The Importance of The Crypto Howey Test

Cryptocurrencies, once considered a far-fetched concept, gained popularity with the creation of Bitcoin in 2009. Today, the world’s cryptocurrency market is worth around $2 trillion, and it is expected to continue disrupting industries.
However, the rapid expansion of digital assets has led to confusion and complicated regulatory challenges. The classification of digital assets as currencies or securities is determined using the Howey test, which is a crucial tool for ensuring the safety and integrity of digital assets.
In this article, we will discuss the criteria for the test and the importance of the crypto Howey test for the digital money industry.
Key Takeaways
- The Howey test helps decide whether a transaction is an investment contract.
- The test uses four criteria to decide if a transaction can be qualified as an investment.
- The most widespread cryptos — Bitcoin and Ethereum — are not qualified as securities according to the Howey test.
- Other tests like the Risk capital test or Reves test can be an alternative to the Howey test.
What is a Howey Test?
The Howey test is a legal test in the US that determines if a transaction is an investment contract exists. If found to be such, it becomes a security and is subject to registration requirements under the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. This test applies to any contract, scheme, or transaction.
The Howey test originated from the 1946 Supreme Court case of SEC versus the WJ Howey Company, which involved the sale of citrus groves to investors in Florida. The Howey Company did not register these transactions as securities, leading to the SEC’s intervention.
The Supreme Court ruled that the leaseback arrangements were investment contracts under the Securities Act of 1933, establishing key criteria for identifying securities. Thus, an asset can be classified as a security if it involves an investment in a common enterprise and the expectation of profits from others’ efforts.
What is an ICO?
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) are similar to crowdfunding, where companies create tokens for their projects. The process involves creating a white paper, pitch, and website and then asking for financial contributions in exchange for crypto tokens. These tokens can serve various purposes, such as access to future goods or services or entitling investors to a share of profits.
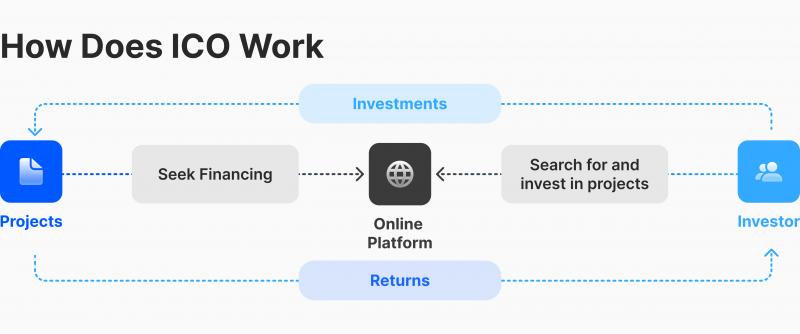
ICOs are largely unregulated in the U.S., making them highly risky and lacking investor protection. The opinion of Gary Gensler, chair of the SEC, on ICOs, includes the statement that there is currently insufficient investor protection in crypto finance, issuance, trading, or lending. This asset class is rife with fraud, scams, and abuse in certain applications.
A 2018 Wall Street Journal study found that one in five ICOs showed “red flags” of being a scam.
What is a Security in Crypto?
Common types of securities include stocks, bonds, ETFs, options, and mutual funds. There are four main types of securities:
- Equity securities. Equity securities represent a share of ownership in a company, trust, or partnership.
- Debt securities. This type of securities allows companies to borrow funds from investors and repay the loan with interest.
- Hybrid securities. They combine debt and equity securities, such as convertible bonds.
- Derivative securities. These are contracts between parties with their value based on the price of an underlying asset.
In the U.S., all securities must register with the SEC, and companies violating regulations face severe penalties. Cryptocurrencies fall under securities regulation due to their complexity and lack of fit within the existing regulatory structure.
As for the crypto testing, Bitcoin and Ethereum do not pass the test as, though they are digital, they act like actual currencies such as dollars or euros. Bitcoin does not pass the test, as it does not rely on collective effort or a specific promoter for its value to increase.
However, ICOs act as a security, as investors invest money to receive a digital token, hoping it will increase in value due to others’ efforts. These tokens must adhere to certain SEC and crypto regulation, and tokens that do not meet the Howey test criteria are often called utility tokens, which are digital vouchers for future services.
Overall, the rise of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology has muddied the waters with securities regulation, leading to some grey areas.
Does XRP Pass The Howey Test?
The legal battle between Ripple Labs and the SEC has been a closely watched case in the cryptocurrency and blockchain world. The SEC claims that Ripple sold XRP coins in an unregistered securities sale, raising approximately $1.3 billion in XRP sales.
The SEC ruled that all XRP transactions were unregistered “investment contracts,” a type of security. The court used the “Howey test” to determine that the investments were securities as they involved money investment in a common enterprise with an expectation of profits.
Have a Question About Your Brokerage Setup?
Our team is here to guide you — whether you're starting out or expanding.
Ripple has refuted these charges, arguing that XRP is not a security but a digital currency akin to Bitcoin and Ethereum.
So, does XRP pass the Howey test? The parties disagreed on many facts in their briefing but agreed on four types of XRP distribution transactions: institutional sales to institutional investors, algorithmic sales on digital asset trading platforms, other distributions to Ripple employees and third parties, and sales by Garlinghouse and Larsen on various platforms. These transactions occurred without the defendants filing any registration statements.
Crypto enthusiasts and investors believe the SEC’s approach to regulating digital currencies has been harsh. If the Howey test is applied to XRP at the point of sale, the digital asset does not pass the test.
The ongoing legal battle between Ripple and the SEC has reached a critical trial scheduled for April 23, 2024.
The Howey Test Criteria
The Howey test is a legal framework that outlines the four criteria for determining if a transaction qualifies as an investment contract:
- Investment of money: Money must be invested in cash, property, or other useful items.
- Participation in a common enterprise: A shared enterprise involves multiple investors pooling their funds, with the project’s success reliant on the collective efforts of others, typically managed by a promoter or third party.
- The expectation of profits: This element evaluates whether investors anticipate a return on their investment, primarily through the labour of others.
- Efforts of others: The success of an investment should be attributed to the talents, knowledge, or managerial efforts of someone else rather than the individual investor, as the promoter or another party must account for the majority of revenues.

If all four criteria are met, the transaction is considered an investment contract and can be governed by U.S. federal securities laws. This means that the offering and sale of securities, as defined by the Securities Act of 1933, may be subject to SEC registration requirements or exemptions.
This 4 elements test is particularly important for evaluating token sales in the context of cryptocurrencies and ICOs. However, the Howey test is unique to American securities law and may not be easily translated to rules in other jurisdictions.
The test determines whether an investment’s profit is mainly or entirely outside an investor’s control. If investors have minimal control over the investment’s management, it’s likely security, while if they significantly influence the investment’s handling, it’s not.
However, its application has been influenced by various views, including “horizontal commonality,” which considers a common enterprise where investors all invest in the same pot, and “vertical commonality,” which focuses on the relationship between investor money and the effort put in by the investor.
The “expectation of profits” is also debated, with some courts focusing on dividends or value increases while others consider different forms of return, such as avoiding losses. The importance of the promoter’s role in the investment’s success is also a topic of debate.
Most courts consider whether the promoter controls business decisions that affect the investment’s success, but some also consider the promoter’s role in the overall success of the investment.
Howey Test in Crypto
The Howey test is crucial for determining whether a cryptocurrency offering should be classified as a security under U.S. law. This is crucial for crypto businesses and investors, as breaking federal securities laws can lead to penalties, legal action, and reputational damage.
Cryptocurrency companies should carefully consider the Howey test before creating offerings. Tokens that don’t pass the test are considered utility tokens, which provide investors with access to future products or services or can be redeemed for discounted fees.
The implications of the Howey test for cryptocurrency depend on how regulators apply the test and how companies structure their offerings to comply with securities federal law.
The application of the Howey test’s criteria to cryptocurrencies is ongoing as the digital currency market expands. This test serves as a guideline for regulators and investors exploring digital assets.
To comply with securities compliance laws, crypto startups, exchanges, and investors must know registration requirements, investor protection, compliance systems, legal advice, and regulatory scrutiny. If a token meets the definition of a security, it must register with the SEC or qualify for an exemption.
Crypto companies must be transparent and truthful in their dealings with investors, establish robust compliance systems, seek legal counsel experienced in securities law and cryptocurrency, and be aware of recent suits by the SEC and other bodies.
Financial regulators are seeking ways to provide proper oversight on the use of crypto worldwide, but it’s not fair to fixate the framework on only one “rule of thumb,” such as the Howey test. Crypto enthusiasts should always monitor projects they invest in, as investors may fall into a tax trap.
Howey Test Alternatives for Evaluating Currencies
Despite its widespread popularity and multiple use cases, including the infamous SEC vs. Ripple case, the Howey test is not the only method that can be used to evaluate if a cryptocurrency is a standard investment. Here are some alternatives that can be used to assess the investment capacity of crypto:

Risk Capital Test
The capital-risk test is a method used to determine if a transaction is considered an investment contract and subject to securities laws. It is applied when a franchisee provides a substantial portion of the capital used by a franchiser to start its operations.
For example, if a franchiser needs $1 million to start a new business and finds a franchisee willing to invest $800,000 in exchange for a share of the profits, the capital-risk test would likely classify the transaction as an investment contract subject to securities laws.
Family Resemblance Test
Established in 1990, this test compares investment deals to common securities, examining investment reasons, selling methods, and desired outcomes.
This test is used to distinguish between notes issued in an investment context (securities) and those issued in a commercial or consumer context (non-securities). To do this, the following criteria are used:
- the buyer’s or seller’s motivation for the transaction in question;
- the plan for distributing the note;
- the public’s reasonable expectation as to whether the note is a security;
- whether another regulatory scheme safeguards the transaction or note.
The family resemblance test also applies to new, complex investments like cryptos.
Discover the Tools That Power 500+ Brokerages
Explore our complete ecosystem — from liquidity to CRM to trading infrastructure.
Reves Test
The Reves test identifies four factors determining whether a note is a security: buyer and seller motivations, distribution plan, public expectations, and risk-reducing factors.
In the 2021 SEC’s proceedings against Blockchain Credit Partners and its founders, the SEC used the Reves test to prove that the offered tokens were securities. They argued that DMM and its founders sold tokens to raise funds, and buyers purchased them solely for a designated return. The tokens were also promoted as investments without any risk-reducing factors, meeting all four elements of the Reves Test.
Capital Contribution Test
The Capital Contribution test is a useful tool for assessing control over money in decentralised systems like Ethereum, and it can be useful when the Howey test fails to yield success.
AAOIFI Standards for Islamic Finance
The AAOIFI develops accounting standards for Islamic financial law. It has issued 117 standards covering Shariah, accounting, auditing, governance, and ethics. The AAOIFI makes its standards accessible on its website on a complimentary basis.
AAOIFI standards have been adopted by several countries, including Bahrain, Malaysia, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Lebanon, Syria, Sudan, and Jordan. These standards are not binding on members but have made significant progress in encouraging widespread adoption.
Crypto investments must adhere to AAOIFI standards, ensuring Sharia law compliance by avoiding interest, uncertainty, and gambling.
Conclusion
The Howey test, introduced in the 1970s, is a crucial tool for determining whether an investment needs regulation. It is a legal framework that aims to prevent deception in investments. It emphasises substance over form, examining the economic realities of transactions rather than just the name or label.
Developed before cryptocurrencies, it has significant implications for the crypto sector. Aligning crypto assets with conventional securities legislation is challenging due to their decentralised nature. However, certain elements of the crypto ecosystem, like ICOs, can pass the Howey test.
The crypto Howey test is crucial for blockchain or crypto business owners since it can help protect their investments and avoid fines. Regulators and legal experts struggle to balance investor protection and innovation in the rapidly changing crypto market.
FAQ
Does cryptocurrency qualify as a security?
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission deems most cryptos securities, with Bitcoin and Ethereum being exceptions.
Can we apply the Howey test to NFT?
Certain NFTs may pass the Howey test if derived from a common enterprise, but they may not be classified as an investment contract by the SEC.
Why does Bitcoin fail the Howey test?
Bitcoin meets the first prong but does not satisfy the second and third elements since the coin lacks a common enterprise, promoter or issuer, and investor success.
Why is the Howey test important for crypto?
The Howey test is a tool used to assess if a cryptocurrency transaction is subject to securities regulations, thereby influencing legal compliance, investor protection, and regulatory oversight.








