What are Options Contracts?

Trading in the financial markets entails comprehending various tools and ways to make money. While the most straightforward way is to buy and sell after a product’s price increases, alternatives exist to cope with the market dynamics, such as options, futures and other derivatives.
Options contracts are commonly used to capitalise on the potential of some of these financial instruments, utilising experience and speculations in predicting future prices of tradable securities, such as stocks, bonds, Forex currencies, commodities, and cryptos.
As simple as an option contract may sound, there are several types and strategies to trade them. So, what is an option agreement, and what benefits does it bring? Let’s explain in detail.
Key Takeaways
- Options are financial contracts involving two parties agreeing to trade particulate assets at an agreed price and date.
- The options contract states the expiration date, strike price and order type to buy or sell the mentioned asset.
- Call options give the traders the right to buy the contracted securities at the given price.
- Put options give the traders the right to sell the contracted securities at the given price.
What is an Option Contract?
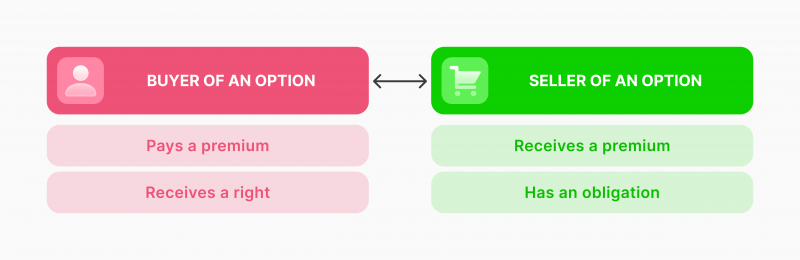
Options are trading agreements between two parties concluding the right to buy or sell a given asset at a predetermined price on a particular date. Thus, when a trader enters into an option agreement to buy stocks, the initial price, future price and date of execution are stated in the contract.
The trader has the right and not the obligation to exercise their option upon the mentioned date.
Understanding the terminologies is crucial to comprehend what an option agreement is, such as the strike price (asset price at execution date), intrinsic value (the difference between the strike price and real market price) and in-the-money (when the executed option contract is profitable). Out-of-the-money is a term also used to describe a losing option contract.
How Options Markets Work
Options financial instruments are used to speculate on the future price action of a specific asset and lock on a particular price and date to trade the product, be it buying or selling.
Let’s say you buy option contracts for asset A that cost $90 per unit, but you expect the market price to increase to $100. By the expiration date, if the stock price rises to $105, you can exercise your right to buy at the strike price and sell the asset for $105, gaining a profit of $5.
The intrinsic value of the above buy call option example is $5. However, if the market declines and the asset price drops below $100, you have the right not to execute the contract and avoid excessive losses.
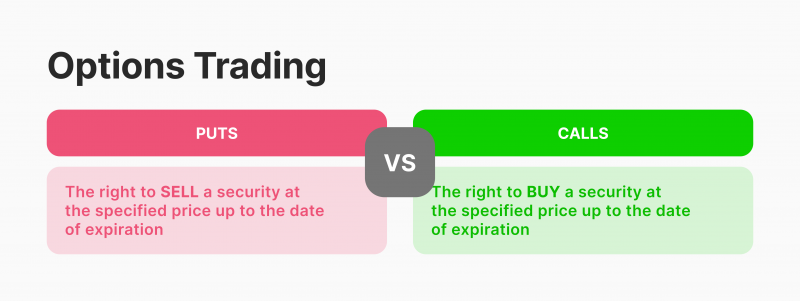
Call vs Put Options
Call and put options are two types of executing these contracts. However, they do not oblige the involved parties to buy/sell the subject instrument.
A call option refers to a trader’s right to buy the underlying asset(s) at the predetermined value (strike price). Therefore, a call option is more valuable when the market price increases.
Put options refer to the trader’s right to sell the underlying asset(s) at the strike price on the execution date, which is similar to short selling. When the market declines, the put options become more valuable because the trader can buy securities at a lower price.
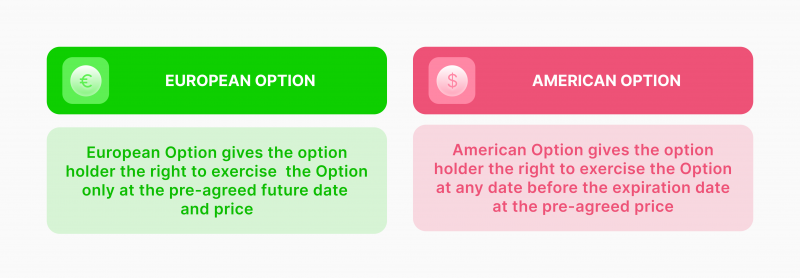
American vs. European Options
American and European options refer to the time of order execution. Thus, European contracts require exercising the right to buy/sell an asset on the expiration date. On the other hand, American contracts entail that options can be exercised anytime between the agreement and expiration dates.
Explore Deeper Industry Insights
Learn from experts shaping the future of financial services — get the latest strategies and trends.
American types of contracts usually come with a higher premium payment because the right to execute one’s option earlier carries some value, making them more appealing option types.
Types of Option Contracts
Option contract types can be understood as call and put (buy vs sell). However, since each of them can be used to open or close a market position, we can explain them as the following 4 types of options.
Buy-to-Open (BTO)
Buy-to-open gives the investor the right to enter a long trade, whether as a call or put. In other words, the trader can open a market position where they buy or sell the underlying asset.
For example, if a trader is bullish about the stock ABC, they would prefer BTO these shares, as they speculate on a potential price surge, allowing them to sell later when the price hits a return point.
Sell-to-Open (STO)
Sell-to-open gives the investor the right to enter a short trade because they are bearish about given shares. Therefore, they enter into an agreement to sell the subject asset on (or before) the expiration date, allowing them to buy later at a lower value and profit from the price difference.
However, this is a risky strategy because if the market surges unexpectedly, the trader needs to buy the underlying securities at the market value from the original lender.
Buy-to-Close (BTC)
Buying to close refers to exiting a short position previously exercised as sell-to-open options. If a trader enters an options contract to sell specific securities, they would need – in most cases – to wait for the maturity date before executing the order, or they can initiate buy-to-close options to offset the STO contract.
Buy-to-close works like a hedging strategy to mitigate losses for the trader if the market moves adversely.
Sell-to-Close (STC)
The sell-to-close options contracts are used to close a trader’s long position. When the investor buys a buy-to-open contract, they can wait for the expiration date to claim ownership of the subject asset.
However, if the market moves in an undesirable direction, the trader may mitigate losses by entering a sell-to-close option and taking profits from this contract to offset losses from the buy-to-open contract.
Why Trade Options
With the growth of electronic trading platforms and the plethora of brokerage and financial services, options trading is becoming more affordable compared to OTC trading or other instruments. Therefore, options trading offers the following advantages.
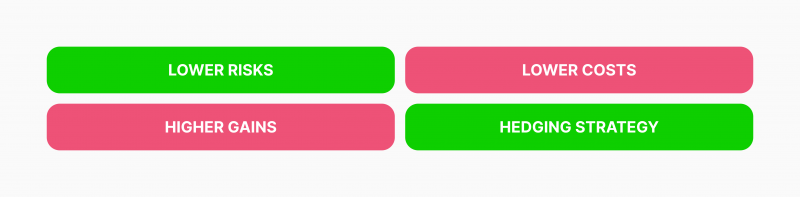
- Lower risks: Options contracts do not oblige the trader to execute the stated order, accommodating for unexpected volatility or price action.
- Lower prices: Traders do not have to pay the stock price when choosing an option contract. Instead, they pay the premium fee, which consists of the intrinsic value and other market factors that come much cheaper than buying the share itself.
- Higher gains: Since options have lower costs, the potential returns are higher if the market moves as the trader expects. In fact, the trader initially pays for the right to enter the agreement rather than the asset’s full purchase price.
- Hedging strategy: Besides the portfolio diversification features options provide, they serve as a hedge against losing positions or unexpected price actions, especially in European contracts that require waiting for the contract expiration date.
Options trading can be traced back to 1872, when an American financier, Russell Sage, established OTC call and put options, which was an unstandardised and illiquid market in the US.
Options in Stock Trading
Options are used as an alternative to directly investing in stocks and purchasing shares. These contracts are easier to get around and manage since they are more affordable and are associated with fewer complexities of asset ownership transfer.
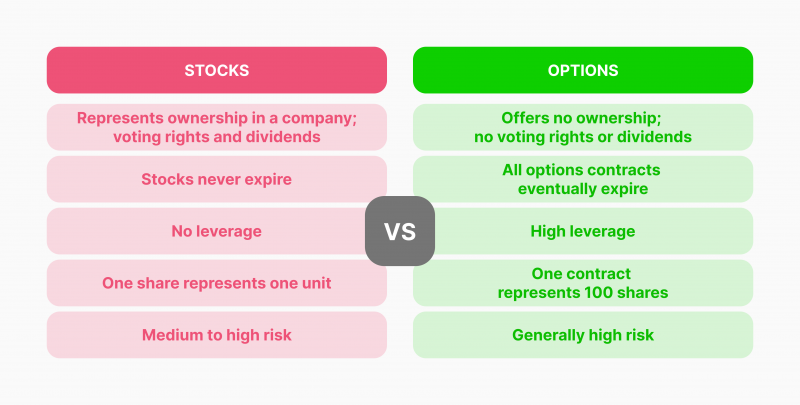
Options Versus Shares
Options entail purchasing the right to trade a particular stock. Therefore, instead of paying the entire share price, investors are charged with the contract premium paid, which usually comes at a fraction of the market value.
Assume you are trading Apple stock options; entering an option agreement associated with this asset would cost cents or a few dollars per share rather than the market price, let’s say, $100.
If the trader pays 30 cents ($0.30) per share in the options contract with a strike price of $110 and the stock price increases to $112, the trader can exercise their call option and buy the underlying stock.
The investor can then sell the shares according to the current market price of $112 and earn a profit of $2 per share, netting $1.70 per share after spending $0.30 per share.
How to Trade Options: Step-by-step Guide
Due to the individuality of options contracts, they require a different approach and careful analysis in choosing the right stocks and executing the right order. Here’s how you can trade stocks with options.
Step 1: Opening an Options Trading Account
Brokerage websites and trading platforms dedicate separate accounts for options trading, which is usually allowed for proficient individuals who have hands-on experience and a few years of activity.
Options trading is recommended for those who have a proven trading history or sufficient time to keep track of market dynamics and make timely decisions. Brokers usually conduct a careful screening before opening an options trading account, ensuring that a trader is fully aware of the associated risks and required capital.
Step 2: Choose The Right Assets
The next step is to select the assets that require hedging or coverage for being risky. This does not mean entering an option agreement with every traded security. However, options work like insurance for highly unpredictable market positions, such as volatile stocks or leverage trades.
Selecting the options contract type relies on the predicted price action. Thus:
- If you expect prices to increase, buy call options or sell put options.
- If you expect prices to decrease, buy put options or sell call options.
Step 3: Analyse The Market
Remember that options contracts give you the right to buy or sell a particular asset without being obligated to. Therefore, this tool enables you to cover up any expected losses you might have on another trade.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Carefully analyse the available options contracts by evaluating the offered strike price against the predicted market movements. Ideally, with call options, you want the expected market price to exceed the strike price by the premium fees to make a profit.
Conversely, if you choose put options, the potential market price must be less than the strike price, allowing you to profit from short-selling the underlying assets.
Step 4: Identify The Contract’s Timeframe
Determine the contract expiration date you are comfortable with. Options contracts may extend from days to weeks, months or years. Short-term options are risky because securities do not have enough time to fluctuate or reach the wanted strike price.
Therefore, long-term contracts are preferable for beginner and average traders, giving them more time and flexibility to exercise their options and track the market.
Pros and Cons of Options Trading
As mentioned before, options trading comes with some challenges, especially if the market moves unpredictably. Let’s find out what the risk of a call option is and what benefits they provide.
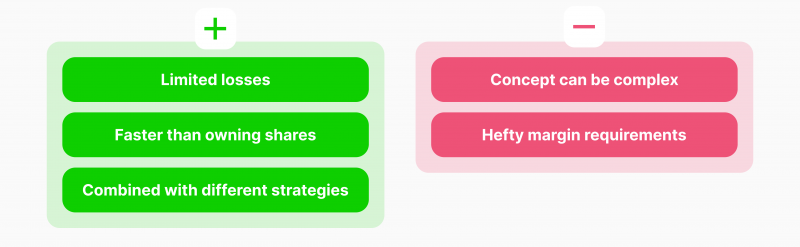
Advantages
- Financial losses are limited to the contract premium payment, which is usually a fraction of the stock price since you are buying the right trade buy/sell rather than paying the stock price.
- Requiring less hassle and procedures than actually buying and trading shares.
- Options can be practised on a wide range of trading strategies according to the contract type and the underlying asset nature.
Disadvantages
- Options can be complicated to grasp, making them a suitable choice for experienced traders.
- Margin requirements for opening the options account vary and can be costly depending on the contract type.
Conclusion
Options are financial instruments that give the trader the right to buy or sell the contracted securities. These tools are common for stock trading. However, options are used for other markets, such as commodities, Forex and cryptocurrencies.
Call and put options are two types of stock options, referring to the right to buy and sell the assets, respectively. Options contracts are used as a hedging strategy against risky positions, allowing the trader an optional market order that allows them to offset predicted losses from another trade.
However, they require careful analysis and consideration, given the complexity of options, as they rely on speculations and predictability.
FAQ
How do options contracts work?
Options contracts give traders the right to buy or sell financial assets at a specified price and date. On the contract expiration date, the trader can execute the mentioned order type and benefit if their price prediction is correct.
How much can you lose on an option contract?
In most cases, the trader’s losses are capped by the price paid for the contract’s premium. Investors pay to obtain the right to buy/sell stocks rather than paying the price of the underlying security.
Is option selling profitable?
Option contract sellers benefit from the premium fees paid to them for selling the contracts. Furthermore, they benefit if the prevailing market price does not match the specified strike price and the option’s call buyer incurs losses.
Why buy options instead of stocks?
Options are cheaper than stocks, and most premiums cost cents or a few dollars compared to one share price. Additionally, if the price predictions are right, the trader benefits from further buying or selling the underlying assets.