What is an Audit Trail? Meaning, Examples, Best Practices

In an age where data fidelity and security are top of mind, audit trails have become indispensable for organisations. Whether tracking financial operations, monitoring cybersecurity activities, or achieving regulatory conformity, audit trails provide a transparent, verifiable record of system activities. But what exactly is an audit trail, and why does it matter?
This guide dives deep into the definition of the audit trail, its importance across industries, and the best practices for implementation. By the end, you’ll also understand why businesses, governments, and healthcare institutions rely on audit tracking to deter fraud, keep laws in mind, and enhance operational efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Audit trails assure transparency and reliability by recording system activities, transactions, and modifications.
- Audit trails are fundamental for conformity with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and SOX, helping organisations avoid legal risks.
- Automation and AI enhance audit trail effectiveness, making tracking and analysis more accurate and efficient.
What is an Audit Trail?
An audit trail is a chronological record of operations, activities, or system changes that provide a step-by-step history of organisational or system actions. It is a transparent and verifiable log that captures details such as who performed an action, when it occurred, and what was changed or accessed.
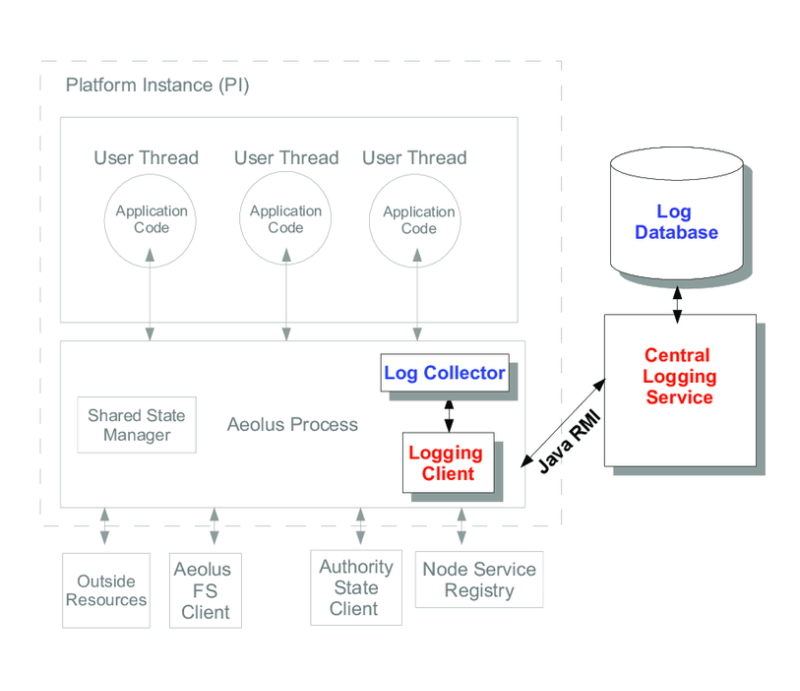
Audit trails are commonly used in financial systems, cybersecurity, healthcare, and legal surveillance to ensure accountability, detect anomalies, and facilitate investigations.
Audit trails play a crucial role in data integrity and security in today’s digital world. They help organisations track user activities, monitor modifications to records, and assure compatibility with industry directives such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), and SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act). Thus, by maintaining an accurate record of events, businesses can safeguard against fraud, unauthorised access, and data breaches.
A compelling audit trail should be tamper-proof, automated, and regularly reviewed. Organisations often implement logging mechanisms that store data in secure environments with restricted access. Plus, modern advancements such as blockchain technology and AI-driven audit analytics enhance how businesses track and analyse audit trails, making them more robust and resistant to manipulation.
Blockchain technology creates immutable audit trails, meaning once a record is entered, it cannot be altered or deleted — making it a game-changer for fraud prevention.
Main Types of Audit Trails
Audit trails play a pivotal role across various industries, acting as a digital footprint that promises accuracy, security, and enforcement. Depending on the sector, these records serve distinct purposes, from safeguarding financial integrity to protecting sensitive healthcare data and reinforcing cybersecurity.
Here are some of the most critical types of audit trails and their impact in different domains.

Financial Audit Trails
Financial audit trails track all organisational transactions, ensuring that payments, receipts, and journal entries are properly documented and comply with financial regulations such as GAAP, IFRS, and SOX. These records help detect fraud, errors, and unauthorised activities while providing transparency for audits and financial reporting.
Example:
When a company records an expense in its financial system, the audit trail logs details such as the employee who made the entry, the date and time of the transaction, and any modifications made. This ensures a clear and traceable financial process.
IT and Cybersecurity Audit Trails
In the digital landscape, IT audit trails monitor user activities, system modifications, and security events to prevent cyber threats and unauthorised access. These logs are crucial for detecting suspicious behaviour and ensuring conformance with ISO 27001, NIST, and GDPR. They also play a vital role in forensic investigations following cyberattacks.
Example:
If a network administrator logs into a company’s server and changes security settings, the audit trail records their user ID, the date and time of access, and details of the configuration change. Security teams can analyse the logs and take corrective action if unauthorised modifications occur.
Healthcare Audit Trails
Healthcare organisations rely on audit trails to protect patient records and comply with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR. These logs track who accessed patient data, when accessed, and what changes were made, ensuring confidentiality and preventing unauthorised access.
Example:
When a doctor reviews a patient’s electronic health record (EHR), the audit trail logs the doctor’s identity, the specific files accessed, and the time of access. Administrators can identify and mitigate security risks if unauthorised personnel attempt to view sensitive information.
Government and Legal Audit Trails
Government institutions and legal entities use audit trails to ensure transparency, accountability, and conformity with laws such as FISMA and FOIA. These records document legal transactions, approvals, and official processes, helping to detect fraud, corruption, and misuse of public funds.
When a government agency processes a permit application, the audit trail captures details about the officials who reviewed and approved the request, any changes made to the application, and time-stamped documentation of the entire process. This ensures accountability and prevents unauthorised alterations.
Manufacturing & Supply Chain Audit Trails
Audit trails in manufacturing and supply chains track product movement, quality control, and fulfillment with industry standards like ISO 9001 and FDA regulations. They help ensure the integrity of the production process, identify defects, and facilitate product recalls.
Example:
In the pharmaceutical industry, an audit trail records the source of raw materials, the manufacturing steps, quality control checks, and distribution details. If a defect is reported, businesses can trace it back to its origin using the audit log.
Cloud and Digital Audit Trails
With the rise of cloud computing, digital audit trails have become essential for monitoring online systems and securing virtual environments. These logs track all user activities in cloud applications, ensuring conformance with SOC 2, PCI DSS, and GDPR while detecting suspicious logins and unauthorised modifications.
Example:
If an employee accesses a cloud-based document management system and edits a contract, the audit trail captures their login details, IP address, and the changes made to the document, along with time-stamps. Administrators can review logs and restore the original file if unauthorised edits occur.
Blockchain-Based Audit Trails
Blockchain technology offers immutable audit trails that enhance transparency and security in financial transactions, supply chains, and digital records. Unlike traditional logs, blockchain-based audit trails store data in an unchangeable ledger, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation.
Example:
Blockchain records every transaction in supply chain management, including shipments, payments, and contract approvals. Because blockchain entries cannot be altered, businesses can verify the authenticity of records and ensure complete transparency in their operations.
Significant Advantages of Audit Trails
Audit trails are essential for ensuring transparency, accountability, and security across various industries. Systematically recording transactions, user activities, and system modifications help organisations maintain compliance, prevent fraud, and enhance operational efficiency.
Following are the details of the key benefits of audit trials.
Enhancing Security and Preventing Fraud
One of the primary advantages of audit trails is their ability to strengthen security by providing a clear and traceable record of activities. They help detect unauthorised access, suspicious behaviour, and fraudulent initiatives within an organisation.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
By maintaining detailed logs of user interactions and system modifications, audit trails act as a deterrent against malicious activities and ensure that any anomalies can be quickly identified and investigated. This is particularly crucial in financial institutions, healthcare systems, and IT environments, where data breaches and fraud pose significant risks.
Assuring Regulatory Compliance
Organisations are subject to various regulatory prerequisites, such as HIPAA (for healthcare), GDPR (for data privacy), SOX (for financial reporting), and PCI DSS (for payment security). Audit trails help businesses meet these governance rules by maintaining a verifiable record of transactions and activities.
Regulatory bodies often require organisations to demonstrate transparency and accountability, and a well-maintained audit trail simplifies this process. Compliance audits become more efficient, reducing the likelihood of legal penalties and financial losses due to non-compliance.
Fostering Accountability and Transparency
Audit trails create a structured record of actions, ensuring that individuals within an organisation are accountable for their activities. They track who accessed or modified data when the action occurred, and what changes were made.
This level of transparency discourages unethical behaviour and reinforces trust within an organisation. Employees and stakeholders are more likely to follow best practices when they know their actions are being logged, ultimately fostering a culture of responsibility and integrity.
Supporting Investigations and Forensic Analysis
When security breaches, financial discrepancies, or system failures occur, audit trails serve as a critical resource for forensic investigations. By analysing the recorded logs, organisations can reconstruct events leading up to an incident, identify the source of the problem, and take corrective action.
This is particularly important in cybersecurity, where identifying the origin of a breach can help prevent further attacks. Audit trails provide essential evidence of fraud, misconduct, or disputes in financial and legal contexts.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Audit trails contribute to process improvement by identifying inefficiencies and areas that require optimisation. Businesses can detect bottlenecks, redundant steps, and recurring workflow errors by reviewing system logs and transaction records.
This allows organisations to refine operations, improve accuracy, and enhance productivity. Beyond that, automated audit trails reduce the need for manual record-keeping, streamlining administrative processes and saving time for employees.
Protecting Data Integrity and Accuracy
Maintaining accurate and reliable data is crucial for any organisation, particularly in industries where data manipulation, such as finance, healthcare, and government operations, can have severe consequences.
Audit trails ensure that records remain unaltered and provide a backup history of modifications. If errors occur, organisations can trace back to the original data, restore previous versions, and correct mistakes without disputes. This level of integrity prevents tampering and unauthorised modifications, ensuring that all records remain trustworthy.
Simplifying Internal and External Audits
Internal and external audits require organisations to provide verifiable records of financial transactions, system changes, and operational activities.
Audit trails facilitate this process by maintaining structured logs that auditors can easily access and review. Instead of relying on fragmented documentation, organisations can present comprehensive, time-stamped records demonstrating their conformity with industry directives.
This reduces the complexity of audits, saves time, and enhances an organisation’s credibility with regulators, investors, and stakeholders.
Strengthening Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Audit trails play a vital role in risk management by ensuring organisations can recover from system failures, cyberattacks, or data corruption. By maintaining logs of all activities, businesses can restore lost or altered data and assure business continuity during an outage or security breach.
In cloud environments, audit trails help track system performance and prevent disruptions by identifying anomalies before they escalate into major issues.
Building Customer Trust and Reputation
Customers expect businesses to handle their data securely and ethically. Organisations implementing robust audit trails are committed to security, transparency, and regulatory compliance. This enhances customer confidence and strengthens brand reputation.
Whether in banking, e-commerce, or healthcare, businesses prioritising accountability and data protection are more likely to gain long-term customer loyalty and avoid reputational damage from security incidents or fraud scandals.
Best Practices for Implementing Audit Trails
For organisations striving to uphold transparency, strengthen security, and meet industry regulations, audit trails serve as an indispensable tool. However, their true value lies in how effectively they are implemented. When designed and maintained precisely, audit trails become more than just logs — they transform into a powerful safeguard against fraud, errors, and regulatory risks.
By following key best practices, businesses can ensure their audit trails are functional, efficient, reliable, and seamlessly integrated into their operations.
Automate the Logging Process
Manually maintaining audit trails can be inefficient, error-prone, and time-consuming. Organisations should implement automated logging systems that capture and store records in real-time without human intervention.
Automated systems ensure accuracy, consistency, and scalability, reducing the risk of missing critical events. Many enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, cybersecurity tools, and financial software come with built-in logging mechanisms that can be configured to track activities automatically.
Ensure Logs are Tamper-Proof and Secure
One of the most important aspects of an audit trail is its integrity. If logs can be altered or deleted, their reliability is compromised. Organisations should implement security measures such as encryption, access controls, and immutable storage to prevent tampering.
Using blockchain technology for certain critical logs can enhance security, as blockchain-based audit trails cannot be altered once recorded. Storing logs in read-only formats and maintaining backup copies in separate locations protect data from unauthorised modifications.
Implement Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
Not all employees should have access to audit trails, as unrestricted access can lead to security risks or data breaches. Organisations should implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to ensure only authorised personnel, such as compliance officers, auditors, and security administrators, can view or manage audit logs. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should also be required to access critical logs and enhance security.
Regularly Review and Audit the Logs
Collecting audit trails is insufficient; they need to be actively reviewed. Organisations should establish a routine for auditing logs to identify suspicious activities, policy violations, or potential compliance issues.
Automated tools powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning can help analyse vast amounts of data, detect anomalies, and generate alerts for unusual activities. Additionally, security teams should conduct periodic manual reviews to ensure thorough analysis.
Maintain Compliance with Regulatory Prerequisites
Different industries have specific regulations that govern audit trails. Organisations must ensure their audit trail policies align with industry regulations to avoid legal penalties.
Compliance checks should be performed regularly, and audit trails should be retained for the required duration set by regulatory bodies.
Store Logs Securely and Maintain Proper Retention Policies
Audit logs should be stored securely, and organisations must follow best practices regarding log retention periods. Retention policies should be determined based on industry regulations, business requirements, and risk factors.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Some laws require logs to be kept for several years, while others allow shorter retention periods. Secure storage solutions, such as cloud-based backups, encrypted databases, or offsite archival systems, should be used to protect logs from accidental loss, corruption, or cyberattacks.
Use Centralised Logging for Better Management
For organisations that operate multiple systems or platforms, centralised logging solutions can simplify the management of audit trails. A Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system can aggregate logs from different sources, making monitoring, analysing, and generating reports from audit data easier.
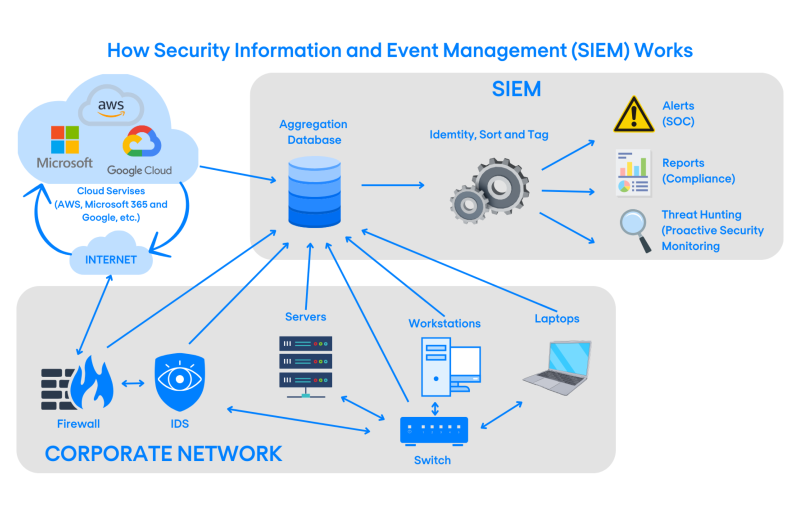
Centralised logging also improves visibility across the entire organisation, reducing the risk of oversight and ensuring that all security events are properly tracked.
Implement Real-Time Alerts and Incident Response Mechanisms
An effective audit trail system should include real-time alerts to identify and react to alleged security threats or policy violations. Organisations should configure their logging systems to trigger alerts when unusual activities occur, such as repeated failed login attempts, unauthorised data access, or system modifications outside normal working hours.
An incident response plan allows security teams to act swiftly, investigate the issue, and mitigate risks before they escalate.
Integrate Audit Trails with Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Plans
Audit trails are essential for business continuity and disaster recovery, as they provide a historical record of system operations and transfers. Organisations should integrate audit logs into their disaster recovery strategy to ensure that critical data can be restored after system failures, cyberattacks, or other disruptions.
Storing backup logs in multiple secure locations and testing recovery procedures regularly ensures that the organisation remains resilient despite unexpected events.
Keep Audit Trails Up-to-Date with Evolving Technologies
Technology is constantly evolving, and so should audit trail implementations. Organisations should periodically assess and update their logging infrastructure to incorporate new security technologies, AI-powered anomaly detection, blockchain-based auditing, and cloud-native logging solutions.
Keeping pace with technological advancements ensures that audit trails can stay practical and aligned with modern security threats and legislative ordinances.
Conclusion
Audit trails go beyond compliance — they are the backbone of reliability, safety, and operational excellence. They create a shield against fraud, unauthorised access, and regulatory pitfalls by systematically capturing every transaction, system modification, and user interaction.
A well-structured audit trail doesn’t just enhance transparency; it fortifies business integrity and builds stakeholder trust. Integrating AI-driven analytics, blockchain surveillance, and automated tracking will revolutionise audit trails as technology advances, empowering organisations to navigate the complexities of a data-driven world with confidence and resilience.
FAQ
What is an audit trail, and why is it important?
An audit trail records performances, transactions, or system alterations, insuring transparency and due diligence. It is crucial for fraud detection, regulatory compliance, and data preservation.
How does an audit trail work in financial systems?
In finance, audit trails track payments, journal entries, and receipts to verify operations, foreclose fraud, and assure alignment with regulations such as SOX and IFRS.
What does an audit trail check for?
Audit trails check for unauthorised access, fraudulent schemes, data modifications, and adherence violations. They help organisations maintain data integrity and security.
How can businesses improve their audit tracking system?
Businesses can enhance audit trail reports by implementing automated logging, using secure storage, enforcing access controls, and integrating AI for anomaly detection.







