What is a Limit Order? – Definition

As traders take the plunge into financial markets, they are armed with one goal: to obtain the ideal market entry price or better. Successful positioning in any given asset requires a strategic approach coupled with knowledge of certain rules. Yet not all trading methods offer such clarity – navigating these uncertain waters presents countless complexities for aspiring investors. The best option for entering the trade at your specified price is via a limit order. But what is a limit order, and how does it work?
This article will shed some light on what it is and how it works. In addition, we will conduct a comparative analysis between a limit order and a market order and determine the discrepancy between them.
What Is a Limit Order?
Limit orders (or limited orders) are orders to buy or sell a certain amount of an asset at a preselected price that is of interest to the trader or investor. When placing limited orders, it does not matter whether the trader trades stocks, Forex or cryptocurrency, the principles of such orders will be the same. A limit order is often used as a risk hedging method because it allows you to limit losses from an incorrect strategy in margin trading or futures trading.
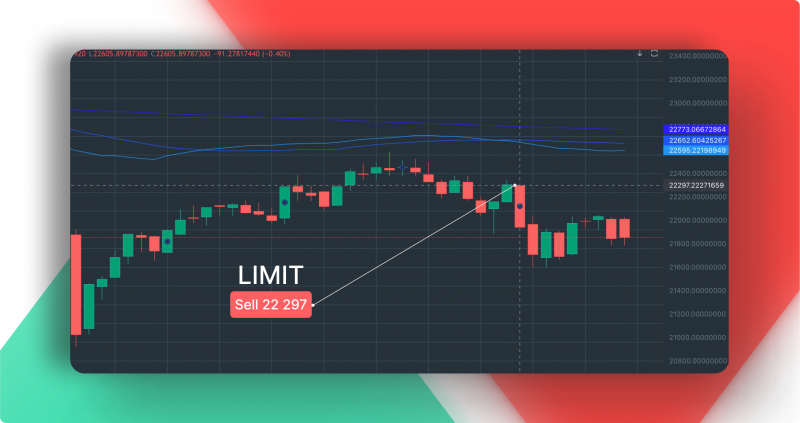
Regardless of which platform you are trading on, the interface with all the necessary trading tools is quite simple and allows you to quickly find all the trading modes and place market orders, limit orders, and any other kinds of orders.
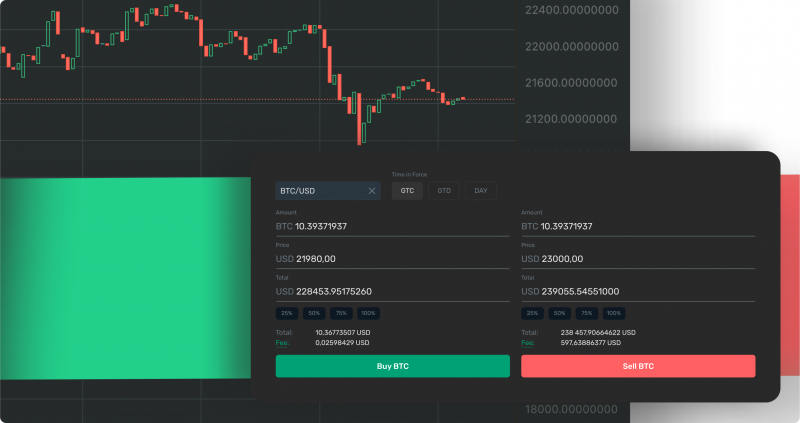
A simple pattern that describes the principle of a limit order follows from all of the above: traders who want to sell at a higher price place limited orders above the actual price in the hope that the price will rise in the future and reach the price set in the limited order. Traders who want to buy cheaper, on the other hand, wait for the price to fall further.
How Does It Work?
Clients are afforded increased control over market prices with limit buy and sell orders. These order types guarantee trades will be executed at the pre-determined, specified level or higher/lower respectively – affording clients greater certainty of their final trade value.

Limit buy orders provide investors with the opportunity to purchase securities at a predetermined price, guarding against undesirable market volatility. However, these types of trades carry risk; if prices don’t meet set requirements then investments may be left unfulfilled and any potential profits lost. This is the opposite of a market order, in which there are no price boundaries and the trade will be filled at whatever rate the market dictates.
A limit order is an effective tool for investors who are looking to take advantage of market conditions. By setting a predetermined price, they can buy or sell at the optimal rate – receiving no less than their desired limit when completing orders. This kind of flexibility provides increased control over stock purchases and sales while also providing greater stability in volatile markets.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
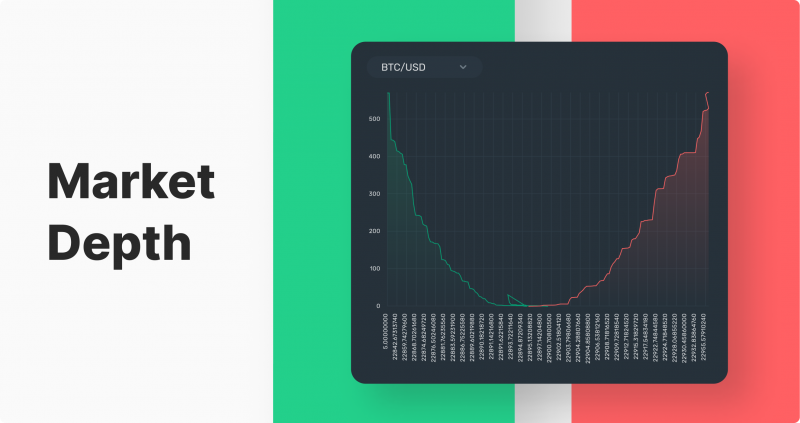
Speaking about orders with limit, it is necessary to mention that the main tool for their accumulation and visual display is the order book, which shows how many pending limited orders are at each price level for each individual financial asset. This helps to understand the mood of investors and traders and approximately predict the direction of the trend in the short term.
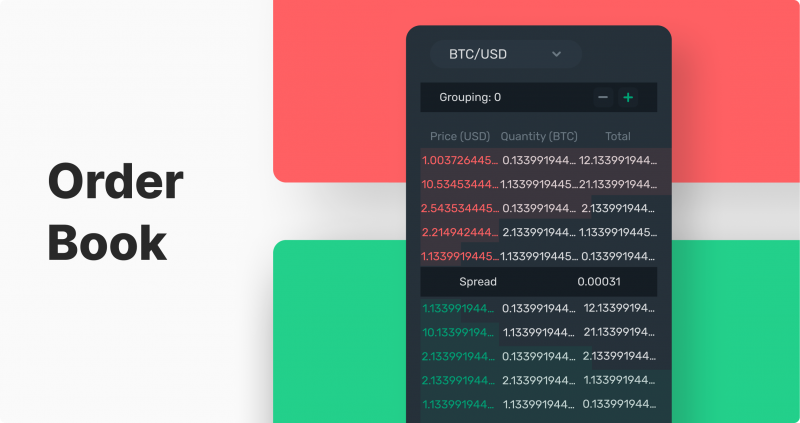
To maximize the effectiveness of buy and sell orders, traders should make use of a market depth chart. This form of visual representation highlights all open limited orders in an order book to provide insights into current trade trends. In doing so, savvy investors can adjust their strategies accordingly for optimal results.
Distinctions Between Limit and Market Orders
It’s time to explore the distinctions between a limit order and a market order. A limit order is placed with an expectation of being filled at no worse than its designated price, while a market order fills your buy or sell request directly according to current prices in the marketplace. Let us dive deeper into these two types of trades and compare their differences!
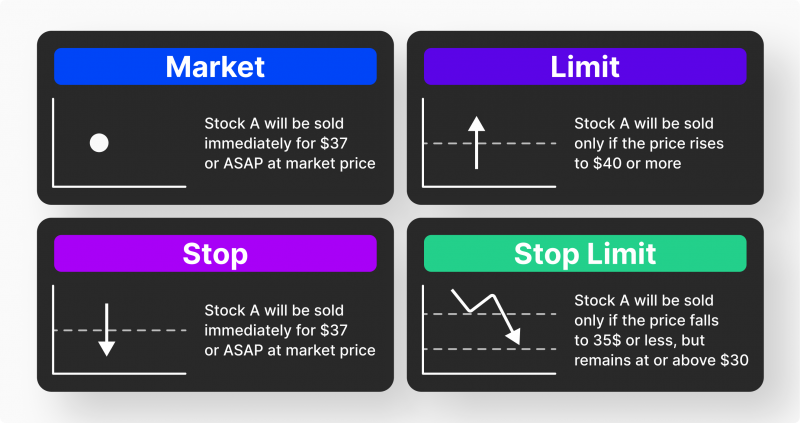
Market Order
Limit orders are like pre-packaged shopping lists and market orders a last minute dash to the checkout – both with their own distinct advantages. Limit orders provide certainty on price, while market orders offer faster execution when you don’t have time to spare!
For a trade to take place, two sides are always involved – the maker and the taker. When you choose to submit a market order, you accept whatever rate is given at that particular time. For example, if a trader enters a market purchase order, the exchange will attempt to fill it at the lowest ask price in the order book. When you submit a sell market order, your price is matched with the highest bid in the order book. This option is used when a position needs to be opened instantly. Instead of focusing on a better price, the emphasis is on the execution speed. The broker instantly executes an order of this kind by looking for a counter-limit order.
The way a market order is filled is predicated on it joining other counter orders and their reciprocal repayment. The closest order with limit price in the opposite direction is chosen from the open price window.
As a rule, orders based on market execution are used in highly liquid markets where it becomes clear that when buying an asset right now, the price can dramatically change the trajectory of its movement, thereby changing the trend. This type of order is also used among scalpers – professional traders who make a small profit by frequently repeating transactions over a certain period of time.
It should be remembered that market orders as well as limited orders are not exhaustive tools for trading. It is also worth paying attention to other varieties of orders, which in combination with the orders described above will allow the best results in the selected strategy.
If you wish to buy or sell an asset at the current market price, you may make a market order by entering the desired purchase or sale price in the corresponding field. This price is calculated from top to bottom in the order book (the stack). For instance, let’s imagine you want to sell 5 BTC with a market order. There are orders to buy 3 BTC at $10,000 and 4 BTC at $9,900, representing the best prices available. Your market order will partially execute the first order, giving you $30,000 for 3 BTC, and the second order, giving you $19,800 for 2 BTC. You will get $49,800 at an average price of $9,960 per BTC.
Limit Order
Despite the ease of operation and use of a limited order, there are several varieties of this tool, which helps to fill orders at preselected prices.
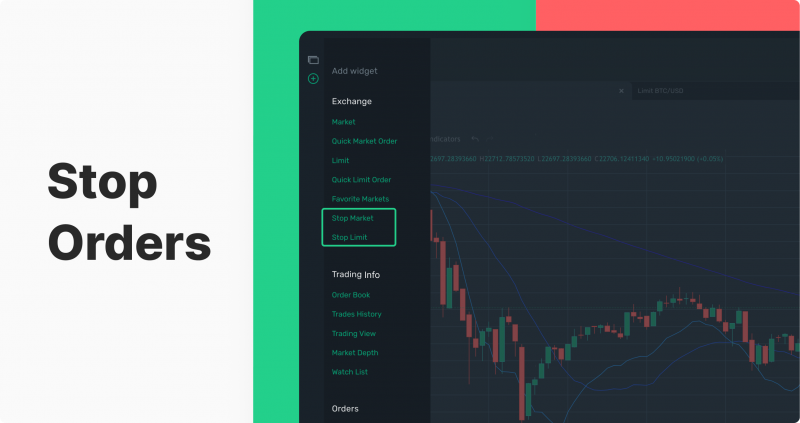
Stop Order
Stop orders are a helpful tool for investors to protect their portfolios from unpredictable market movements. When an asset reaches the customer-specified stop price, it automatically switches into either limit or market order status and is quickly filled at the best available price. This can be particularly beneficial in short term investments where swings may cause losses if left unchecked – allowing traders to ensure swings don’t go further than expected against them on any given day!
Stop-Limit
A stop-limit order is an instrument that allows you to send a limited order to buy or sell when the established stop-trigger price is reached or exceeded. Such an order consists of two main components: the stop price and the limit price. When the trade hits or above the stop price, the order becomes active and may be executed. It enters the market as a limited order (i.e., a buy or sell order at the established or more favorable price).
The major benefit of such an order is that it will not be completed at a price lower than the trader’s limit, but there is also the danger that the execution will not occur at all owing to this restriction.

Stop Market
A stop-market order is activated by the stop price, much as a stop-limit order. That being said, a market order will be placed once the stop price is achieved.

OCO
An OCO order offers the convenient option of placing two orders simultaneously – one limit price, and one stop-limit. With this interchangeable system, when either order is partially or completely filled, the second will be automatically canceled; allowing you to maintain control over your trading decisions without sacrificing efficiency.

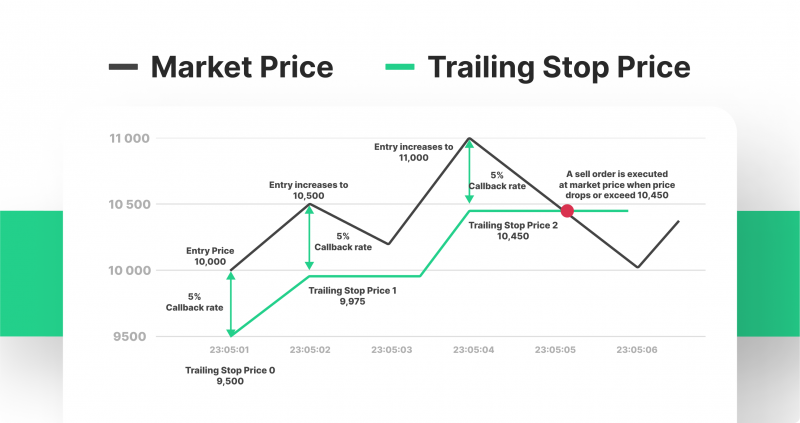
Trailing Stop
Trailing stop orders offer an innovative solution for traders who want to ride the market waves, yet are unable to continually monitor their trades. This powerful tool automatically adjusts itself based on preset parameters, continuously tracking your asset’s quote movement and capturing maximum profits from even the most dynamic of trends.
Conclusion
When trading on any market and with any instrument, a limit order is essential to hedge risks in volatile situations. This type of order gives you the ability to minimize losses if poor strategy decisions were made. Market orders enable entry at an advantageous time; however, it’s wise for traders to use both types depending on current conditions.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Recommended articles
Recent news