How to Create a DEX Platform in 2026: Detailed Guide

As time passes and various technologies develop, fewer people find a centralised economy trustworthy and fair. An opposing concept is a decentralisation.
Peer-to-peer trading platforms that do not depend on a central authority are known as decentralised exchanges. They provide enhanced privacy, security features, and reduced transaction costs while letting customers keep control over their money.
As cryptocurrency investors and companies seek safe and transparent trading environments, the need for decentralised exchange development keeps increasing.
In this article, we cover the development process, essential components, and tactics for establishing a prosperous decentralised trading system.
Key Takeaways
- P2P trading without middlemen happens via DEX, which provides improved security, transparency, and user control.
- DEX types include order book DEXs, AMMs, and aggregators, which use order tracking, liquidity pools, or a combination of liquidity sources to streamline trading.
- Depending on your needs, flexibility, and budget, choose between custom development, white-label solutions, or clone scripts for the build.
What is a DEX and Why Create One?
DEXs allow P2P crypto trading, which are blockchain-based platforms that do not require a central authority or middleman. DEXs use smart contracts to automate and secure the trading process rather than having a centralised organisation handle transactions and funds.
DEXs do not retain user funds, unlike centralised exchanges. Instead, individuals maintain complete ownership of their digital assets during trading. Because transactions are carried out directly on the blockchain, transparency is guaranteed, and the risks associated with middlemen are decreased.
Now, let’s say you wish to exchange your Bitcoin for Ethereum. You can utilise a DEX instead of a conventional one where a business holds your asset.
This is how it works:
- You link the DEX platform to your cryptocurrency wallet.
- You indicate the quantity of Ethereum you wish to receive in exchange for the amount of Bitcoin you want to sell.
- The DEX’s smart contract automatically matches your order with another Ethereum buyer and a Bitcoin seller.
- No middleman is involved; the trade between your wallet and the other user’s wallet is carried out.
How Does DEX Make Money?
Transaction fees on trades are how the DEX platform generates revenue. Their fees are typically lower than those of centralised exchanges because they don’t rely on middlemen, which draws more users and helps them finance their operations.
Decentralised Exchange Types
There are several types of DEXs, and let’s discuss their characteristics.
AMMs
Automated market makers use liquidity pools and smart contracts to make deals. In return, users receive some transaction fees for contributing assets to liquidity pools. The system automatically sets token prices according to the pool’s supply and demand.
Order books are no longer necessary because of AMMs, which streamline trading. When there is insufficient liquidity, especially for large orders, slippage may happen. In addition, liquidity providers suffer temporary losses when price fluctuations affect the pool’s asset balance.
Order Book DEXs
Order Book DEXs keep track of buy and sell orders for specific trading pairs. Both off-chain and on-chain order books can be used with these platforms. Off-chain methods process orders faster and cheaply, whereas on-chain systems keep order data directly on the blockchain, guaranteeing transparency.
Order book DEXs allow for leveraged trading, in which customers borrow money to make larger trades. Although this strategy has more possible benefits, there are also more risks. Due to their limited liquidity, these platforms are frequently less competitive than centralised exchanges.
DEX Aggregators
DEX aggregators give users the best token prices and minimal slippage by combining liquidity from several decentralised platforms. These platforms streamline the trading process by distributing big orders among several liquidity sources. Aggregators provide a more seamless trading experience by addressing problems like fragmented liquidity and excessive transaction fees. To determine the best trade routes for users, they rely on algorithms.
Core Components of DEX
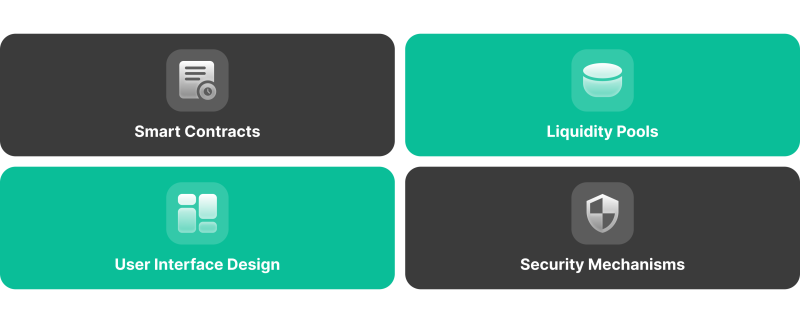
Let’s break down the essential elements of DEXs that create a powerful mechanism.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts automate trade execution without the need for middlemen and power decentralised exchanges. Order matching, liquidity pool management, and token exchanges are among the functions that these contracts oversee. Security audits are necessary to guarantee platform integrity and safeguard user payments.
Liquidity Pools
To enable smooth asset exchange, liquidity providers donate tokens to liquidity pools. Providers receive a portion of trading fees in exchange. By giving providers governance tokens or other assets, liquidity mining encourages participation. The overall activity of the platform is gauged by the total value locked in liquidity pools.
User Interface Design
A user-friendly design increases user engagement and streamlines the trading process. Crypto investors may conduct trades effectively thanks to responsive features and easy navigation. Platform usability is improved by incorporating user feedback during development.
Mechanisms of Security
DEX development requires strong security measures, such as frequent security audits and bug bounty schemes. These safeguards guarantee the platform’s dependability and safeguard user payments. Features like multi-signature wallets, encryption, and safe transaction execution further improve security.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Your Options: Clone Script, WL Solution, Custom Development
If you have decided to create a DEX, you need to research several methods you can use to build it, and below, we discuss a few of them:
Clone Script
A clone script is a pre-made software program that duplicates the essential features of an already-existing decentralised exchange platform. Token swaps, liquidity provision, and AMM features are made possible via clone scripts that are designed to mimic well-known DEX models.
Clone scripts are affordable for companies creating a decentralised exchange with little development work. With strong security measures, these scripts facilitate smooth asset exchange and function with blockchain networks.
Decentralised exchange script provides user-friendly interfaces, the ability to modify features, and the option to swap contracts in response to market trends or particular company objectives. They are perfect for firms offering decentralised trading services and dispersed trading fees while concentrating on yield farming, automated market makers, and liquidity pools.
This is how it operates:
- You find a profitable DEX.
- You purchase a pre-made software program that mimics the main features of the DEX of your choice.
- By changing the user interface or adding special features, you can change the script to meet your own requirements.
- You install the modified script on a blockchain network, such as Binance Smart Chain or Ethereum.
The White Label Solution
WL decentralised exchange solutions are pre-configured platforms for companies that wish to start their own DEX without starting from scratch. These systems offer a comprehensive architecture that includes smart contract development, exchange contracts, and liquidity pool connectivity. Companies can target their audience by incorporating particular features, customising user accounts, and adding their logo.
Organisations joining the DEX ecosystem use this strategy to take advantage of the developments in DeFi. WL platforms often have pre-tested security features, protecting user money while facilitating quick trade and strong DEX performance.
Most white-label solutions have security audits and bug bounty programs as essential features, lowering the risks of developing a DEX crypto platform.
Custom Development
Maximum flexibility is provided by custom decentralised cryptocurrency exchange development, which enables companies to create a platform that meets their particular needs. Custom development offers total control over features, core and peripheral contracts, and blockchain platform compatibility, in contrast to the previously mentioned methods.
Advanced features like AMMs, derivatives trading, and user-friendly interfaces are supported by custom DEX development. Projects needing creative token swaps or specialised asset trading solutions are especially well-suited. Security measures are created from the bottom up to fix vulnerabilities and improve the entire DEX environment. A committed development team ensures the platform incorporates blockchain development upgrades and follows market trends to stay competitive.
Advanced liquidity provision techniques are frequently incorporated into custom-built platforms, enabling liquidity providers to participate in decentralised exchanges and earn fees. Development teams often incorporate tools to execute trades effectively and guarantee a smooth trading experience for users.
Since the inception of Bitcoin, centralised exchanges have been the only form of trade. Although the first DEX was only introduced in 2014, few individuals were utilising their services then. When thousands of new coins emerged in 2017–2018 due to the ICO fever, these platforms became even more popular.
Defining Your Vision and Target Audience
Now, let’s follow the steps of creating a platform. The establishment of DEXs requires defining a clear goal and a target audience.
Your decentralised exchange platform’s features, design, and operation are all determined by your target audience. Instant trading capabilities and streamlined user interfaces are essential for retail investors. Institutions require strong security measures, adaptable trading options, and sophisticated analytics.
Blockchain enthusiasts and developers might concentrate on creating tools, including smart contracts, and participating in liquidity pools on decentralised exchanges. Beginners look for platforms that offer smooth asset exchange procedures and instructional materials.
The user needs to determine your decentralised exchange’s features. Beginners prefer the DEX platform with its easy-to-use UI and simple features to protect user cash. Institutional customers need capabilities for allocating trading fees, improved security measures, and tools for trading derivatives. To create new features on blockchain systems, developers prioritise access to core and peripheral contracts.
Customised decentralised exchange platforms include, for instance:
Retail-Focused DEX: For token swaps and yield farming, platforms prioritise liquidity pools and automated market maker AMM models.
Institutional DEX: With strong DEX security, these exchanges facilitate high-volume asset trading and complex decentralised trading alternatives.
Developer-Oriented DEX: Open-source initiatives enable programmers to create a decentralised exchange with blockchain technology’s adaptable core and periphery contracts.
By establishing a clear goal and target market, the DEX ecosystem’s features align with current market trends, guaranteeing its relevance and competitiveness.
Choosing the Right Blockchain Platform

The choice of blockchain affects a decentralised exchange’s functionality and performance. Below, we discuss some of the options:
Ethereum
Ethereum supports an established decentralised exchange ecosystem with a wide range of smart contract development capabilities. Strong developer tools and decentralised financial integrations are advantageous for liquidity pools in Ethereum-based decentralised exchanges. High transaction costs remain problematic, particularly for smaller DEX operations and retail customers.
Binance Smart Chain
Unlike Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain provides quicker confirmation times and lower transaction prices. BSC’s decentralised crypto exchange platforms use its practical design to facilitate instant trade and smooth asset exchange. Because BSC lacks decentralisation, it might affect some security features and appeal to users who value decentralisation.
Solana
Solana is appropriate for constructing decentralised exchanges that need to be highly scalable. Its rapid transaction speed facilitates smooth asset exchange and resource-intensive applications. Solana-based decentralised exchanges are competitive for high-frequency decentralised trading because their liquidity pools function with reduced latency.
Consider the following when assessing blockchain systems for a decentralised exchange:
- Scalability is necessary to sustain performance in an expanding DEX market.
- Transaction Speed affects liquidity provision and real-time trading.
- Cost impacts whether token swaps and trading fee distribution are feasible.
- Security measures protect user money and provide stable DEX operations.
- Developer tools make the creation of decentralised exchanges and the deployment of core and peripheral contracts easier.
Developing Secure and Efficient Smart Contracts

The foundation of the development of decentralised exchanges is smart contracts. They facilitate smooth asset exchange without the need for middlemen, execute trades, and oversee liquidity pools in decentralised exchanges.
DEX platform requires frequent audits and rigorous testing. These steps aid in locating weaknesses and stopping attacks that can endanger liquidity availability or fail to secure customer funds.
Here are the essential procedures for safe, smart contract creation:
Open-Source Framework Utilisation
Developers can use well-established, tested codebases to create a decentralised exchange with open-source frameworks. They improve the general effectiveness of decentralised exchange DEX operations and help security measures.
Conducting Audits by Third Parties
Third-party audits offer an unbiased assessment of the smart contracts utilised in decentralised exchange systems. These audits ensure no serious problems with the automated market maker protocols, liquidity pools, or core and peripheral contracts.
Continuous Updating and Repair
Decentralised crypto exchange platforms are kept up to date with changing DEX market trends through post-launch maintenance. Frequent upgrades improve speed, handle emerging risks, and strengthen the decentralised exchange ecosystem’s overall security.
Liquidity Management in DEX

The growth of DEXs depends on liquidity. It facilitates smooth asset exchange across decentralised trading platforms, reduces price slippage, and makes efficient deal matching possible.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Here are the methods for drawing in LPs:
Programs for Liquidity Mining and Fee-Sharing Structures
Liquid mining schemes encourage liquidity suppliers by paying trading fees or platform-specific incentives. This strategy guarantees that liquidity pools on DEXs continue to be accessible and active.
Collaborations with Pre-existing Liquidity Pools
Working together with already-existing liquidity pools eliminates the need to start from scratch when creating a decentralised exchange. Additionally, it draws customers looking for strong DEX features and increases the first trading volume.
AMMs Function
Order books are no longer necessary because automated market makers streamline decentralised trading. LPs can contribute assets and receive a share of the dispersed trading fees since AMMs rely on liquidity pools for immediate trading. Smart contracts are used by well-known AMMs, including those in a DEX, to guarantee effectiveness and protect user cash.
A strong DEX combines security measures and AMM protocols to preserve liquidity and offer dependable, compelling trading experiences. Long-term growth for DEX initiatives is supported by efficient liquidity management.
Cost Considerations for DEX Development
Now, let’s discuss how much developing a decentralised exchange will cost based on different approaches.
White label solutions usually cost between $8,000 and $14,000. Because these solutions require no from-scratch development, they may be implemented more quickly.
A custom-built DEX, on the other hand, can cost between $50,000 to $100,000 or more and offers greater freedom in terms of functionality and appearance. The degree of security, the intricacy of the features, and the integration with liquidity pools and decentralised exchanges are some variables that affect the ultimate cost.
Continuous upkeep and improvements are likewise very expensive. Even if the original development could appear expensive, budgeting for ongoing updates and maintenance is crucial. Updating security methods is part of maintenance to safeguard user cash and guarantee that strong security measures are in place.
When developing a DEX, particular care must be taken to make sure the DEX facilitates smooth asset exchange, has robust security features, and has enough liquidity pools for decentralised exchanges to offer incentives to liquidity providers. The total development cost can be determined by selecting the best strategy for these parameters.
Final Thoughts
It is essential to understand the components of a DEX, select an appropriate development methodology, and guarantee strong security, as they are all necessary for its construction.
Choosing the right blockchain platform affects both price and performance. You should give secure coding procedures, frequent audits, and ongoing upgrades to fix vulnerabilities top priority.








