How Do Volatility and Liquidity in Forex Impact Businesses?
Financial markets flow freely according to the buying and selling pressures that define the market forces. Investors execute orders and earn gains from natural movements in prices, demands, supply and speculations, where each of these factors affects the other.
Variations in these determinants cause changes in volatility and liquidity in Forex trading, impacting how frequently prices change and expected profitability from investing in currency pairs.
Financial market volatility and liquidity are two key factors skilled traders consider before investing in financial securities and asset classes. Let’s review the difference between liquidity and volatility and how to use them to succeed in trading.
Key Takeaways
- Volatility in Forex refers to the range of price fluctuations, marking zones where gains and losses are made.
- Liquidity is associated with how easily and quickly trading orders can be made with low slippage and tight spreads.
- Volatility and liquidity are negatively correlated, where high liquidity is associated with low volatility and vice versa.
Understanding Volatility in The Forex Market
Volatility refers to the frequency of price movements in a given market or for a particular currency pair. For example, in the currency market, volatility is the degree of exchange rate changes between two currencies.
Asset volatility can be explained as price stability, how often the price changes and by how much. For example, the EUR/USD is the most stable currency pair, involving the largest two economies and the most used currencies worldwide.
This pair’s stability comes from the fact that both economies are in almost the same development stage, with similar central bank policies toward interest rates and lending.
However, currencies with considerable diversion between their economies, like USD/ZAR or GBP/JPY, are highly volatile currency pairs and can lead to profitable Forex trading.
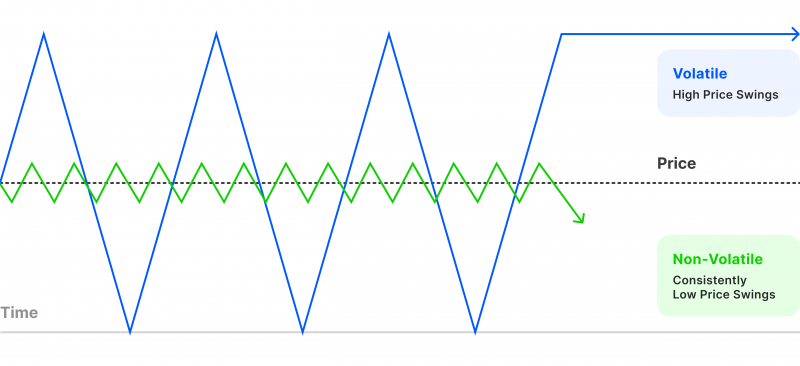
When it comes to investing in the foreign exchange market, trading a stable currency pair will result in a moderate rate of return but is more consistent in the long run.
However, volatile assets have higher potential gains, but they are also unstable, causing their prices to rise and fall significantly.
What Causes Volatility in The Forex Market?
Volatility is affected by multiple external factors, such as the national economy, geopolitical conditions, supply levels, and investor confidence.
National economic factors, such as GDP, employment rates and inflation, play a major role in central banks’ policies, based on which they derive their interest rate policies. When inflation rates are moderately high and GDP increases, investors are optimistic about a country’s economy, indicating a stable currency and potential.
Geopolitical disputes like trade wars, embargos, and international trade agreements play a major role in economic growth and currency stability, which greatly affects volatility rates and investors’ confidence.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Liquidity is another important factor that affects volatility. When a market experiences low supply, it makes prices prone to purchasing activities, indicating a high volatility level, and vice versa.
During the 2008 financial crisis, the EUR/USD volatility rates skyrocketed to 30% in the two-week analysis, while the AUD/USD surged to around 80%.
The Best Forex Market Volatility Indicators
Forex traders measure market volatility using different indicators, such as the Bollinger bands and the relative volatility index (RVI).
The Bollinger bands consist of a line (simple moving averages) surrounded by an upper and lower limit. These two limits form a stretching band that expands and contracts according to market forces, indicating the price fluctuation limits or the volatility.
On the other hand, the relative volatility index measures historical price movements and volatility and generates a value based on which the trader is recommended to either enter a buy or a long position.
Understanding Forex Market Liquidity
This concept refers to the ease with which market participants can buy and sell financial instruments, which relates to asset availability and volatility.
Large financial institutions and banks supply financial markets with securities and assets by engaging in significant trading activities, making these products more available and increasing the number of trading counterparts in a given market.
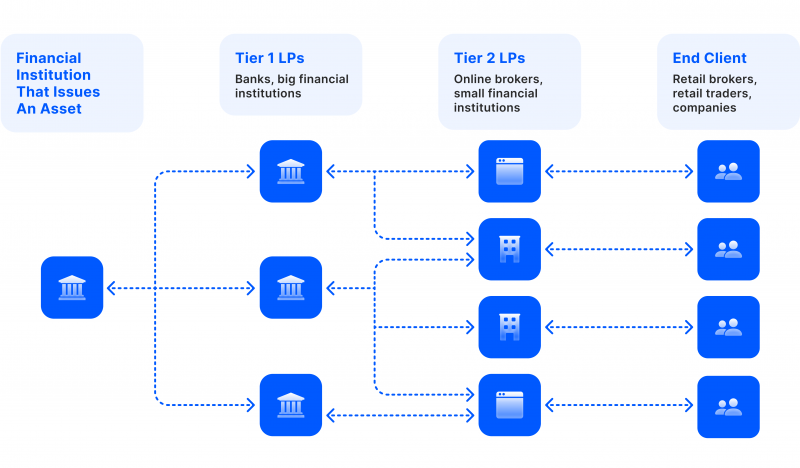
This also pertains to price stability. For example, the high liquidity of the Forex pair EUR/USD makes it one of the most stable assets with low volatility ratios.
On the other hand, an insufficient supply of a particular product and executing a buy order will result in changes in market prices.
What Affects Liquidity in The Currency Market?
Financial instruments are usually supplied by large financial institutions, investment banks and hedge funds which engage in trading markets offering brokerage services to their investors or as part of trading for themselves to increase their wealth.
Many economic and geopolitical factors affect these institutional investors’ activities, affecting Forex’s liquidity levels.
Economic figures, such as inflation and interest rates, affect investors’ willingness to expand their engagement in trading markets. During economic growth, traders are more likely to increase their investments, which boosts liquidity levels.
Technological advancements also affect liquidity provision. For example, trading platforms are capable of serving a huge number of market participants, executing many transactions simultaneously, contributing to supply levels and increasing market efficiency.
Reading The Forex Market Liquidity Indicator
Supply patterns change in different ways. Daily fluctuations and trading hours affect the demand for currency pairs. Investors can also track patterns by checking the trading volume, which indicates the activity level in a given marketplace.
Reading the trading volume chart, investors can identify markets with high demand. However, they need to take into account volatility changes to ensure supply is sufficient.
Liquidity zone indicators can be utilised to identify stages where demand and supply levels are high, indicating a high supply level.
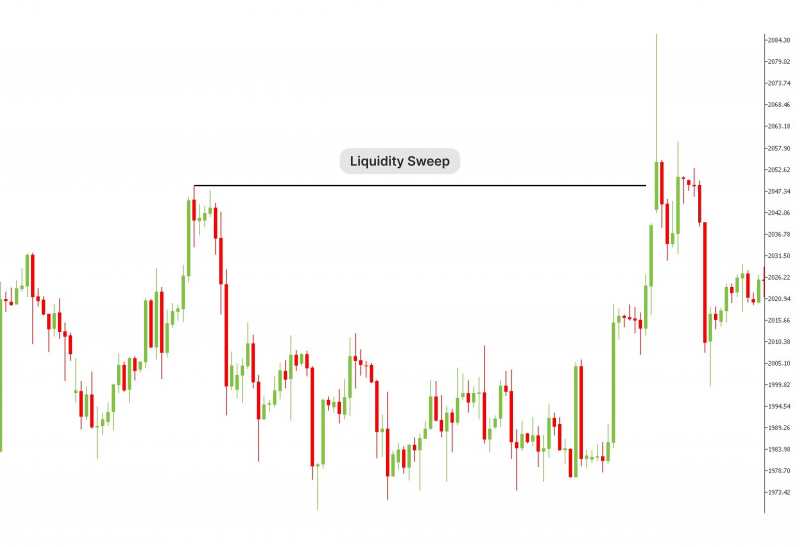
Additionally, investors can check liquidity sweeps associated with executing large trading orders. These activities check order books and scan through the entire market to find the best prices, which are usually associated with drops in prices and liquidity.
The Relation of Volatility and Liquidity in Forex Trading
Volatility and liquidity go hand in hand and are considered key factors that drive most investors’ decisions. They are affected by economic growth, geopolitical stability, market cycles, trading hours, and more.
There is a negative correlation between liquidity and volatility, fluctuating alongside the market forces and dictating the market sentiment between buying and selling activities.

During economic growth, FX liquidity providers increase their investments, raising the supply levels, stabilising market prices and decreasing the volatility levels. Liquid markets have low volatility where one or many buy/sell orders do not affect the entire market.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
On the other hand, if there is a liquidity crisis in banking systems, uncertainty increases, leading to low trading activity and liquidity, which causes high volatility. Illiquid markets have high volatility where assets are not sufficiently supplied, and one or more buy/sell orders majorly impact the market.
How to Check Forex Market Volatility and Liquidity?
Traders can analyse the relationship between these two factors by tracking trading volumes, global market time and trading trends.
For example, the Forex market volatility hours are at their peak when the US and European markets overlap, between 08:00 and 17:00 ET, where many traders join to make the most out of the EUR/USD pair.
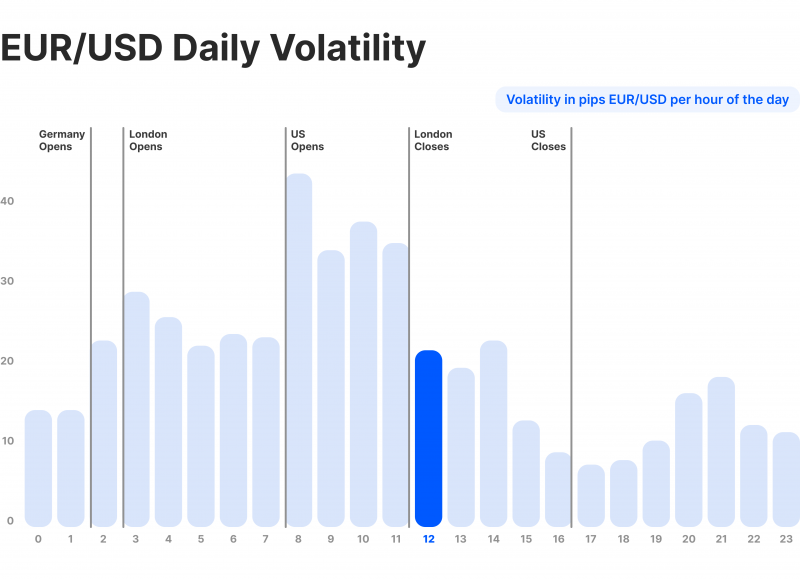
Additionally, leading up to major announcements, like the European Central Bank currency supply changes or the Federal Reserve interest rate reports, traders speculate on the expected outcomes while being cautious about their investments.
However, once the announcement is made, price fluctuations increase on the live Forex market volatility charts due to a surge in trading activity.
Conclusion
Volatility and liquidity in Forex are vital aspects that drive investors’ decisions and shape their trading strategies. High volatility refers to high price fluctuations and increased opportunities to gain because prices can widely increase or decrease.
On the other hand, liquidity is explained by the supply of tradeable securities, making order execution efficient, with low slippage chances and at low spread ranges. These two concepts correlate negatively, where a drop in one is associated with an increase in the other.






