What is a Merchant Account? How do You Get One?

Owning modern billing technologies is vital for businesses of any size and industry. This is where merchant accounts occupy one of the leading places. They bridge your business and the financial institutions handling credit and debit card transactions, and other electronic transfers. These accounts are essential for any company looking to process electronic payments, whether in-store or online. Merchant accounts play a pivotal role in modern commerce by facilitating transactions between the customer’s and business’s banks.
Key Takeaways
- A merchant account acts as a middleman between your company and banks, allowing you to accept credit cards, debit cards, and other electronic payments.
- Understanding merchant account fees, types, and how to choose a provider empowers you to make informed decisions.
- Whether you’re a small business or a high-risk merchant, there’s a solution for accepting payments securely and efficiently.
- Crypto merchant accounts are helpful in international transactions, as they offer lower fees and faster processing times than traditional methods.
Understanding Merchant Accounts
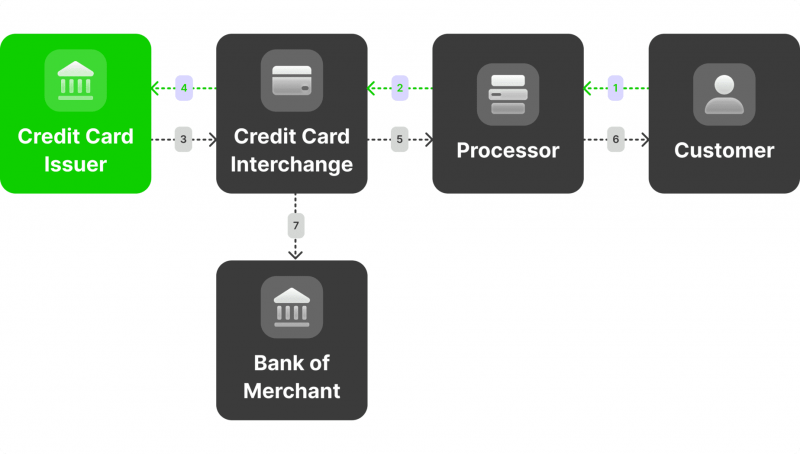
Merchant accounts are intermediaries between the business, the customer’s bank, and the payment processor. They are crucial for companies that wish to offer flexible payment options to their customers, thereby enhancing the overall shopping experience and potentially increasing sales.
When a customer pays with a credit or debit card, the funds are deposited into the merchant account before being transferred to the business bank account. This process ensures that the transaction is validated, funds are available, and the necessary security checks are performed.
Beyond basic payment processing, merchant account services can include various additional features. These may encompass fraud detection and prevention, chargeback management, detailed reporting, and analytics. Merchant account providers offer robust support to help businesses overcome the complexities of payment processing.
An acquiring bank, sometimes called an “acquirer, ” is an institution with the Cards Schemes authorisation to process a transaction. A merchant can process credit and debit card transactions by signing a contract with the acquirer.
Types of Merchant Accounts
There are several types of merchant accounts. Here are well-known ones:
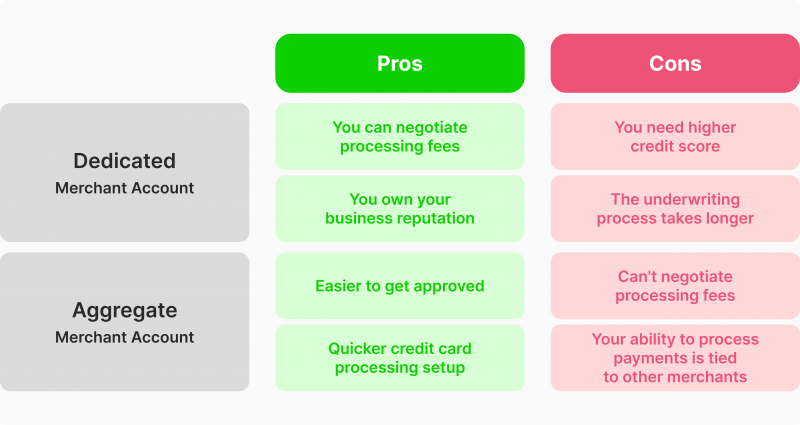
Dedicated Merchant Account
A dedicated merchant account is unique to a single business, offering personalised services. It provides low processing fees, requires a credit history review and may involve higher monthly fees. This type is ideal for established businesses with consistent sales volume.
Aggregate Merchant Account
Aggregate Merchant Account groups multiple businesses under a single account. It’s easier to obtain but comes with higher transaction fees. This type is ideal for startups, low-volume companies, and those in high-risk industries.
Retail Merchant Accounts
Retail merchant accounts are used primarily for brick-and-mortar stores where transactions are made in person. It typically involves a POS system where customers swipe or insert their cards. This type generally comes with lower transaction fees due to the reduced risk of fraud in face-to-face transactions.
E-commerce Merchant Accounts
E-commerce merchant accounts are designed for online businesses accepting payment through their websites. It involves integration with payment gateways to process online transactions securely. Furthermore, it requires robust security measures like SSL certificates and PCI compliance to protect customer data.
MOTO (Mail Order/Telephone Order) Merchant Accounts
MOTO merchant accounts are used by businesses that process payments via mail or over the phone. This type of Card Not Present (CNP) Transactions come with higher risk due to the absence of the physical card, often leading to higher transaction fees. However, it must be mentioned that enhanced verification processes, such as the Address Verification System (AVS), minimise fraud risks.
High-Risk Merchant Accounts
High-Risk Merchant Accounts are used by businesses in industries deemed high-risk by banks and payment processors, such as travel, gaming, or adult entertainment. This type comes with increased transaction and account fees due to the elevated risk of chargebacks and fraud. It often requires specialised merchant account solutions that cater to high-risk industries and offer tailored solutions. High-risk merchant accounts are designed to accommodate these industries, ensuring they can process payments despite the elevated risk.
International Merchant Accounts
For businesses looking to expand globally, international merchant accounts are essential. These accounts are designed to handle transactions in multiple currencies, making it easier for companies to accept payments from customers worldwide. International merchant accounts often come with advanced fraud prevention tools and multi-currency support.
Crypto Merchant Accounts
As cryptocurrency gains popularity, many businesses are exploring crypto merchant accounts. These accounts allow businesses to accept cryptocurrency payments like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and more. They often integrate with cryptocurrency payment gateways, which convert the crypto payments into fiat or directly deposit them into a crypto wallet, depending on the business’s preferences.
Crypto merchant accounts can be particularly beneficial for international transactions, as they offer lower fees and faster processing times than traditional methods. By accepting cryptocurrencies, businesses can attract customers who prefer using digital currencies for their transactions. This is particularly beneficial for reaching tech-savvy and international customers who may find traditional payment methods cumbersome.
A subset of crypto merchant accounts are Bitcoin merchant accounts that specifically handle Bitcoin transactions. These accounts can help businesses tap into the growing market of Bitcoin users and provide a secure, efficient way to process Bitcoin payments. Crypto payments can be processed quickly, often within minutes, compared to traditional banking systems, which may take several days. This speed can improve cash flow and reduce waiting times for fund transfers.

Understanding these different types of merchant accounts helps businesses choose the one that best fits their operational needs and customer payment preferences. Selecting the right merchant account is crucial for optimising transaction efficiency, minimising costs, and ensuring secure payment processing.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
How Do Merchant Accounts Work?
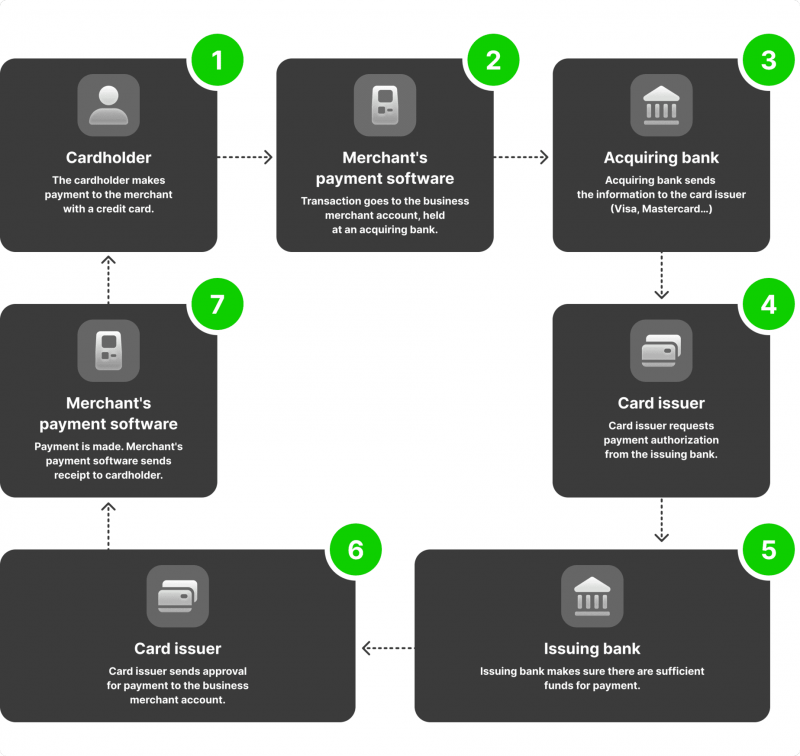
The process begins with businesses researching and comparing various merchant account providers to find the best fit for their needs. Once a provider is chosen, the company must submit an application. This application typically includes detailed information about the business, such as its financial history, projected transaction volumes, and supporting documents like bank statements, tax returns, and business licences.
Once the application is submitted, the provider conducts an underwriting process to assess the risk associated with the business. This involves evaluating the business’s creditworthiness, financial stability, and the nature of its products or services. Factors such as the business’s industry, average transaction size, and chargeback history are considered during this assessment. The merchant account is approved if the company meets the provider’s criteria. This approval process can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the complexity of the business and the thoroughness of the provider’s evaluation.
After approval, the merchant account is ready to facilitate transactions. When a customer purchases using a credit or debit card, the payment information is sent to the payment processor via a secure payment gateway. The payment processor then contacts the customer’s bank to verify the funds’ availability and the transaction’s validity. If the transaction is approved, the funds are transferred from the customer’s bank to the merchant account. This process typically happens within seconds, allowing for quick and efficient transactions.
Once the funds are deposited into the merchant account, they are usually held for a short period before being transferred to the business’s primary bank account. This holding period allows the provider to ensure the transaction’s legitimacy and handle potential issues, such as chargebacks or disputes. Throughout this process, the merchant account provider also ensures compliance with security standards, such as PCI compliance, to protect sensitive customer data and minimise the risk of fraud.
Overall, merchant accounts play a crucial role in modern commerce by enabling businesses to accept various payment methods, manage cash flow efficiently, and provide a seamless payment experience for their customers.
Benefits of Using a Merchant Account
Having a merchant account offers several benefits:
Increased Sales
A key advantage of having a merchant account is the potential for increased sales. By accepting various payment methods, including credit and debit cards, businesses can cater to a broader customer base. Many customers prefer the convenience and security of using cards over cash, and being able to accommodate this preference can lead to higher sales volumes and increased revenue.
Enhanced Customer Convenience
Merchant accounts significantly enhance customer convenience. With the ability to process credit and debit card transactions, businesses can offer a quick and seamless payment experience. This is especially important for e-commerce businesses where customers expect smooth and efficient checkout processes. The convenience of multiple payment options can also lead to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Improved Cash Flow Management
Merchant accounts facilitate better cash flow management by ensuring quicker access to funds. Instead of waiting for checks to clear or dealing with cash deposits, businesses receive electronic payments that are processed and deposited into their accounts promptly. This efficiency in fund transfers helps companies maintain a steady cash flow, which is critical for covering operational expenses and investing in growth opportunities.
Secure Transactions
Merchant accounts provide a layer of security for both businesses and customers. Providers implement robust security measures, such as encryption and tokenisation, to protect sensitive payment information during transactions. Additionally, compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) ensures that businesses adhere to industry standards for data protection. This reduces the risk of fraud and data breaches, providing peace of mind for both parties.
Detailed Transaction Records
Another benefit of using a merchant account is access to detailed transaction records. These records offer valuable insights into sales patterns, customer preferences, and overall business performance. Businesses can make informed decisions about inventory management, marketing strategies, and customer service improvements by analysing transaction data. Detailed records also simplify accounting and financial reporting, making tracking revenue and managing finances more manageable.
Competitive Advantage
Having a merchant account can provide a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Businesses offering diverse payment options are more likely to attract and retain customers than those accepting only cash. In a competitive business environment, accommodating customer preferences and providing a seamless payment experience can differentiate a business from its competitors and drive growth.
Global Reach
For businesses looking to expand internationally, a merchant account is essential. It enables the acceptance of various currencies and payment methods, facilitating cross-border transactions. This capability opens up new markets and customer segments, providing global growth and diversification opportunities.
In summary, merchant accounts offer numerous benefits that can enhance sales, improve customer convenience, and streamline financial management. By providing secure, efficient, and versatile payment processing solutions, merchant accounts are a valuable tool for businesses looking to thrive in today’s dynamic marketplace.
Merchant Account Fees

When setting up and maintaining a merchant account, businesses should be aware of various fees associated with these accounts. Understanding these fees is crucial for managing costs and selecting the right provider. Common merchant account fees include:
Setup Fees
Setup fees are one-time charges that businesses pay to establish their merchant accounts. These fees cover the initial setup and integration of payment processing systems. While some providers may waive setup fees as part of promotional offers, others might charge several hundred dollars, depending on the complexity of the setup.
Transaction Fees
Transaction fees are charged for each processed transaction and typically consist of a percentage of the transaction amount plus a fixed fee. For example, a fee structure might be 2.9% + $0.30 per transaction. These fees can vary based on factors such as the type of card used (credit vs. debit), the method of transaction (in-person vs. online), and the business’s industry. Transaction fees are among the most significant costs for companies with high sales volumes.
Monthly Fees
Monthly fees are recurring charges that businesses pay to maintain their merchant accounts. These fees can cover various services, including account maintenance, customer support, and access to payment processing tools. Monthly fees can range from $10 to $50 or more, depending on the provider and the level of service offered.
Monthly Minimum Fee
Some providers impose a minimum monthly fee, ensuring the business generates a certain amount in monthly transaction fees. If the business’s transaction fees fall below this threshold, the provider charges the difference to meet the minimum requirement. This fee structure encourages businesses to maintain consistent transaction volumes.
Chargeback Fees
Chargeback fees are imposed when a customer disputes a transaction, resulting in a chargeback. These fees cover the administrative costs of managing the chargeback process. Chargeback fees can range from $20 to $50 per incident, and frequent chargebacks can significantly impact a business’s profitability and reputation.
PCI Compliance Fees
To ensure the security of cardholder data, businesses must comply with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). PCI compliance fees cover the costs of maintaining compliance, such as regular security assessments and updates. These fees can be monthly or annual and typically range from $50 to $200 per year.
Payment Gateway Fees
For online businesses, payment gateway fees are charged for using the gateway that processes online transactions. These fees are usually a combination of a fixed monthly fee and a per-transaction fee. Payment gateway fees can range from $10 to $50 per month, with additional per-transaction charges similar to standard transaction fees.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Statement Fees
Some providers charge statement fees for generating and delivering monthly account statements. These fees cover the administrative costs of compiling transaction data and providing detailed reports to the business. Statement fees are typically around $5 to $10 per month.
Early Termination Fees
If a business decides to close its merchant account before the end of the contract term, it may incur an early termination fee. These fees compensate the provider for the loss of anticipated revenue and can vary widely, from $100 to several hundred dollars. Businesses must review contract terms carefully to understand the potential early termination costs.
It’s crucial to carefully compare the fee structures of different providers to find the most cost-effective option for your business. Some providers offer transparent pricing models, while others may have hidden fees or complex fee structures.
Merchant Account vs Payment Gateway
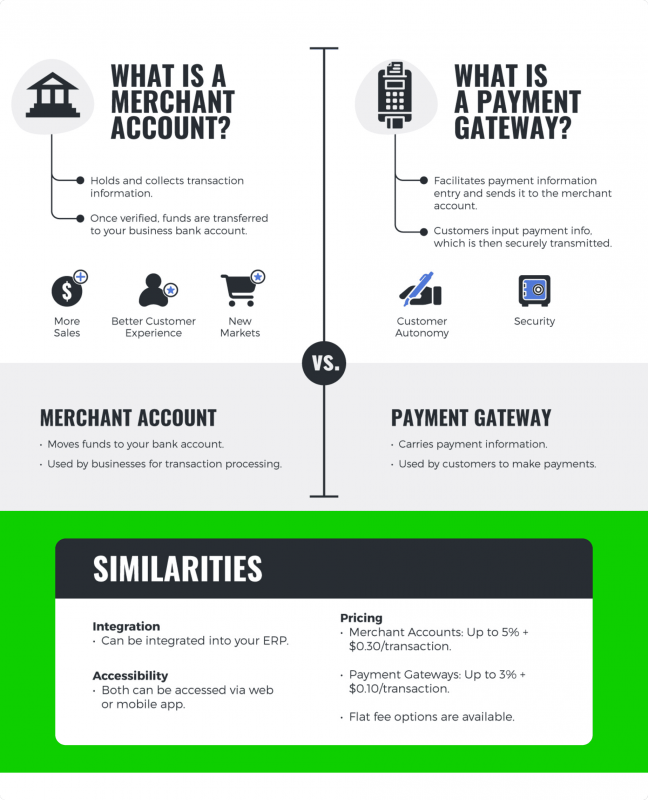
When arranging acceptance of online payments, it’s crucial to distinguish between a merchant account and a payment gateway, as both are integral to the payment processing ecosystem but serve different purposes. While a merchant account is necessary for processing payments, a payment gateway is a technology that facilitates the transfer of payment data between the customer, the merchant, and the bank. In essence, the payment gateway is the digital equivalent of a point-of-sale terminal, enabling online transactions.
Integrating a payment gateway with a merchant account is crucial for online businesses. This integration ensures that payment data is securely transmitted and processed, reducing the risk of fraud and errors. Many merchant account providers offer bundled services that include both the account and the gateway, simplifying the setup process.
Choosing the Right Provider
Selecting a merchant account provider is crucial for any business. Providers vary in terms of fees, services, and support. Key considerations include transaction fees, monthly fees, customer service, and integration capabilities with existing business systems. Top providers often offer comprehensive merchant account services, including payment gateways and fraud prevention tools.
Excellent customer service is a vital aspect of any merchant account provider. Businesses should seek providers that offer 24/7 support, fast response times, and knowledgeable staff.
When selecting a crypto merchant account provider, businesses should consider several factors:
- Ensure the provider supports the specific cryptocurrencies you want to accept.
- Compare the fees associated with processing crypto transactions and converting to fiat.
- Evaluate the security measures provided by the provider to protect against fraud and cyber threats.
Conclusion
Merchant accounts are essential for businesses looking to accept credit and debit card payments. Companies can make informed decisions that support their payment processing needs by understanding the different types of merchant accounts, the associated fees, and the importance of choosing the right provider. Whether you’re a small business owner or operating in a high-risk industry, finding the right merchant account solution is crucial for your success and financial performance.
FAQ
What is the best merchant account for small businesses?
The best merchant account for small business owners typically offers competitive rates, minimal fees, and excellent customer support. Additionally, these accounts often include features like mobile payment processing and integration with popular e-commerce platforms.
How does a merchant account for crypto exchange work?
If the retailer has chosen to receive payment in a cryptocurrency, the payment gateway provider will forward the funds to their wallet directly, minus fees. For fiat settlements, the crypto payment processor will convert the cryptocurrency and send the fiat funds to the merchant’s bank account, minus their fees.
Does the business need a merchant account?
Merchant accounts are essential for retail stores, restaurants, mobile businesses (such as food trucks), and e-commerce sites. However, companies of all sizes that want to accept card payments, whether service-based, healthcare-related, or nonprofit, will most likely need a merchant account.
How do you get a merchant account?
Companies must apply through a merchant account provider to obtain a merchant account. This process typically involves an application, a review of the business’s financial health, and an assessment of the potential risk associated with the company.








