What Is Crypto Spot Trading? How Does It Differ From Other Trading Methods?
Articles


In this guide, we will explore crypto spot trading, how it works, its strengths and weaknesses, and how it differs from other trading methods.
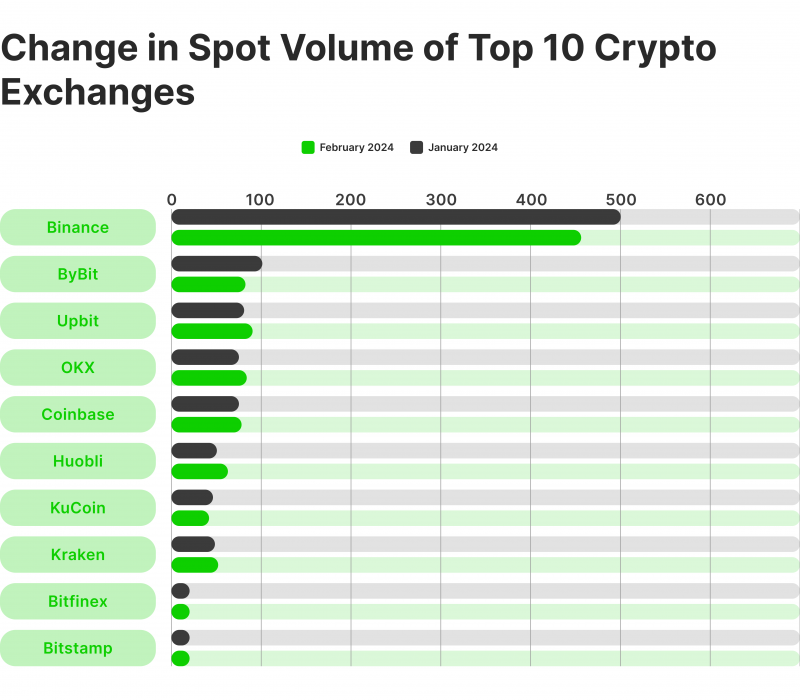
Recent data reveal that spot trading’s dominance in the crypto market is on the rise, with the ten largest exchanges recording $960 billion in spot volumes in February 2024. This amount constitutes nearly half of the total crypto market capitalisation, surpassing $2 trillion during the same period.
Spot trading is the most prevalent method in the market today, which allows traders to buy or sell cryptocurrencies at the current market price for immediate delivery. It is widely favoured for its simplicity, making it a popular choice for both new and experienced traders.
Key Takeaways
- In spot trading, profits are limited to the difference between buying and selling prices.
- Spot is a lower-risk option compared to futures and margin trading due to the absence of leverage.
- When trading spot, traders have complete ownership of their purchased assets, while in futures and options trading, they only enter into agreements to buy or sell assets at a predetermined price.
- The three primary types of crypto spot markets are cryptocurrency exchanges, over-the-counter trading, and peer-to-peer trading.
Basics of Spot Trading
What is spot trading in crypto? Spot trading refers to buying or selling digital assets at their current market prices for immediate delivery. It is a straightforward method that involves directly exchanging one cryptocurrency for another or exchanging crypto for fiat currency.
Unlike other trading methods, such as futures or options, spot trading does not involve any contract agreements or future commitments. Instead, the transaction settles instantly, and both parties receive their respective assets.
How Does Spot Trading Work?
Spot trading starts with a trader placing an order on a cryptocurrency exchange for a specific digital asset at its current market price. The exchange then matches the buy and sell orders, enabling the immediate transfer of assets between traders.
To facilitate these transactions, traders use digital wallets provided by the exchange or external wallets that support their preferred cryptocurrencies.
Let’s discuss the example of spot trading:
For instance, a trader wants to buy 1 BTC at its current market price of $60,000. They would place a buy order for 1 BTC, and once the transaction is completed, they would receive the coin in their digital wallet.
Similarly, if a trader wanted to sell their 1 BTC at its current market price of $60,000, they would place a sell order for 1 BTC. Once the transaction is completed, they will receive the equivalent amount in their preferred currency.
Spot Trading vs. Futures Trading
While spot trading and futures trading both involve buying and selling digital assets, they differ in several key aspects, making them two distinct methods of trading in the crypto market.
Ownership of Assets
One of the main distinctions between spot and futures is ownership. In spot trading, traders own the underlying assets upon transaction completion. They have complete control over their purchased cryptocurrencies and can immediately transfer or hold them as desired.
In contrast, futures trading involves buying and selling contracts rather than actual assets. Traders do not have ownership of the underlying assets, but instead hold a contract that promises to deliver the asset at a predetermined price and time in the future.
Leverages
Another significant characteristic of futures trading is leverage. In futures trading, traders can use leverage to control a larger position with less capital, which means that they can take on bigger trades and potentially earn higher profits.
However, leverage also amplifies both potential gains and losses, making it a riskier option for traders compared to spot trading. In spot trading, leverage is not used, reducing the risk of significant losses.
Timeframes of Trading
Futures trading is often used for short-term speculative trading, where traders take advantage of an asset’s future price movements within a specific time frame. These trades usually last anywhere from a few hours to a few days.
On the other hand, spot trading is more suited for long-term investment strategies. Traders who engage in spot trading usually hold their positions for extended periods, sometimes even years, to benefit from potential long-term price appreciation.
Spot Trading vs. Margin Trading
Another commonly used trading method in the cryptocurrency market is margin trading. While it may seem similar to spot trading at first glance, the two have crucial differences.
Margin Requirements and Borrowing
In spot trading, traders can only use the funds they have deposited into their accounts to buy or sell cryptocurrencies. On the other hand, margin trading allows traders to borrow funds from a third party or the exchange itself to increase their trading capital.
This borrowing capability enables margin traders to take larger positions and potentially generate higher profits. However, it also carries a higher risk of significant losses as traders may face a margin call if the market moves against their position.
Risk and Profit Potential
Due to the use of leverage, margin trading offers a higher profit potential. However, it also amplifies the risk of significant losses in case of adverse market movements. On the other hand, spot trading limits potential profits and losses to the difference in purchase and sale prices, making it a lower-risk option for traders.
Advantages of Spot Trading
Spot trading offers several advantages that make it an attractive option for many traders:
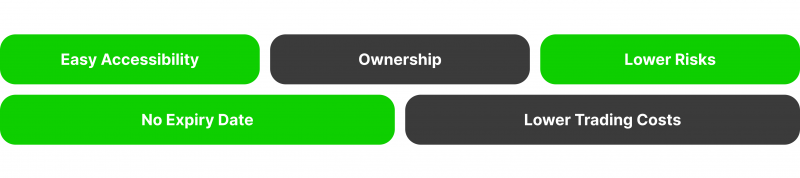
- Easy Accessibility: Spot trading requires minimal knowledge or experience in trading financial instruments. Spot trading is very simple, unlike other trading methods involving complex financial instruments. Traders can simply buy low and sell high without the need for advanced trading strategies or knowledge of derivatives.
- Ownership: In spot trading, traders actually own the cryptocurrencies they purchase. This ownership provides several benefits, such as the potential for airdrops or hard-fork benefits. Being a direct owner of the assets also allows traders to exercise control over their investments.
- Lower Risk: Compared to margin or futures trading, spot trading poses a lower risk. In spot trading, traders can only lose the amount they invest. The absence of leverage and borrowing limits the potential losses, making it a safer option for risk-averse traders.
- No Expiry Date: Unlike options or futures contracts, spot trading does not have an expiry date for the assets. Traders can hold onto their investments for as long as they choose and are not bound by any time constraints.
- Transparency: Spot trading is based on real-time supply and demand dynamics, which makes the prices of cryptocurrencies in the spot market highly transparent. Traders can easily access information on market prices and liquidity, allowing them to trade more effectively.
- Lower Trading Costs: Compared to other trading methods, spot trading typically incurs lower trading costs. Traders are not subject to additional fees or interest charges associated with margin or futures trading. The absence of leverage also eliminates the costs associated with borrowing funds.
Disadvantages of Spot Trading
While spot trading can be a profitable venture, it also has its own set of disadvantages:
- Limited Profit Potential: One limitation of spot trading is that profits are limited to the difference between the buying and selling price. Unlike margin or futures, spot trading does not provide the opportunity for amplified gains through leverage.
- Security Risks: Cryptocurrencies stored in digital wallets are vulnerable to hacking and security breaches. Traders engaging in spot trading need to take additional measures to secure their digital assets and protect themselves from potential cyber threats.

Types of Crypto Spot Markets
The crypto spot market can be categorised into two primary types:
Crypto Exchanges
Crypto exchanges are online marketplaces that bring together buyers and sellers of cryptocurrencies. Such a crypto broker platform allows traders to buy and sell cryptocurrencies at market prices.
Crypto exchanges typically offer a wide range of cryptocurrencies and provide features such as order books, price charts, and trading tools to facilitate spot trading.
There are two types of crypto exchanges:
Centralised Exchanges: These are traditional exchanges that function as intermediaries between buyers and sellers. They hold custody of the digital assets and facilitate trades on their platform.
The most popular spot trading exchanges (by trading volume) include Binance, Coinbase, ByBit, and OKX. The most popular spot trading platform for crypto currently is Binance.
Decentralised Exchanges (DEX): DEXs operate without a central authority, allowing traders to exchange cryptocurrencies with each other directly. These exchanges use smart contracts to automate the trading process, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
Among the popular decentralised exchanges are Uniswap, dYdx, Jupiter and Orca.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Trading
Over-the-counter trading refers to the direct transaction of cryptocurrencies between two parties without the involvement of an exchange. OTC trading is often used for large-volume trades and provides greater flexibility in terms of price negotiation and transaction size.
OTC trading can be particularly useful for institutional investors or high-net-worth individuals who require large amounts of cryptocurrencies without causing significant market volatility.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Trading
Peer-to-peer trading strategy, also known as person-to-person (P2P), allows individuals to trade cryptocurrencies with each other directly. Unlike OTC and centralised exchanges, P2P platforms do not require any intermediaries or third parties.
P2P trading gives traders more control over their transactions, allowing them to choose their preferred sellers, buyers, settlement time, pricing, and payment methods. However, there is a higher risk involved in P2P trading as it lacks the security and protection provided by intermediaries such as escrow services.
Potential risks of P2P trading include scams, fraud, low liquidity, and slower settlement times. It is essential to carefully research and choose a reputable P2P platform when engaging in this type of trading.

Risks of Spot Trading
Spot trading, like any form of investment or trading, carries certain risks, which traders should be aware of:
Lack of Regulation
The crypto market, including spot trading, is still in its early stages and is relatively unregulated compared to traditional financial markets. There are no comprehensive laws or regulations governing the buying, selling, or holding of cryptocurrencies.
While this may provide a sense of freedom for traders, it also exposes them to potential fraudulent activities, market manipulation, and inadequate investor protection.
Liquidity Risks
Sometimes, certain crypto assets may have low liquidity in the spot market. A trader needs to be aware of the liquidity of the cryptocurrencies they trade and consider their potential impact on their trading strategies. Low liquidity can lead to unfavourable execution prices and potentially larger bid-ask spreads.
Final Thoughts
Spot trading is a popular and straightforward method of dealing with cryptocurrencies at the current market price. It offers accessibility, transparency, and control over digital assets. While spot trading carries certain risks, such as market volatility and liquidity challenges, it also provides numerous advantages, including simplicity and lower trading costs.
Remember, before engaging in any form of trading or investment, it is important to do your own research, understand the risks involved, and consult with a financial advisor if necessary.
FAQ
Is crypto spot trading profitable?
Yes, spot trading can be profitable, but it is not guaranteed. The potential profits of spot trading are highly dependent on various factors such as market conditions, the timing of trades, and the individual trader’s knowledge and experience in the crypto market.
Is crypto spot trading risky?
Spot trading can be risky given cryptocurrencies’ volatile prices, when the value of a token can fluctuate rapidly within a short period of time, resulting in potential losses for traders. However, traders can reduce their risks with proper risk management strategies and stay updated with market trends.
Spot trading is safer compared to other forms of trading such as margin trading or crypto futures trading, which involve leverage and higher levels of risk.
Can you lose money in spot trading?
Yes, there is a possibility of losing money in spot trading. As already mentioned, cryptocurrency prices can be highly volatile, meaning traders can potentially lose all the money they invested in a trade.
Should I trade spot or futures?
The choice of whether to trade spot or futures is ultimately determined by the trader’s objectives, risk appetite, and time horizon. The futures market is better suited for long-term traders or those who want to hedge their positions against potential losses.
What is spot crypto?
Spot crypto refers to buying and selling cryptocurrencies at their current market price for immediate settlement. This straightforward approach gives traders full ownership of their purchased digital assets without the complexities of futures or margin trades.














