What is Restaking? Comprehensive Guide

Every year, billions of dollars in cryptocurrency are locked in staking protocols, generating steady rewards for users. As of January 2025, over $119 billion was secured in these systems. While standard staking is profitable, it often locks assets and makes them unavailable for other uses, limiting their potential.
Restaking changes that. It allows staked assets to do more, supporting multiple blockchain networks simultaneously. This not only boosts rewards but also enhances the security and efficiency of the entire ecosystem.
In this guide, we’ll explain restaking, how it works, and why it’s reshaping the future of blockchain technology.
Key Takeaways
- Staking locks up assets to secure networks, but liquid staking and restaking improve flexibility and rewards.
- Liquid staking provides tradable tokens that keep staked assets usable in DeFi while restaking amplifies their utility by securing multiple networks.
- Liquid restaking combines liquidity and multi-network support, offering maximum rewards through tokens like Liquid Restaking Tokens.
- Protocols like EigenLayer and Etherfi drive restaking adoption, allowing staked assets to enhance security across several blockchains.
What Is Staking?
Staking is a core component of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains. Users lock up their tokens to support network operations like transaction validation and block production. In return, they earn rewards, typically in the form of additional tokens. While staking ensures network security, it comes with limitations:
- Illiquidity: Staked assets are often locked and unavailable for other uses.
- High entry barriers: Significant capital and technical expertise are sometimes required to participate.
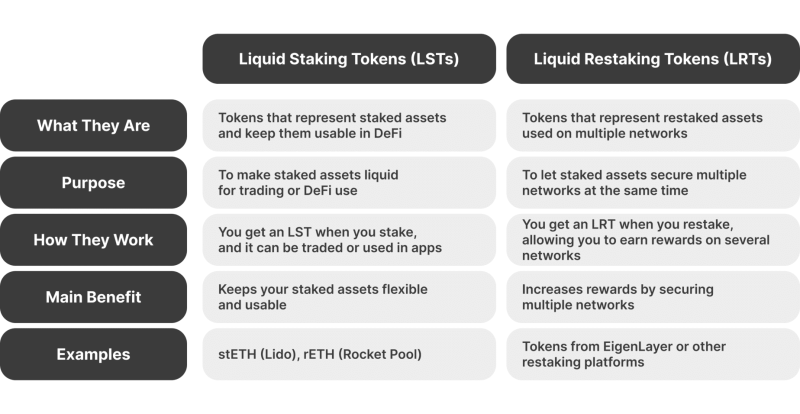
To solve these issues, liquid staking was introduced. It allows users to stake their assets while retaining liquidity through Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs). These tokens represent your staked assets and can be traded or used in DeFi, making staking more flexible and efficient.
Restaking Explained
Restaking enhances this model by enabling the same staked tokens to be redeployed across multiple PoS-based chains or protocols. This means that a single-staked asset can now contribute to the security and functionality of various platforms simultaneously, effectively extending its utility and potential rewards.
The process relies on validators—the people or systems that keep blockchains running smoothly. They use their staked cryptocurrency to secure additional networks or services, which lets them earn extra rewards.
However, this also carries higher risks, as validators are responsible for multiple networks, and problems in one network could result in penalties.
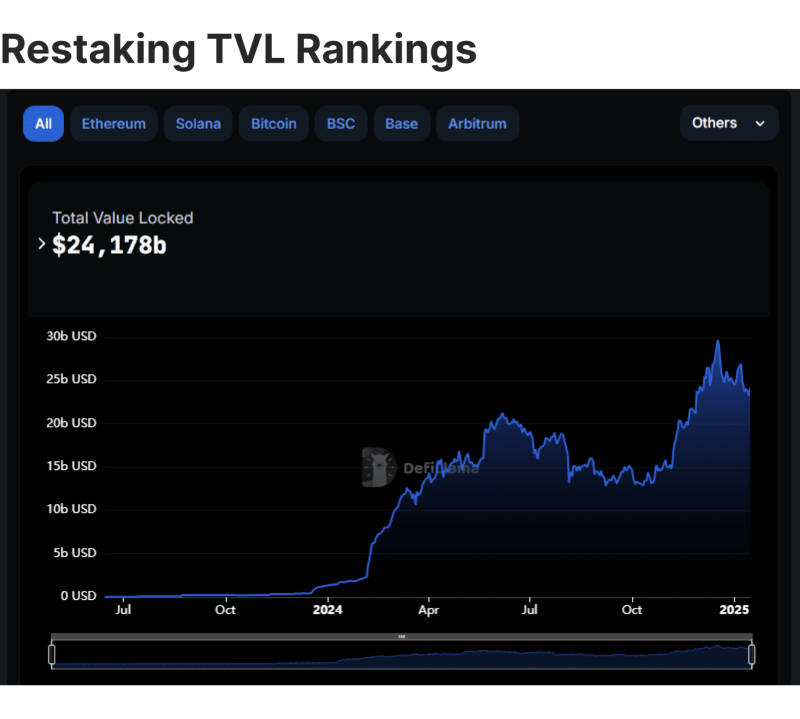
Restaking has grown very quickly over the past year, with $24.178 billion locked in restaking protocols by early 2025. In fact, the total value locked has more than tripled since the middle of 2024, showing just how popular it has become.
Restaking is now an important part of DeFi, with blockchains like Ethereum, Solana, and Binance Smart Chain leading the way.
Liquid Staking vs Restaking
While both restaking and liquid staking aim to enhance the efficiency and utility of staked assets, they operate differently:
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Liquid Staking
Liquid staking lets you stake your tokens while keeping them accessible. When you stake through a liquid staking protocol, you get Liquid Staking Tokens that represent your staked assets. These tokens can be traded, transferred, or used in DeFi apps, so you can earn staking rewards while still using your assets for other activities.
Restaking
Restaking focuses on making staked assets even more useful by letting them secure multiple networks at the same time. Instead of just providing liquidity, restaking allows your staked tokens to work on several protocols, increasing their role in keeping the blockchain ecosystem secure.
What Is Liquid Restaking?
Liquid restaking combines the best parts of liquid staking and restaking, making it a more flexible way to use staked assets.
When you stake your assets through liquid restaking, you get Liquid Restaking Tokens (LRTs), which provide liquidity and enable the staked assets to support multiple networks or protocols. This integration helps maximise the rewards and participation across different platforms without the need for additional capital.
Protocols like EigenLayer are leading the way in liquid restaking. For example, Ethereum validators can use their staked ETH to secure additional networks and applications while earning extra rewards and improving the security and scalability of the entire blockchain system.
EigenLayer, launched in June 2023, was the first restaking protocol on Ethereum.
Benefits of Restaking
Restaking brings several key benefits that make it a valuable addition to the blockchain world.
Boosting Returns Without Extra Investment
In regular staking, your assets are locked up in one network, and you are only earning rewards there. Restaking changes this by letting you use those same staked assets across multiple networks. This means you can earn rewards from several sources at once, all without needing to add more money. It’s like getting multiple paychecks for the same effort.
Making Networks Safer
Restaking helps improve the security of blockchain networks. Allowing staked assets to support multiple platforms spreads security across the ecosystem. This makes it harder for attackers to target any one network. For example, protocols like EigenLayer let Ethereum validators restake their ETH to secure not only Ethereum but also other networks and services.
Helping New Projects Grow
New blockchain projects often struggle to attract enough validators to secure their network. Restaking solves this problem by letting these smaller projects borrow the security from established networks like Ethereum. This makes it easier for new ideas to take off while staying safe and reliable.
Risks and Considerations of Restaking
Restaking can be a great way to earn more rewards and support multiple networks, but it’s not without its challenges.
Slashing Risks
Slashing is a penalty that happens when a validator—someone responsible for securing the network—behaves improperly, or a network experiences a problem. With restaking, your assets are spread across multiple networks, which increases the chances of something going wrong.
If one of the networks your assets are supporting gets hacked or has technical issues, you might lose part of your staked assets as a penalty.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Restaking relies on smart contracts—automated programs that manage how your staked assets are shared across networks. While these contracts make restaking possible, they’re not perfect and can have bugs or security flaws.
If a hacker finds a weakness in the smart contract of the restaking platform, they could steal funds or disrupt the system.
Complexity and Management
Restaking isn’t as simple as traditional staking. When you restake, you’re spreading your assets across multiple networks, which means you need to keep track of everything.
Mistakes like choosing the wrong settings or failing to act quickly in case of an issue could result in losing rewards or even part of your stake.
Liquid Restaking Protocols
Restaking protocols are platforms that make it possible to use staked assets to secure multiple networks, unlocking new earning opportunities and enhancing blockchain security. Here’s a look at some of the top restaking protocols and what they offer:
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
1. EigenLayer
EigenLayer is a leading restaking protocol on Ethereum. It allows Ethereum validators to reuse their staked ETH or LSTs to secure additional services and applications within the Ethereum ecosystem. Validators earn extra rewards while helping secure multiple networks. EigenLayer is particularly popular because it adds security without requiring new capital.
2. Etherfi
Etherfi is another Ethereum-based protocol that focuses on liquid restaking. When users stake their ETH with Etherfi, they receive a liquid restaking token called eETH. This token can be used in DeFi while also allowing users to earn rewards from restaking. Etherfi also integrates with EigenLayer, letting stakers secure even more Ethereum-based networks.
3. Solayer
Solayer is a restaking protocol designed for the Solana blockchain. It provides tools for users to restake their assets across various Solana-based networks and applications. By doing so, Solayer enhances the earning potential of staked assets while improving the overall security of the Solana restaking ecosystem.
4. Picasso
Picasso is a restaking platform that supports cross-chain integrations, allowing users to restake their tokens across different blockchains. This protocol maximises earning potential and capital efficiency by expanding the use of staked assets to multiple networks.
5. Pendle
Pendle is a DeFi protocol that helps users manage and trade the rewards from their staked assets. It splits these assets into two parts: Principal Tokens (PT) and Yield Tokens (YT). Pendle operates primarily on the Ethereum mainnet and Arbitrum.
Conclusion
Restaking is a powerful tool that lets you earn rewards from multiple networks simultaneously, opening up new possibilities in the blockchain world. Whether experienced with crypto or just starting out, learning about restaking can help you take advantage of exciting new opportunities in the decentralised space.
FAQ
What is the difference between staking and restaking?
Staking locks your assets to support a single network, earning rewards for securing it. Restaking allows you to reuse those staked assets to secure multiple networks, increasing your rewards and boosting blockchain security.
Is restaking the same as liquid staking?
No, they are different. Liquid staking focuses on keeping staked assets usable by providing tokens (LSTs) that represent them. Restaking, on the other hand, allows staked assets to secure additional networks, often alongside liquid staking.
What is the difference between LST and LRT?
Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) represent your staked assets and keep them tradable or usable in DeFi. Liquid Restaking Tokens (LRTs) extend this by allowing assets to secure multiple networks while still being liquid.
Is liquid staking halal?
The permissibility of liquid staking in Islam depends on the specific implementation and adherence to Islamic principles like avoiding excessive uncertainty (gharar) and interest (riba). It’s best to consult a knowledgeable Islamic scholar for clarity.