will learn what kinds of Forex licenses exist and the main types of regulatory bodies which issue them. At the end of the article, we will tell you the basic steps to help you choose the suitable regulator to obtain a license.
Key Takeaways
- A Forex license is the most important document which entitles a broker to carry out his activities.
- Some of the most famous and reputable regulatory and licensing bodies for Forex activities are NFA, DFSA, FSC, CySEC and FSA.
- In order to choose the right Forex regulator and obtain a license, one must first decide on the jurisdiction in which the company is registered.
What is a Forex License and Why is It Essential For Forex Brokerage’s Operation?
In today’s international foreign exchange market, there are thousands of participants trading and exchanging different currencies. Forex brokers are one kind of market participant, as they act as intermediaries between private traders and investors and the interbank market in order to provide traders an ability to trade Forex. Despite the popularity of foreign exchange brokers, a brokerage company is only permitted to process transactions with a foreign exchange license. The broker should obtain a Forex license in order to avoid conflict with the regulatory authorities or loss of potential clients. Brokerage companies lacking a Forex license are avoided by traders since their operations are viewed as unlawful and unreliable. The regulatory authorities may also raise a number of questions regarding such a brokerage firm.

There is no one centralized regulatory authority in the Forex market. In other words, every international body or organization would have authority over every aspect of the activities of market participants. The foreign exchange market cannot have a regulator of this kind since the operations are independent, and the providers of these operations do not interact with each other. Nevertheless, some players in the Forex market still have their activities regulated, such as brokers. In addition to the local regulators for individual countries, there are also international regulators because the algorithms of control over brokers are constantly evolving and developing.
A license is a guarantee of the security of clients today, and all brokers strive to obtain one. Different financial commissions issue such licenses after checking the legitimacy of the broker’s activities, auditing it, and monitoring it after the license has been issued. The reason for requiring a license for an online Forex broker is to ensure the legality of its actions, as well as to confirm that it actually places trades for its traders on an interbank market and owes them obligations.
Main Categories of Jurisdictions for Forex Regulation
A Forex broker’s license is the most valuable and important document which guarantees its reliability and stability in matters related to the provision of brokerage services. However, despite the universality of this document, there are different categories of Forex regulation jurisdictions which have certain differences and features.
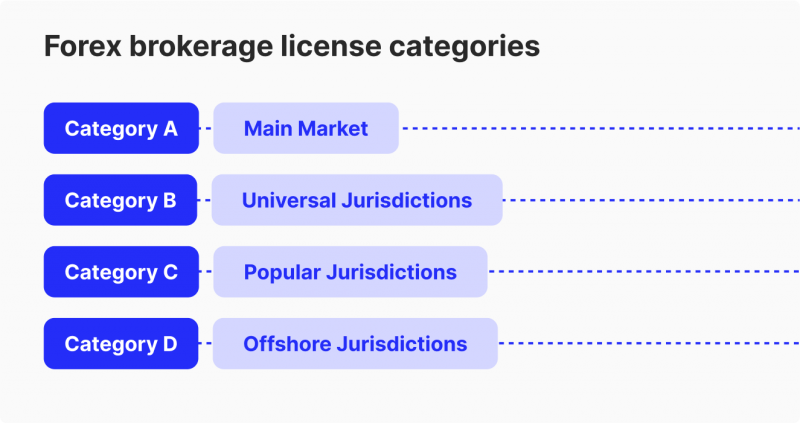
Category A (Main Market)
The United States of America and Switzerland are the two main jurisdictions for this category. In addition to granting access to the world’s largest foreign exchange market, the U.S. license for Forex brokerage is considered quite prestigious. To obtain these licenses, it is necessary to prove that a broker has $20 million in free access — not counting client funds. Forex brokers in Switzerland are subject to a complete monitoring system. Local licensees are considered reliable because they adhere to the terms of the contract unconditionally and are subject to significant warranty obligations.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Category B (Universal Jurisdictions)
An example of such a group would be Australia and Great Britain. Licensing requirements are less stringent in those countries and their licenses are considered as highly regarded and valued in the Forex niche. Forex brokers must have the qualifications and experience in addition to residing in the United Kingdom to get this type of license. The process of obtaining a Forex broker license in Australia includes setting up a brokerage and demonstrating the company is financially qualified to carry out the business.
Category C (Popular Jurisdictions)
This category includes such jurisdictions as Cyprus, New Zealand and Malta. Forex brokerage companies must have a physical office in order to obtain their license, but unlike the previous category, C licenses do not impose reporting burdens on regulated brokers. The main characteristic of firms licensed in these jurisdictions is their freedom to interact and cooperate in the European market.
Category D (Offshore Jurisdictions)
This category includes the British Virgin Islands, Vanuatu, Cayman Islands, and Belize. In these jurisdictions, foreign exchange market conditions are favorable, tax rates are moderate, and documentation requirements are minimal. Furthermore, Forex offshore licenses are not subject to preliminary audits. Licenses are issued based on the submission of documentation.
On the other hand, in order to obtain a license in this category, opening a bank account and connecting the payment system to the business is required and sometimes can be challenging. The country may introduce new regulations or restrictions under pressure, with stricter rules to get offshore licenses.
Main Types of Regulatory Authorities Licensing Forex Activities
Brokers’ activities are regulated by organizations known as regulators. Such organizations are responsible for preventing circumstances in which the broker cannot meet its obligations to traders. Regulatory agencies perform three actions concerning Forex brokers: checking for compliance with license issuance requirements, monitoring compliance with these requirements during the broker’s activities, and withdrawing the broker’s license if the broker fails to meet these requirements.

Following is a list of the most popular regulators whose activities constitute the legal framework for the Forex market.
FSC – Financial Services Commission
The regulator controls the operations of brokerage firms registered in Mauritius and encourages the growth, effectiveness, and transparency of financial institutions. The FSC is creating policies and guidelines to improve financial institutions’ transparency while looking into potential growth areas for the financial services industry. Companies that adhere to the standards for financial safety, security, and transparency are eligible for licenses from the FSC. The primary responsibility of the Commission is to take action to stop financial fraud in brokerage services and abuses in the investing industry.
NFA – National Futures Association
The Association is a freestanding financial watchdog organization whose mission is to defend American futures and commodity markets against financial institutions’ mistreatment. Any financial institution offering futures exchange and trading services in the US must be a member of the Association. The NFA assures equal rights and opportunities for all market participants, as well as investor protection. Depending on the degree of harm caused by the actions of financial institutions, the regulator has the authority to impose sanctions and penalties on those who violate business regulations.
FSA – Financial Services Authority
More than 70,000 financial institutions are regulated by the Financial Services Authority, all of which must comply with prudential risk management standards to mitigate the risk of harm to the industry and to individual investors. In the U.K., it serves as a central regulator for the financial services industry. Generally, the regulator is responsible for protecting consumers of financial services, ensuring the stability of the industry, as well as maintaining a healthy level of competition among service providers. Despite reporting to the U.K. Treasury, the FSA is an independent organization and does not receive government funding.
CySEC – Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission
One of the most important and significant regulators for Forex brokers and dealing centers that offer services on global financial markets is the CySEC, which is the state regulator in the Republic of Cyprus. The CySEC grants licenses for the financial markets in Europe and regulates the operations of brokerage and investment firms. As a full member of the EU, Cyprus grants the CySEC all the authority of the European Forex regulation together with favorable economic conditions for brokers. Obtaining a license from this regulator and registering in Cyprus are popular options for Forex brokers.
DFSA – Dubai Financial Services Authority
The DFSA operates under stringent guidelines. Obtaining a license in Dubai and doing business in the region is challenging. The regulator is keen to avoid mistakes and complications, so it is up to all applicants to follow the department’s guidelines appropriately. The Dubai regulator has real leverage over companies that operate in the region’s financial sector. In addition, the DFSA can supervise accountable companies and assist young projects in their start-up phase. With its broad mandate and access to effective regulatory tools, the DFSA is a highly regarded regulator and is the choice of the best Forex brokers.
Besides cryptocurrency, a Forex brokerage is the most popular form of making money on the financial markets that is regulated and licensed.
How to Choose a Regulatory Body for Obtaining a Forex License?
Registering a Forex brokerage firm is not an easy process that requires patience, time, and finances. The legal regulation of brokers obliges regulators to comply with all rules regarding comprehensive monitoring of their activities, both before and after obtaining a license. There are some important things to know in order to choose a reliable regulator. Let’s start with the most important:
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Establishment and Approval of a Brokerage Firm
In order to obtain a license and start providing services in the Forex market, it is necessary to carefully approach the issue of creating and approving a brokerage firm. Consider everything to the very last detail — from design to selecting a trading platform. In order for Forex traders to have an unforgettable trading experience, it is necessary to integrate the best of the Forex trading platforms, make a beautiful design and ensure the stability of the entire brokerage infrastructure. This will help your company to feel confident in the market full of competitors who strive to provide quality services.
Budgeting
As mentioned above, registering a Forex brokerage firm and obtaining a license for trading Forex tools is a very difficult task and requires large investments. In order to be able to purchase a license, you will have to pay a large amount of money, including the costs of reviewing documents by the regulator, accepting an application, paying various fees, registering a company in a special register, where all comprehensive data on the activities of the Forex company are entered, etc. Before considering obtaining a license, it will also be necessary to consider professional advice from lawyers, economists, and other professionals working in the field who are familiar with all aspects of the licensing process.
Choice of Jurisdiction for Forex Broker Registration
After you have planned the budget and analyzed all the essential aspects that contribute to the licensing of a Forex brokerage company, it’s time to decide on the jurisdiction where its office will be located. To date, there is no one-size-fits-all or best solution that industry professionals prefer. As already described above, four categories of jurisdictions make up the entire system for regulating and licensing Forex activities. Each includes a specific list of countries and regulators that can issue licenses to brokers whose offices are located in their territory. The choice of the place of registration of the company will primarily depend on what requirements will be imposed on it, not to mention the cost of services that will need to be paid in order to obtain all the documents and permits necessary for conducting Forex activities, including a license.
Conclusion
Choosing a regulator for licensing Forex can be a tedious and time-consuming exercise, but it is worth remembering that having such an important document as a license not only allows the Forex broker to provide its services legally, but also serves as a guarantee of the reliability of the company, which can provide a full range of necessary for Forex trading tools and services on the one hand and full support to their clients on the other.
FAQ
Why is forex broker regulation important when operating in the currency market?
Forex broker regulation ensures that a broker adheres to strict standards, protecting clients and guaranteeing transparency and accountability in every transaction.
How does forex broker regulation influence the choice of a regulatory authority?
Forex broker regulation sets the requirements and standards that vary by jurisdiction. Selecting the right regulator depends on meeting these criteria and maintaining a broker’s credibility and trustworthiness.
In what way does forex broker regulation enhance a broker’s reputation?
Strong forex broker regulation improves a broker’s public image, increases investor confidence, and allows easier expansion into various international markets.