Cross Margin vs Isolated Margin: A Broker's Guide to Risk & Capital Efficiency

In leveraged trading, how you manage margin defines how you manage risk. For brokers and professional traders, the choice between cross and isolated margin determines how efficiently capital is used and how exposure is controlled across positions.
In 2025’s volatile markets, these models shape everything from portfolio stability to liquidation outcomes. Cross margin supports flexible, portfolio-level management. Isolated margin enforces strict limits per position.
This guide explains cross margin vs isolated margin, when to use them, and how they affect trading performance and broker infrastructure.
Key Takeaways
- Cross margin uses shared collateral for all positions, improving capital efficiency and flexibility.
- Isolated margin limits risk per trade, offering strict control and clearer P&L segmentation.
- Brokers choose margin models based on strategy: cross for scale and speed, isolated for precision and risk separation.
- B2BROKER supports both, with institutional-grade liquidity, margin infrastructure, and risk systems.
Understanding Margin Trading Fundamentals
Margin trading allows traders to borrow funds to increase position size and potential returns. Despite its inherent risk, leverage remains central to modern trading. Recent Addleshaw Goddard’s report on current trends in leveraged finance shows that leveraged strategies continue to thrive despite ongoing macroeconomic challenges.
For brokers and institutional traders, margin isn’t just about amplifying profit — it’s about controlling exposure. Every leveraged position introduces both opportunity and liquidation risk. The balance between those two outcomes depends on how margin is structured and maintained within a trading account.
Leverage helps professionals:
- Expand market exposure without committing all available capital.
- Diversify strategies by opening multiple positions simultaneously.
- Increase liquidity efficiency by reallocating capital dynamically across assets.
But leverage also magnifies loss. A small adverse price move can trigger liquidation if collateral thresholds are breached. That’s why understanding margin mechanics is a foundational skill for any serious market participant.
The key difference lies in how margin risk is distributed. Cross margin combines account balances to support all positions, offering flexibility but increasing systemic risk. Isolated margin confines risk to individual trades, limiting losses but requiring more precise capital allocation.
What Is Cross Margin?
Cross margin uses the entire account balance to back all open positions. The platform continuously reallocates equity across the book, so winning trades support losing ones. You manage risk at the portfolio level, not per ticket. That design improves capital efficiency and keeps more strategies live during normal volatility.
Unrealised profits offset drawdowns elsewhere. As long as total equity stays above the maintenance margin required for the portfolio, positions remain open. You don’t top up each trade separately; the account’s surplus covers temporary stress and reduces avoidable liquidations caused by isolated fluctuations.
Example:
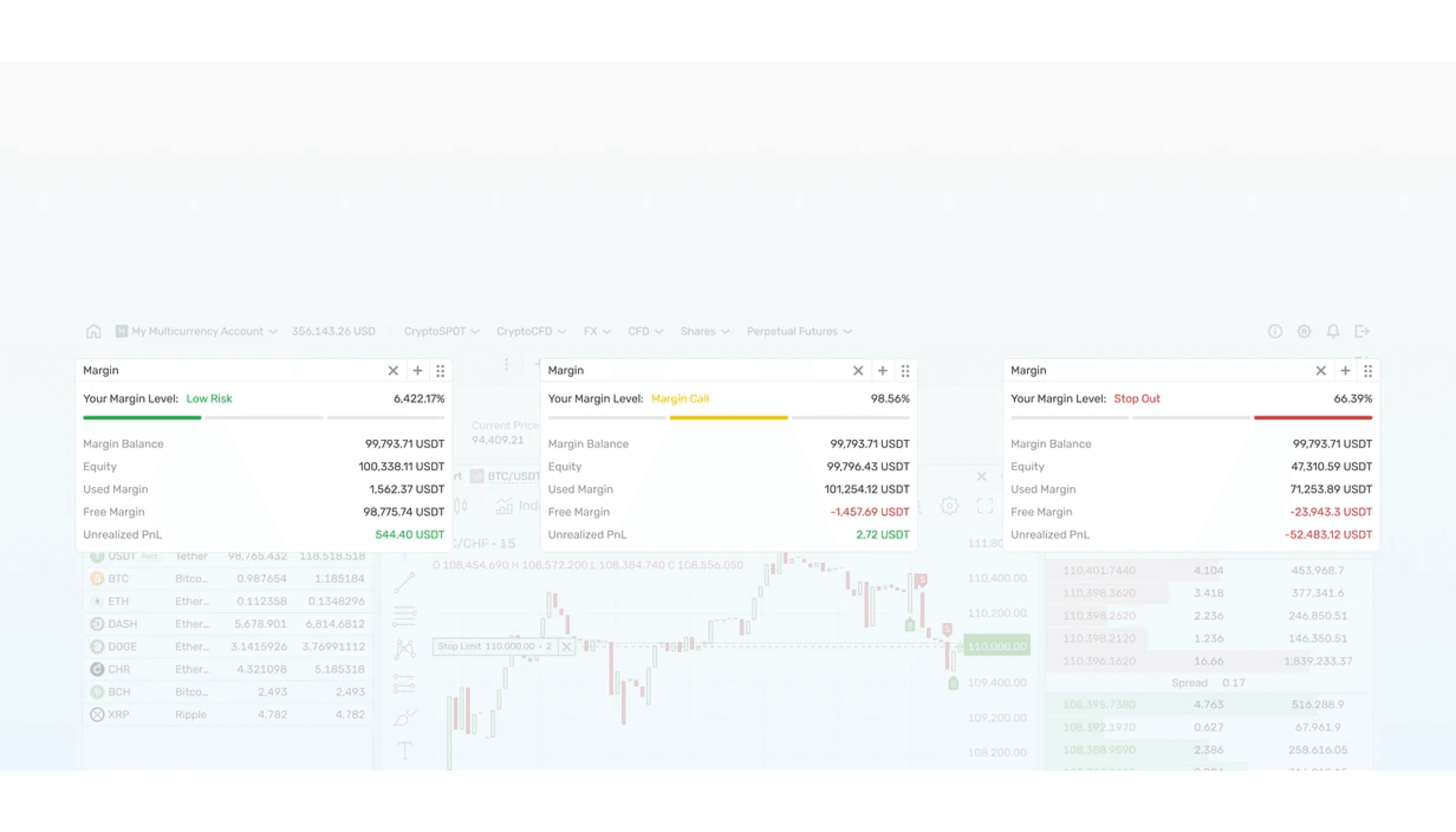
You hold two futures: Position A shows +$6,000 unrealised P&L; Position B shows –$4,000. Net P&L equals +$2,000.
If the portfolio’s maintenance requirement is $30,000 and your account equity sits at $52,000, both positions stay safe. If markets turn and net equity falls below $30,000, the system starts liquidating to restore margin.
Why traders use cross margin:
- Capital efficiency: One collateral pool supports multiple positions.
- Fewer forced closes: Profits cushion temporary losses.
- Portfolio strategies: You can hedge, run basis trades, or deploy pairs without over-funding each leg.
Cross margin isn’t free of risk. A sharp move in one large position can drain equity and jeopardise the rest of the book. You need disciplined limits, real-time monitoring, and a reserve buffer.
When used well, cross margin suits traders who manage multiple, often correlated positions and operate portfolio-level strategies such as hedging, arbitrage, and market-making, where flexibility and efficient collateral use drive results.
What Is Isolated Margin?
Isolated margin assigns dedicated collateral to each position. You decide how much margin backs a trade, and the platform contains any loss to that allocation. Other positions and available balance stay untouched. You manage risk per ticket, not across the entire book.
Operationally, each position has its own maintenance requirement. If that position’s equity drops below the threshold, you can add funds to that specific trade or allow liquidation. The system does not pull collateral from the rest of the account, which preserves capital for other strategies.
Example:
Your account holds $50,000: Position A (BTC perpetual) uses $5,000 margin; Position B (ETH perpetual) uses $5,000. A sharp BTC move drives Position A’s equity to its liquidation level. Only Position A liquidates and realises its loss. Position B remains open, and your unallocated $40,000 stays intact.
This model fits traders who want strict risk segmentation and precise control over exposure. You define the maximum loss per idea in advance and avoid cross-contamination between strategies or client sub-accounts. That clarity improves decision-making and aligns with conservative mandates.
Why traders choose isolated margin:
- Predictable, ticket-level loss limits
- Cleaner performance attribution and P&L review
- Lower contagion risk across strategies or clients
- Easier to meet policy, mandate, or compliance constraints
The trade-off is lower capital efficiency and occasional manual rebalancing. Still, isolated margin excels for strategy testing, speculative or event-driven trades, and structured risk programs where loss caps matter more than maximum leverage. If you value containment and control, isolated margin provides the discipline to protect the rest of your book.
Build a Margin Exchange Without Starting From Scratch
Launch your own cryptocurrency margin platform with integrated cross and isolated margin support.
How Cross Margin Works and Main Benefits
Cross margin gives traders and brokers the freedom to manage capital as one flexible pool. Instead of funding each trade separately, all available equity supports every position. Profits from one trade automatically balance short-term losses in another, keeping portfolios more stable through daily market swings.
This setup helps advanced trading teams operate efficiently. When liquidity flows freely between positions, capital isn’t locked up unnecessarily — it works where it’s needed most. That efficiency matters to brokers managing multiple accounts or traders running complex, multi-asset books.
Collateral Sharing Across All Positions
With cross margin, all open trades draw from the same balance. The platform automatically redistributes funds to keep underperforming positions afloat, as long as total account equity stays above the maintenance threshold.
This means fewer forced liquidations during temporary drawdowns and a smoother trading experience overall. Managing a single margin pool also reduces operational friction — traders can focus on strategy rather than manual margin adjustments.
Capital Efficiency for Experienced Traders
Cross margin supports hedging, arbitrage, and pairs trading, where flexibility and capital agility are critical.
For example, a trader running a hedge between BTC spot and BTC futures can let one side’s gains offset the other’s losses. The system balances exposure dynamically, freeing up capital for new opportunities without needing additional deposits.
For brokers, this structure maximises leverage potential across clients and products, which enhances liquidity and profitability when managed responsibly.
Potential for Higher Liquidation Risk
The freedom of cross margin also raises the stakes. Because every trade shares the same collateral, a sharp loss in one large position can impact the entire account.
Mitigating this risk requires structure — monitoring total exposure, setting position limits, and maintaining reserve margins. When backed by proper risk systems and clear internal rules, cross margin becomes a powerful framework for professional, portfolio-level trading.
Modern derivatives venues, such as the CME Group, have adopted portfolio margining models to help institutions optimize collateral use and reduce liquidation risk.
How Isolated Margin Works and Main Benefits
Isolated margin creates structure and control. Each position has its own margin allocation, and the platform treats every trade as a self-contained unit. That separation keeps one loss from spreading across the rest of the account, giving traders predictable outcomes and clear oversight of every position.
This approach appeals to brokers and professional desks that manage client funds or structured portfolios. It supports disciplined risk management and transparent reporting — both essential when strategies must be tracked independently.
Separate Collateral for Each Position
Every position operates on its own capital. You decide how much collateral to allocate, and that amount defines the maximum loss. If a trade fails, only that margin is affected.
This setup simplifies performance tracking and auditing. Traders can review each strategy’s profit and loss in isolation, while brokers gain cleaner insight into client exposure. The result is stronger capital preservation and fewer surprises during volatile periods.
Controlled Losses and Risk Management
By design, isolated margin limits contagion risk. Liquidation acts like an automated stop-loss — the system closes an individual position once its collateral is depleted. This enforces consistent discipline and prevents a single bad trade from eroding the broader portfolio.
For risk teams, that control supports better planning and compliance alignment. It ensures exposure remains visible and bounded, even when markets move fast.
Lower Overall Leverage but Enhanced Safety
The trade-off is straightforward: you sacrifice some leverage potential for greater account survivability. Because collateral can’t flow between trades, total available margin feels tighter — but stability improves.
For conservative traders, new strategies, or managed client accounts, that’s an acceptable compromise. Isolated margin offers clarity, structure, and protection — the foundation of sustainable, long-term trading.
How Margin Models Affect Broker Operations
Margin design shapes a broker’s balance sheet, risk posture, and client experience. Cross margin centralises liquidity into one pool, which smooths cash flow and reduces idle balances. Isolated margin segments capital per trade or sub-account, which simplifies control but increases total collateral required.
Cash flow and liquidity. Cross margin lets you glide collateral between products and venues, improving fill rates and reducing emergency top-ups. Isolated margin locks funds in silos. You gain certainty per position, but you fund more margin overall, which tightens operating liquidity.
Credit and counterparty risk. Cross margin concentrates exposure at the portfolio level. You need real-time risk engines, concentration limits, and correlation checks. Isolated margin reduces contagion: one client blow-up or strategy failure stays contained, which simplifies escalation and collections.
Client fund allocation. With cross margin, clients enjoy flexible leverage and fewer interruptions, but they rely on your monitoring discipline. With isolated margin, clients get clear loss caps and a cleaner P&L by strategy or sub-account, which supports managed accounts and policy-driven mandates.
Operational levers to get right:
- Set house maintenance buffers and intraday calls.
- Enforce per-client and per-instrument leverage caps.
- Monitor net and gross exposures by asset, factor, and venue.
- Automate alerts, throttles, and circuit-breakers.
- Align treasury, bridge, and liquidity hub for instant transfers.
Choose cross margin to maximise capital velocity for active, multi-asset books with strong risk infrastructure. Choose isolated margin for conservative mandates, client-segmented portfolios, and programs where transparency and containment outweigh maximum leverage.

Discover how to launch a compliant crypto margin exchange in 2026 with practical, turnkey strategies for brokers, trading desks, and crypto platforms.
17.04.20
Cross Margin vs Isolated Margin: Key Differences
Choosing between cross and isolated margin sets the rules for capital use, risk limits, and operational workflow. Cross margin prioritises capital velocity and portfolio-level control. Isolated margin prioritises containment, clarity, and per-position accountability. Use the matrix below as a quick reference.
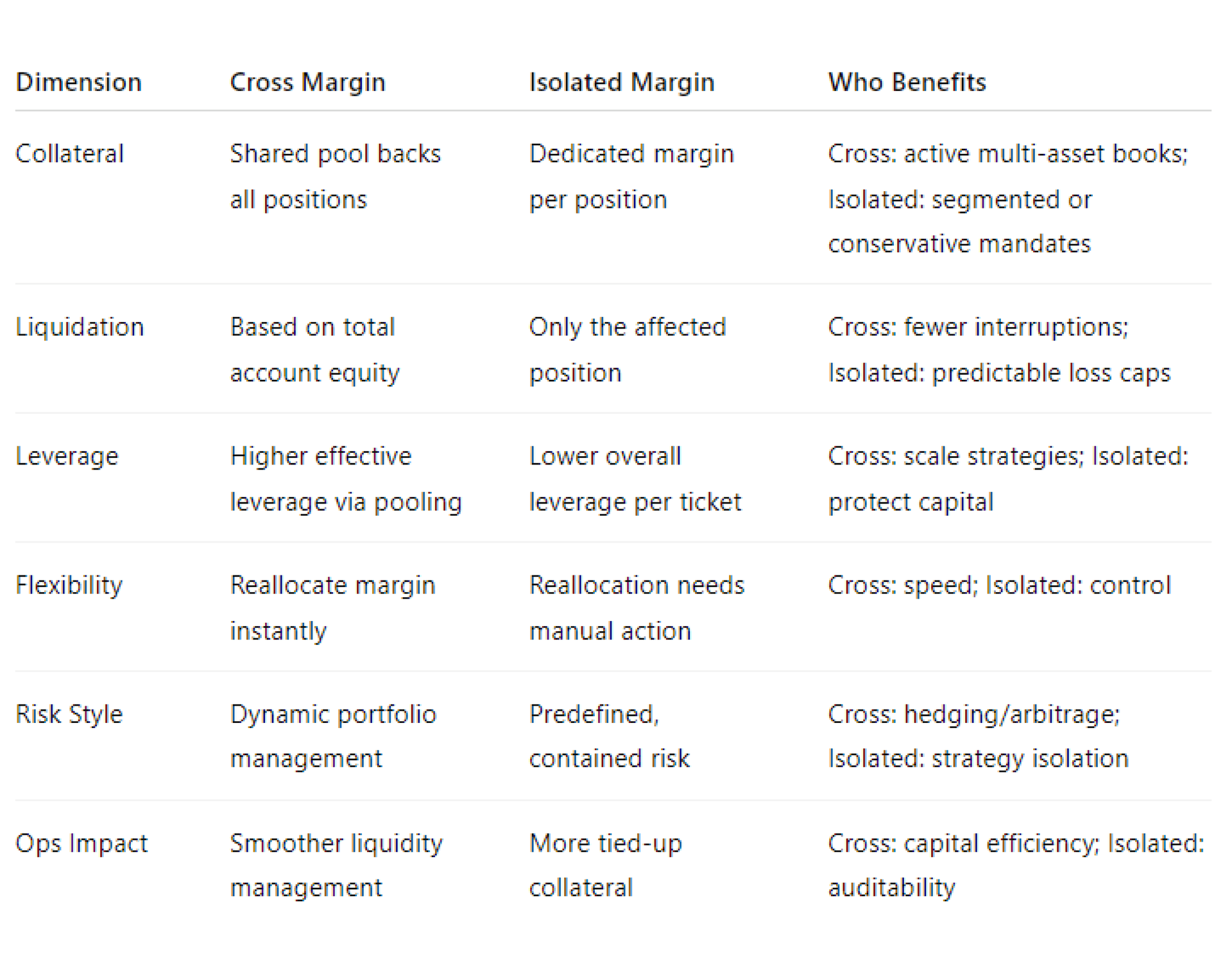
1. Collateral Distribution
Cross margin uses a shared collateral pool to support every open trade. Isolated margin locks margin per position. Cross boosts liquidity flexibility and reduces idle capital. Isolated improves operational control and makes allocation rules explicit for each strategy or sub-account.
2. Liquidation Thresholds
In cross margin, liquidation triggers when total equity drops below the account’s maintenance requirement. In isolated margin, only the individual position liquidates. Example: a failed oil short closes in isolated mode, while your FX positions remain untouched and fully funded.
3. Leverage
Cross margin often delivers higher effective leverage because profits and idle balances support new exposure. Isolated margin caps leverage per trade, which reduces tail risk. Choose cross to scale complex books; choose isolated to enforce strict per-idea limits.
4. Flexibility
Cross margin enables instant reallocation of capital across instruments and venues, which speeds execution and improves fill quality. Isolated margin demands deliberate re-funding. You gain control and audit trails, but you sacrifice speed when markets move quickly.
5. Risk Management Style
Cross margin fits dynamic, portfolio-level risk with continuous monitoring and guardrails. Isolated margin supports rule-based risk with hard boundaries. Use cross for adaptive strategies; use isolated when policies require predefined maximum loss per position.
6. Clearing and Settlement
With cross margin, positions settle as one portfolio; gains and losses offset before the final margin is set. Brokers hold less total collateral with LPs or clearing partners, improving funding efficiency. Isolated margin settles per position or sub-account, inflating total requirements and reducing clearing flexibility.
7. Technology and System Requirements
Cross margin needs real-time risk engines, portfolio analytics, and tight integrations between the platform, bridge, and liquidity hub. Isolated margin is simpler to implement and suits earlier-stage stacks or programs that prioritise modular control and clear segregation.
8. Use Cases
- Cross: Hedging programs, basis trades, pairs, market-making, multi-venue routing.
- Isolated: Strategy testing, event-driven bets, client-segmented mandates, regulated programs with strict loss caps.
Map the mode to your objectives: speed and efficiency across a book (cross) or precise, enforceable limits per idea (isolated).
Deep, Reliable Liquidity Across 10 Major Asset Classes
FX, Crypto, Commodities, Indices & More from One Single Margin Account
Tight Spreads and Ultra-Low Latency Execution
Seamless API Integration with Your Trading Platform

Which to Choose for Advanced or Beginner Strategies
Start with your operating reality: experience, risk tolerance, and position complexity. Margin is not one-size-fits-all. Pick the mode that supports how you trade today and the controls you can enforce consistently.
For beginners:
Choose isolated margin. It teaches capital discipline and defines loss per idea. You learn to size positions, place stops, and review results without cross-contamination. That structure builds good habits before you scale leverage or complexity.
For advanced traders:
Use cross margin for multi-leg and portfolio strategies. It improves capital velocity and keeps hedges, basis trades, and pairs funded through routine swings. Pair it with real-time monitoring, hard limits, and automation across risk, treasury, and execution.
Use a hybrid when possible. Switch modes by strategy and market regime. For example, run cross margin for core hedges and inventory management, while keeping event-driven or high-volatility bets in isolated margin to cap downside cleanly.
Decision checklist:
- Experience: Do you have a process to monitor risk intraday?
- Strategy type: Single-ticket bets vs. portfolio construction?
- Correlation: Will losses cluster across positions?
- Volatility: How fast can P&L and margin change?
- Capital size: Do you need efficiency more than containment?
Choose the mode that aligns with these answers. Then document rules, measure outcomes, and adjust as your team and infrastructure mature.
Power your Brokerage with Next-Gen Multi-Asset & Multi-Market Trading
Advanced Engine Processing 3,000 Requests Per Second
Supports FX, Crypto Spot, CFDs, Perpetual Futures, and More in One Platform
Scalable Architecture Built for High-Volume Trading

Create a Tailored Crypto Trading Ecosystem With B2BROKER
The right margin model is only part of the equation. Brokers also need liquidity, infrastructure, and technology that scale with client demand. We at B2BROKER help brokers and exchanges build unified trading environments with deep liquidity, institutional connectivity, and automated risk management.
Our ecosystem combines multi-asset liquidity, margin aggregation, and turnkey infrastructure into one platform. You get direct access to 10 asset classes — from Forex and crypto CFDs to commodities and indices — all under a single margin account. This structure lets brokers run cross-asset strategies efficiently while maintaining full transparency and control.
For brokers looking to integrate a proven trading platform, explore our cTrader White Label solution — a ready-made, institutional-grade framework for margin and liquidity management.
With 24/7 technical support, 10 global offices, 10 regulatory licenses and 500+ professional clients, B2BROKER delivers reliability and scale for brokers at any stage. Whether you’re launching a crypto exchange, expanding your CFD offering, or upgrading your liquidity stack, our solutions reduce time to market and operational risk.
Build your own high-performance trading ecosystem today — powered by B2BROKER’s liquidity and technology expertise.
Ready to Build Smarter Margin Infrastructure?
Speak with our team to design a platform that fits your strategies, margin model, and growth goals.
FAQ
- Is it better to trade cross or isolated margin?
It depends on your strategy. Cross margin offers higher capital efficiency and flexibility for portfolio trading, while isolated margin limits losses per position and ensures tighter risk control.
- When should you use isolated margin in futures trading?
Use isolated margin when testing strategies, trading volatile instruments, or managing client accounts where each position needs a defined loss limit.
- How does cross margin work in futures trading?
Cross margin uses all available account equity to support every open position, allowing profits in one trade to offset losses in another and reducing unnecessary liquidations.
- Are there platform-specific rules or fees for cross margining?
Yes. Exchanges and brokers apply different margin requirements, funding rates, and liquidation mechanisms, so always review the platform’s margin policy before trading.
- What are the regulatory requirements for margin trading?
Requirements vary by jurisdiction but generally include leverage caps, disclosure obligations, and client classification rules to ensure transparent and responsible use of leverage. For example, CySEC recently updated its CFD framework, introducing new restrictions on leverage for retail clients to align with EU directives.